Define Stress
"a perceived threat to homeostasis"
"an event or stimulus that causes an often abrupt but always large change in autonomic activity and hormone secretion, particularly cortisol secretion"
Hypothalamus Nuclei - Wiki
just need to know a couple of these
| Region | Area | Nucleus | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Preoptic | Preoptic nucleus | Thermoregulation |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Preoptic | Ventrolateral preoptic nucleus | Sleep |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Medial | Medial preoptic nucleus | Regulates the release of gonadotropic hormones from the adenohypophysis Contains the sexually dimorphic nucleus, which releases GnRH, differential development between sexes is based upon in utero testosterone levels Thermoregulation |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Medial | Supraoptic nucleus | Vasopressin release Oxytocin release |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Medial | Paraventricular nucleus | thyrotropin-releasing hormone release corticotropin-releasing hormone release oxytocin release vasopressin release somatostatin round arousal (wakefulness and attention) appetite |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Medial | Anterior hypothalamic nucleus | thermoregulation panting sweating thyrotropin inhibition |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Medial | Suprachiasmatic nucleus | Circadian rhythms |
| Anterior (supraoptic) | Lateral | Lateral nucleus | See Lateral hypothalamus § Function – primary source of orexin neurons that project throughout the brain and spinal cord |
| Middle (tuberal) | Medial | Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus | blood pressure heart rate GI stimulation |
| Middle (tuberal) | Medial | Ventromedial nucleus | satiety neuroendocrine control |
| Middle (tuberal) | Medial | Arcuate nucleus | Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) feeding Dopamine-mediated prolactin inhibition |
| Middle (tuberal) | Lateral | Lateral nucleus | See Lateral hypothalamus § Function – primary source of orexin neurons that project throughout the brain and spinal cord |
| Middle (tuberal) | Lateral | Lateral tuberal nuclei | Empty cell |
| Posterior (mammillary) | Medial | Mammillary nuclei (part of mammillary bodies) | memory |
| Posterior (mammillary) | Medial | Posterior nucleus | Increase blood pressure pupillary dilation shivering vasopressin release |
| Posterior (mammillary) | Lateral | Lateral nucleus | See Lateral hypothalamus § Function – primary source of orexin neurons that project throughout the brain and spinal cord |
| Posterior (mammillary) | Lateral | Tuberomammillary nucleus | arousal (wakefulness and attention) feeding and energy balance learning memory sleep |
Cortisol Effects
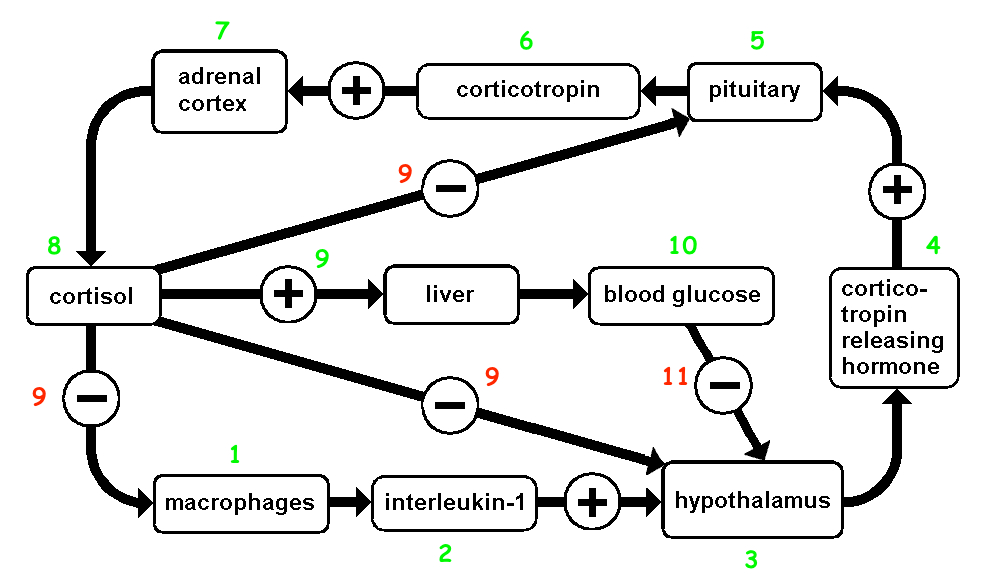
Draw HPA Axis

How the HPA Axis Helps with Stress
Detects stressors via the limbic system ( amygdala , hippocampus ).
Hypothalamus ( PVN ) releases CRH , signaling the pituitary gland
Anterior pituitary releases ACTH , which stimulates the adrenal cortex
Adrenal cortex secretes cortisol , which :
Increases glucose availability ( energy boost )
Suppresses non-essential functions ( immune , digestion , reproduction )
Enhances alertness and behavioral adaptation
Negative feedback loop : Cortisol eventually inhibits CRH & ACTH release to prevent excessive stress response
How the HPA Axis Can Go Wrong
Overactive HPA (Chronic Stress): Too much cortisol → anxiety, depression, metabolic disorders, immune suppression, neurodegeneration.
Underactive HPA (HPA Dysfunction): Low cortisol in PTSD, chronic fatigue, Addison’s disease → fatigue, low BP, poor stress tolerance.
Faulty Feedback (HPA Overdrive): Seen in MDD, anxiety disorders → leads to chronic inflammation, hippocampal atrophy.
Stress Damage to Hypothalamus:
PVN Overactivation : Excess CRH → hypertension, anxiety, metabolic issues.
SCN Disruption : Messes up circadian rhythms, causing insomnia, fatigue, immune issues, mood disorders.
Cytokines Effects on Nervous System
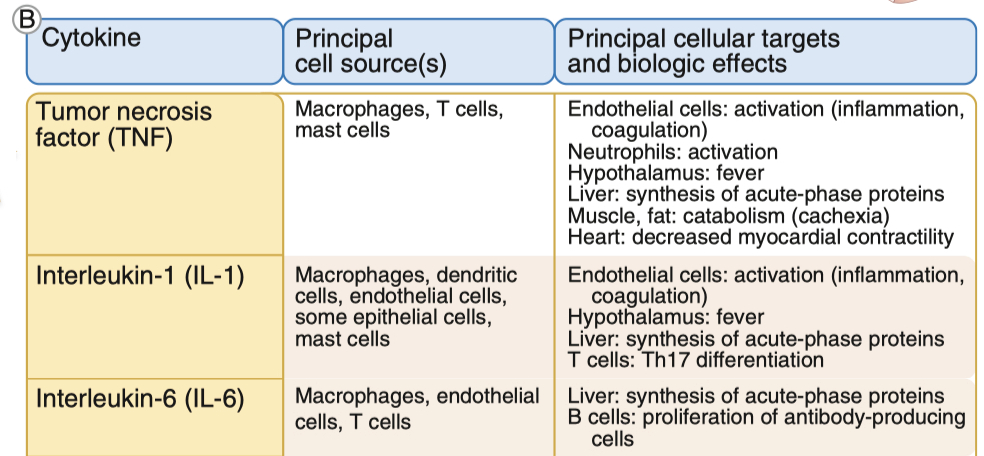
TNF :
induces apoptosis , which is damaging , but limits the spread of more damage in the long-term
increases inflammation , and BBB permeability
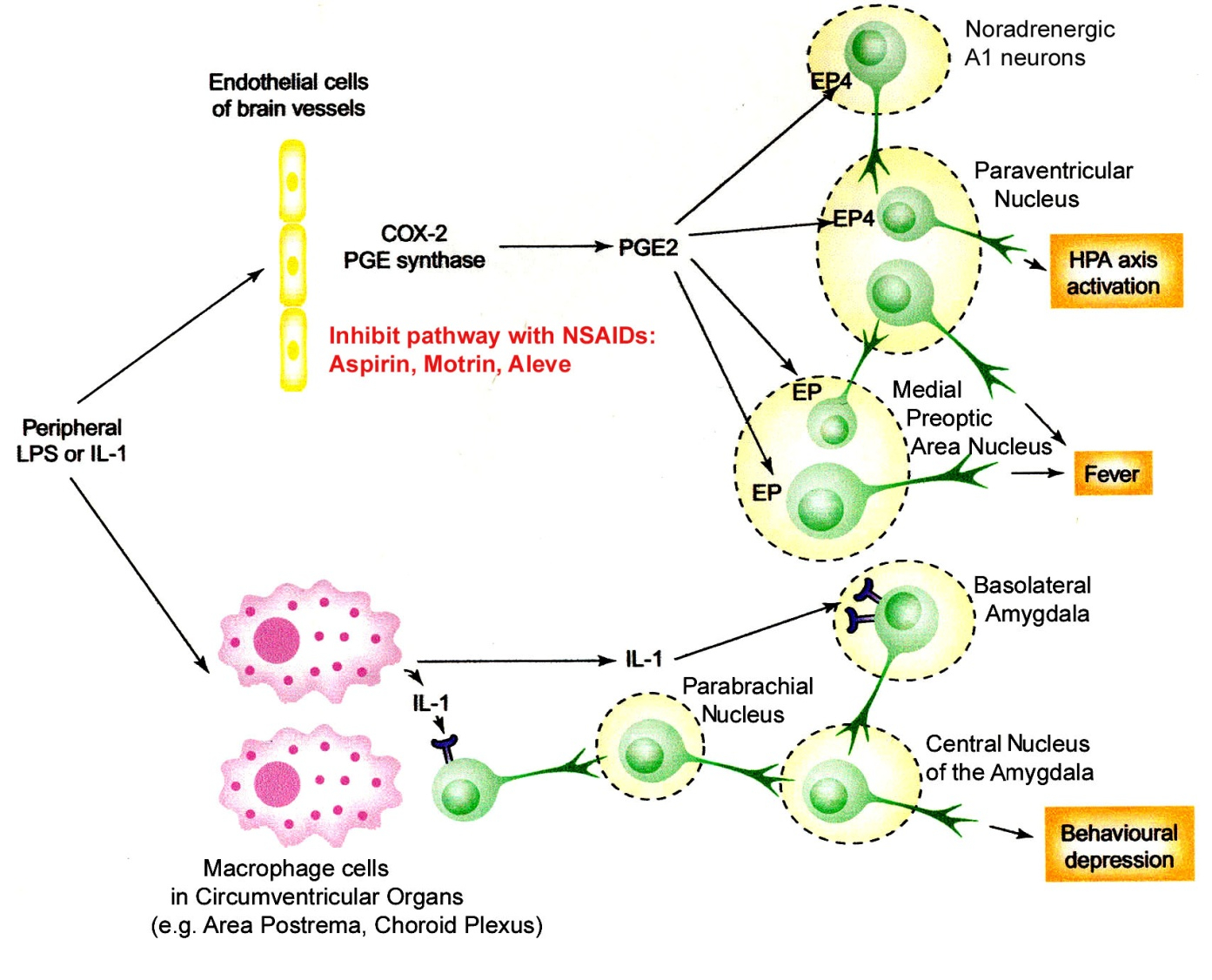
IL-1 :
Key driver of sickness behavior: fatigue, loss of appetite, fever, and social withdrawal.
Enhances HPA axis activation by stimulating CRH release → leads to higher cortisol levels.
In stroke and inflammation, IL-1 stimulates neurotrophic factors (like NGF), helping neurons recover.
Role in Stress Adaptation
Short-term : Enhances alertness , mobilizes energy, and promotes fever, which can help fight infections.
Long-term : Chronic IL-1 elevation disrupts cognition and mood ( linked to depression and anxiety in chronic stress conditions )
IL-6 :
Activates Janus Kinase (JAK) and STAT signaling, which turn on genes related to immune response and neuronal plasticity.
Increases astrocyte proliferation (helps with neuroprotection but can also contribute to neuroinflammation).
Induces fever, sleep regulation, and food intake changes.
Helps modulate glutamate-induced neurotoxicity, protecting neurons.
Role in Stress Adaptation
Promotes neuronal survival, especially in glutamate toxicity scenarios.
Enhances resilience to stress by regulating the HPA axis.
However, excessive IL-6 can increase pain sensitivity (allodynia, hyperalgesia) and worsen neuroinflammation.
Define Hyperalgesia and Allodynia
Hyperalgesia = normal pain is way/hyper more painful
Allodynia = an otherwise normal sensation is suddenly painful