ECs :
receive and translate signals from the blood
Barrier
Blood flow - via interaction with VSMC
Hemostasis ( stop bleeding )
Anti-coagulant
Angiogenesis
Inflammatory response - extravasation of leukocytes into tissues
Intracellular calcium increases in response to G protein coupled receptor binding proinflammatory mediators such as chemokines, activated complement
Low pH and lactate induce massive amounts of intracellular calcium release dysregulate vascular tone and lead to EC apoptosis
Calcium Mediates Release of Various Relaxing Factors from Endothelial Cells
Know the layers of blood vessels , their cellular composition , and difference between arteries , veins , and capillaries
Layers of blood vessels :
Tunica intima : Endothelial cells + basement membrane
Tunica media : Primarily smooth muscle cells ( VSMCs )
Tunica externa ( adventitia ) : Fibroblasts , vaso vasorum , extracellular matrix
Differences :
Arteries :
Thick tunica media
Internal and external elastic lamina ( IEL / EEL ) present
Veins :
Thinner tunica media
No IEL or EEL
Thicker tunica externa
Capillaries :
Single layer of endothelial cells
Three types : continuous , fenestrated , and sinusoidal ( based on permeability and location : e.g., adipose , intestine , spleen )
Describe the functions of smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells
Act as a barrier
Regulate blood flow and vascular tone via signaling with VSMCs
Maintain hemostasis :
Anti-coagulant surface
Mediate angiogenesis ( formation of new blood vessels )
Facilitate leukocyte trafficking and respond to inflammation
Smooth muscle cells ( VSMCs ) :
Maintain vascular tone and blood pressure via contraction and relaxation
Can undergo a phenotypic switch from quiescent ( contractile ) to proliferative ( synthetic ) in response to injury or disease
Regulated by intracellular calcium , NO ( nitric oxide ) , and calmodulin
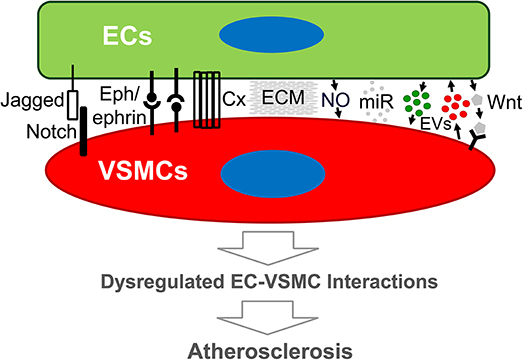
Understand the various ways that endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells communicate and their implications
Mechanisms of EC-VSMC communication :
Direct contact :
Myoendothelial junctions ( MEJs ) : Transfer ions ( Ca²⁺ ) , second messengers ( IP₃ , cAMP )
Notch signaling ( e.g., Jagged1 / Notch3 )
Ephrin / Eph interactions
Nitric Oxide ( NO ) from ECs :
Activates myosin light chain phosphatase → VSMC relaxation
Anti-atherosclerotic effects : inhibits VSMC proliferation , reduces platelet aggregation , and leukocyte adhesion
Extracellular matrix ( ECM ) :
EC glycocalyx and perlecan ( HSPG ) regulate cytokine binding ( e.g., IL-2-induced VSMC proliferation )
miRNAs :
EC-derived miR-92a modulates VSMC phenotype , increases blood pressure , reduces NO levels
Extracellular vesicles :
Exosomes ( 30–150 nm ) , microvesicles ( 100–1000 nm ) , apoptotic bodies
Carry miRNAs , proteins , and signaling molecules
Implications :
Dysregulation leads to atherosclerosis , hypertension , vascular stiffness , and endothelial dysfunction
Describe different means by which endothelial and smooth muscle cell interactions can be studied in vitro
Indirect co-culture :
Transwell ( Boyden chamber ) : ECs and VSMCs are cultured separately but share soluble factors
Conditioned media : Media from ECs applied to VSMCs ( or vice versa )
Isolated extracellular vesicles : Applied to target cells to study paracrine effects
Direct co-culture :
Matrix-like gels : ECs and VSMCs co-seeded on substrates mimicking ECM
Spheroids : 3D aggregates showing enhanced tissue-specific behavior , exosome production
Organoids : Derived from pluripotent stem cells
Vessels-on-a-chip : Microfluidic devices using ECs and VSMCs to mimic vasculature
Paper Discussion
VSM and EC cells are required for vascular homeostasis
calmodulin = required for VSMc function
Unknown = if EC's regulate vascular functions
Background = CAM interacts with over 300 cellular proteins
smooth muscle cells have about 5% availability of CAM
Rationale = increase CAM in VSMs
Gap in Knowledge = VCs use CAM to regulate function
Methods = Ca Sensor Protein = calmodulin
Endothelial Cells Secrete Soluble Factors
eNOS has high affinity for calmodulin
20% EC with 70% VSMc co-culture = greatest amount of calmodulin expression
Negative FRET analysis = used to find degree of calmodulin present
Greater amount of comodulin in co-cultured cells ,
no difference in calcium levels
Calmodulin mRNA and protein is upregulated in VSMs co-cultured with 20% ECs
Some unknown factor regulates calmodulin levels
VEGF = enhances calmodulin expression
Block VEGF = blocks angiogenesis in tumor formation
VEGF uses IP3 to promote calmodulin expression
Can't be contact based signal , must be soluble diffusion factor