Describe 5 Routes of Drug Administration
Oral : Drugs are taken through the mouth and absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract
Rectal : Administered through the rectum , useful when oral administration is not feasible
Topical : Applied to the skin or mucous membranes , such as creams or eye drops
Injection : Includes intravenous ( IV ) , intramuscular ( IM ) , and subcutaneous ( SC ) methods for direct delivery into blood or tissue
Respiratory : Inhaled drugs ( e.g., nasal sprays, inhalers ) absorbed through the respiratory tract
O - R - T - I -R
Identify the 3 Compartments of Body Water
Intervascular = blood plasma within blood vessels
3 Liters = 4%
Interstitial = fluid surrounding the cells in tissues
9 Liters = 13%
Intracellular = fluid inside cells ( cytosol )
28 Liters = 41%
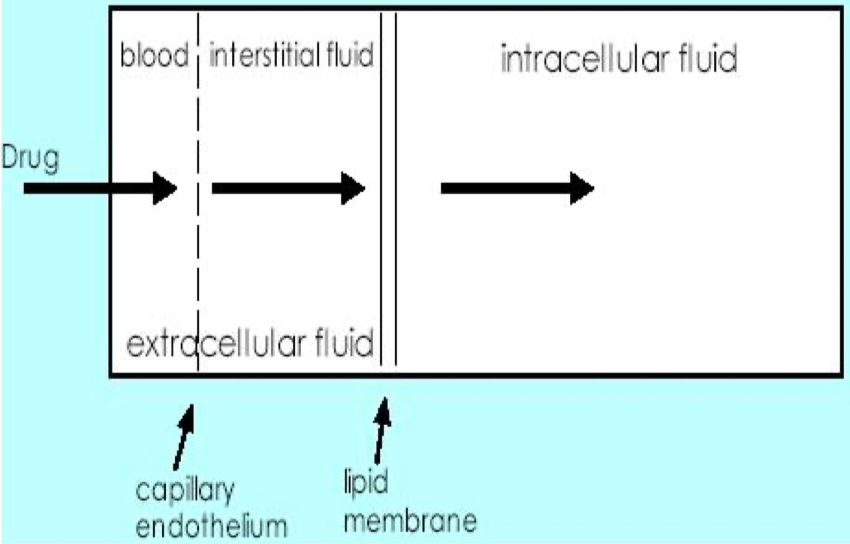
Identify 3 Things that Will Affect Drug Bioavailability
Absorption : Passage through membranes , impacted by drug solubility and ionization
First-Pass Metabolism : Degradation in the gut wall or liver before reaching systemic circulation
Chemical Stability : Destruction of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract ( e.g., stomach acid )
Describe the 2 Phases of Metabolism
Phase I :
Convert parent compound into a more polar / hydrophilic metabolite
Involves oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis to add or unmask functional groups ( e.g., -OH , -NH2 ) , often preparing the drug for Phase II
Phase II : Conjugation reactions with endogenous substrates to further increase water solubility for excretion.
conjugation with glucoronide , sulfate , acetate , amino acid
try to make them even more polar , to get them out of the body and into the urine
Phase II is the true “detoxification” step in the metabolism process

Describe the 3 Ways that the Body Excretes Drugs
Renal Excretion : Through urine , involving filtration , secretion , and reabsorption in the kidneys
Biliary Excretion : Through bile , often leading to fecal elimination
Respiratory Excretion : Drugs exhaled through the lungs , especially volatile compounds