Inhibitory synapses release neurotransmitters, typically GABA or glycine, onto other neurons.
A major difference compared with synapses releasing ACh is the reversal potential of the current through the neurotransmitter receptors.
Note that the resting potential in these simulations is set to –65 mV, as is characteristic of neurons ,
rather than the –90 mV typical of muscle fibers
( The Neuromuscular Junction tutorial )
Two means of stimulation are available :
through the postsynaptic GABA-gated channels
( AlphaSynapse panel )
through the stimulating electrode inserted in the postsynaptic neuron
( Stimulus Control panel )
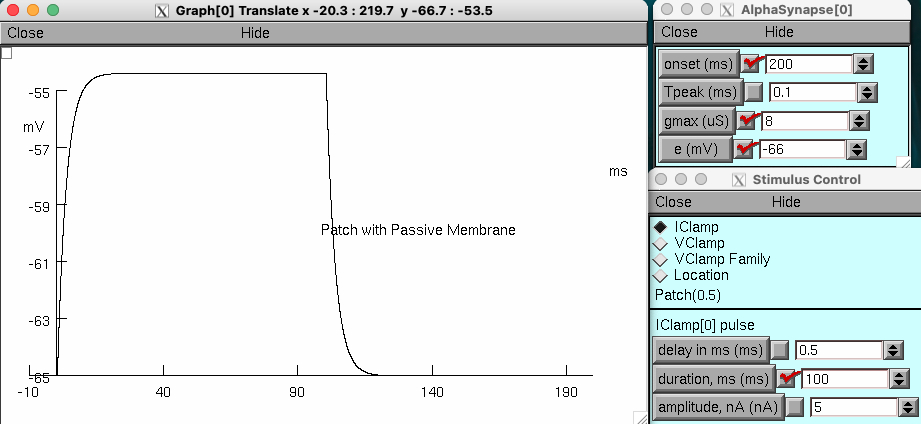
The AlphaSynapse panel controls the parameters of the inhibitory postsynaptic potential
onset : time of onset for the IPSP , in ms
Tpeak : time to peak of the synaptic conductance change , in ms
gmax : postsynaptic conductance change caused by the inhibitory transmitter , in μS
e : reversal potential ( Vrev ) of the transmitter-gated channels ( default at –65 mV )
Part 1 - Changing GABA Receptor Conduction in the Membrane
Choose tutorial "Postsynaptic Inhibition"
Click on Start the Stimulation
Reposition Voltage vs. Time plot to the top of your screen
Increase Total # ms to 4 ms
Change Vrev ( e ) to –66 mV
Click on Reset & Run
Keep Lines
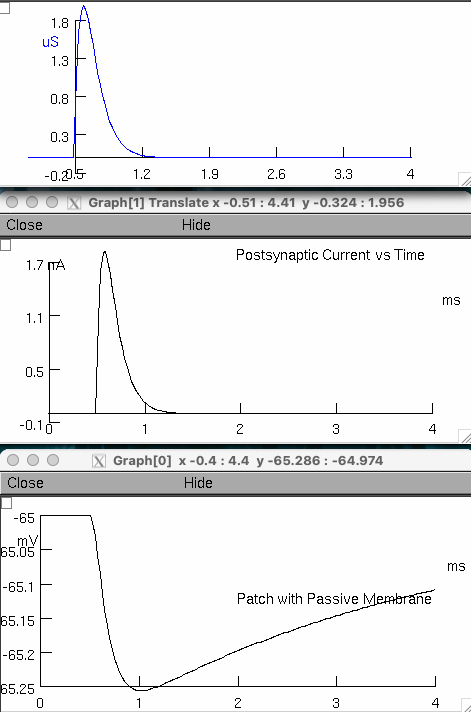
Double postsynaptic conductance to 4 μS , and then to 8 μS
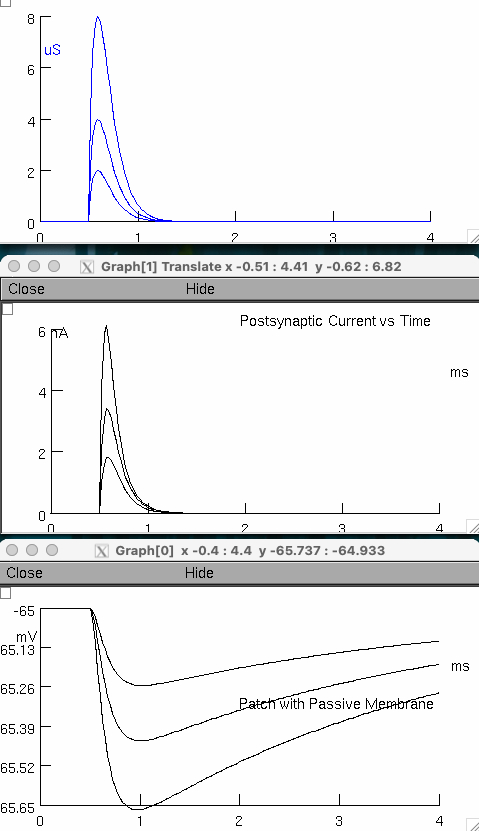
Describe the relationship between opening neurotransmitter receptors ( postsynaptic conductance ) and the response of membrane voltage and current.
opening more GABA receptors ➡️ more
Click on the Stimulus Control panel and select I-Clamp to inject 5 nA ( +5 ) of depolarizing current into the postsynaptic neuron.
Click on run control and change the total #( ms ) to 30.
Change onset to 15 ms ( AlphaSynapse panel ). { delays stimulating the inhibitory neuron }
Assure that gmax for the inhibitory conductance is 8 μS.
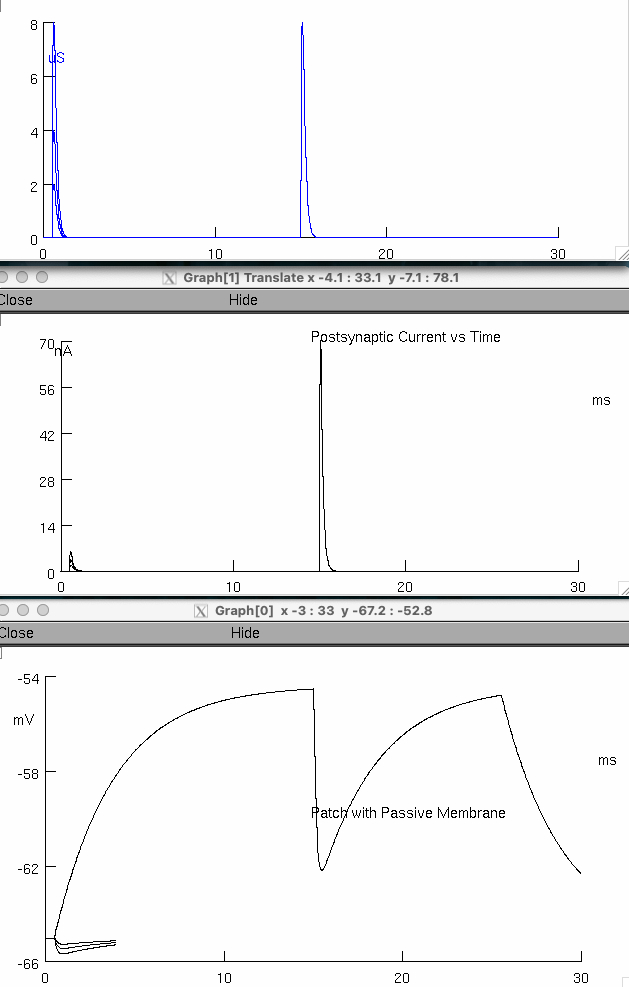
Describe the relationship between opening neurotransmitter receptors ( postsynaptic conductance ) and the response of membrane voltage or current.
the reversal potential is -65 mV
this is NOT the Vm
because the reversal potential is negative , its inhibitory
so we inject current for 25 milli seconds ,
so we depolarize
if you increase the duration of current injection long enough ,
the membrane will eventually reach full charged capacity ,
so for the first 15 seconds it was still charging
then some inhibitory channel opens from the alpha synapse , and we hyperpolarize the membrane as it approaches its Nernst at
the alpha synapse quickly inactivates , and we continue with our current injection until 25 ms
Change the current injection to –5 nA.
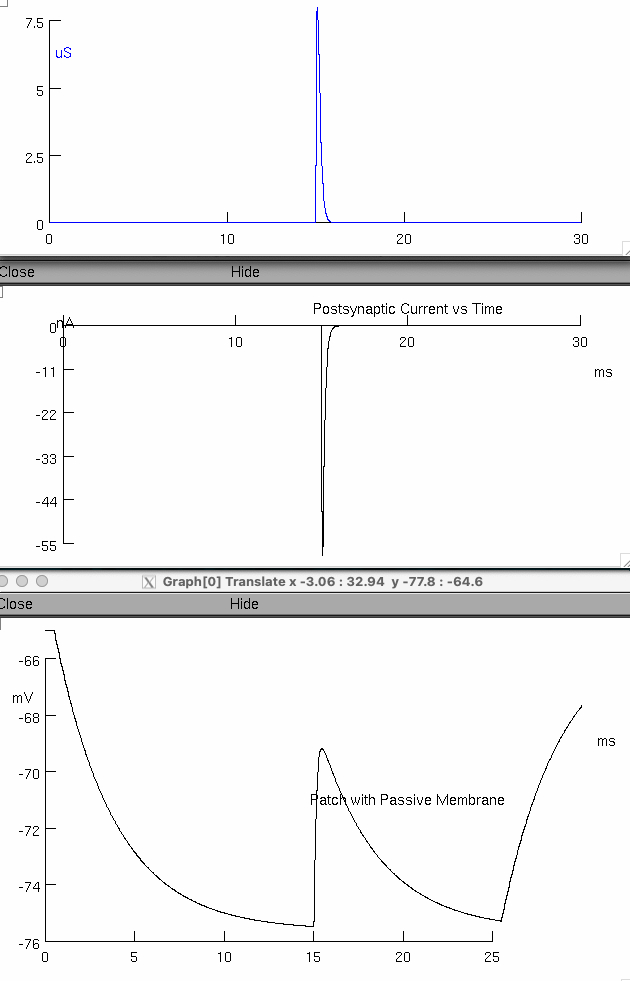
Describe the relationship between opening neurotransmitter receptors ( postsynaptic conductance ) and the response of membrane voltage or current.
the opposite happens
we charge the membrane with negative current
then at 15 ms we open inhibitory channels open ,
or either way we now balance going towards its reversal potential at -66 mV
Comment on the description of this neurotransmitter.
GABA or glycine
reversal potential is hyperpolarizing at -66 mV
Part 2 - Inhibitory Synapse Influence on Action Potential Excitability
Click on add HH Channels
The AlphaSynapse panel automatically adjusts inhibitory neurotransmitter conductance to 0 μS when adding HH channels
In the Run Control panel change total #(ms) to 20 ms.
In the Stimulus Control panel set the delay at 2 ms , the duration at 2 ms , and the current at 5 nA
triggers action potentials by injecting depolarizing current into the neuron
Click Reset & Run
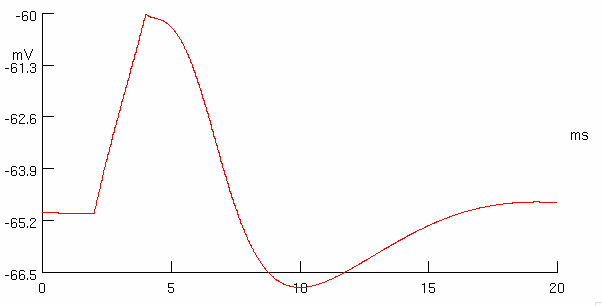
Increase the injected current to 6 nA , 7 nA , and then 8 nA
Describe the response
you see an action potential at 6 nA
the more current you inject :
the quicker an action potential occurs
the larger
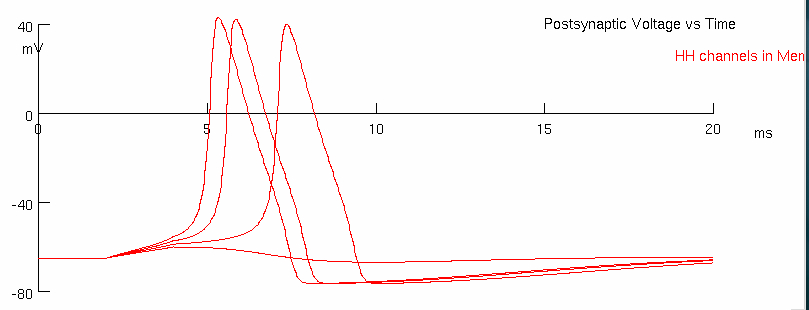
Now adjust ( AlphaSynapse panel ) onset to 2 ms , Tpeak to 2 ms , and gmax to 2 μS.
Note the change in these parameters , whether it was an increase or a decrease
onset = increase
Tpeak = increase
gmax = increase ( from 0 to default of 2 )
Maintain the reversal potential ( e ) at –66 mV.
Repeat the current injections of 5 nA , 6 nA , 7 nA , and 8 nA.
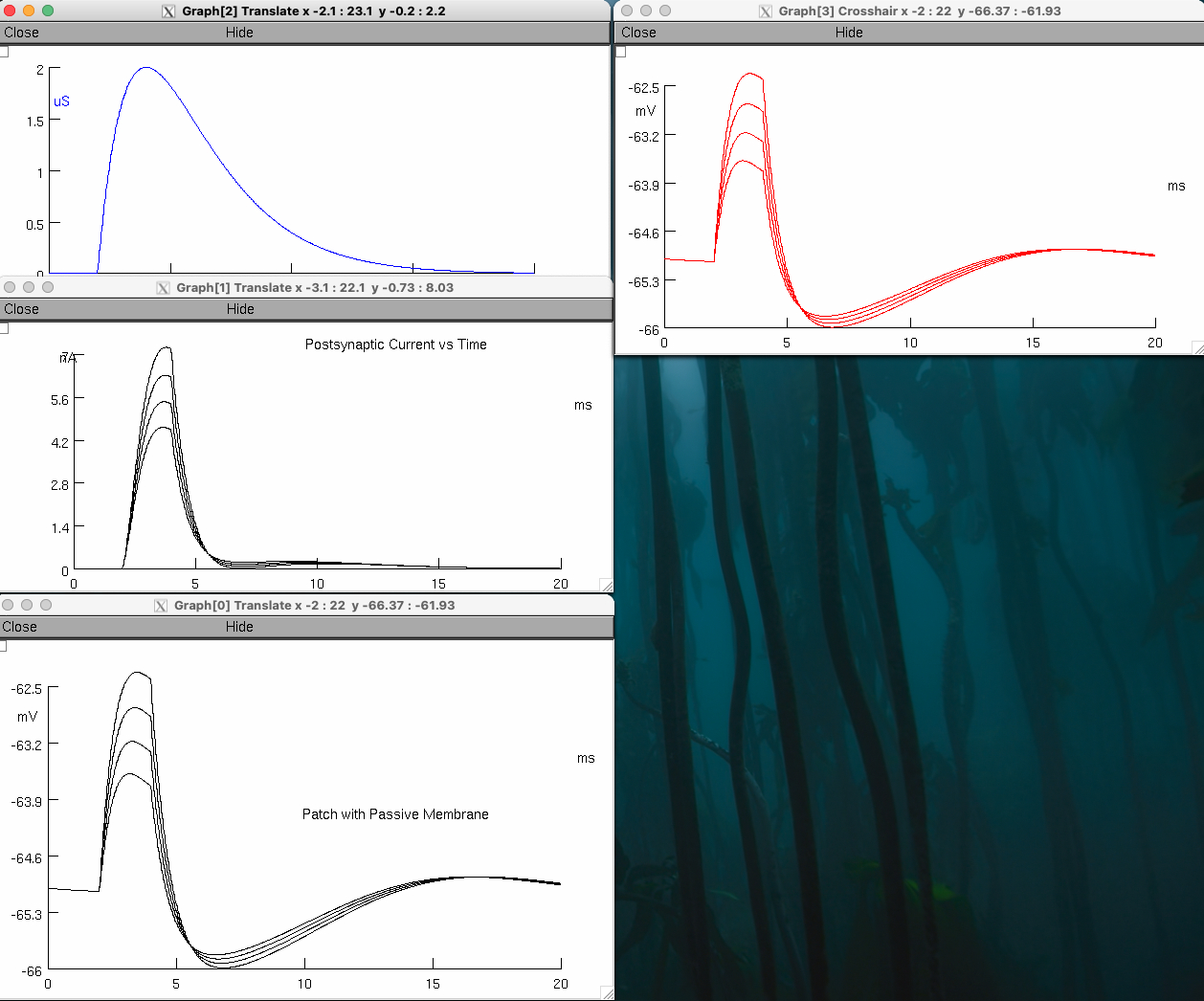
Describe how these action potentials compare with the previous set.
at 2 ms we inject both positive current and open an inhibitory ion channel ( negative current )
these compete for their delivered durations of 2 ms
but then the cell continues to hyperpolarize ,
the alpha synapse shows we have current until 15 ms
so they are still open , hyperpolarizing the membrane potential
they eventual close at around 16 ms
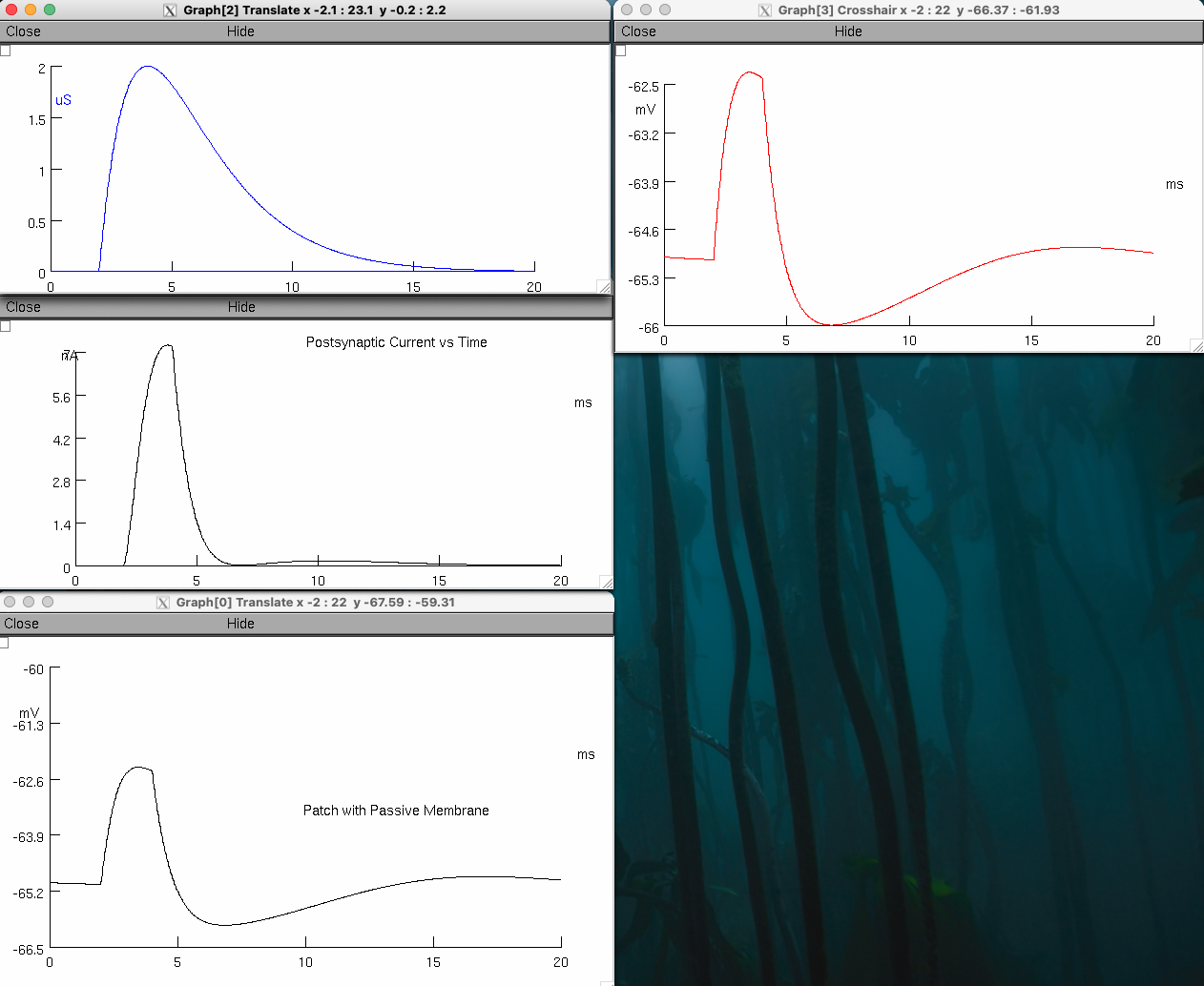
Describe how the postsynaptic current is altered ( current through the neurotransmitter receptors )
the driving force is larger when the membrane depolarizes farther away from reversal potential ( –66 mV )
synaptic conductance stays the same
current increases through the inhibitory channels
Describe the ability of the neuron to generate actions potential during opening of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors
suppressed
the opening of inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors prevents the membrane from reaching threshold