Learning Objectives :
Name 3 different types of post-translational modification of proteins
Be able to describe what exactly occurs during this modification
Be able to describe how it affects the protein's function
Hydroxylation
Definition : Adds hydroxyl ( -OH ) groups , primarily to proline or lysine residues.
What Occurs :
Example: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor ( HIF-α )
Under normal oxygen levels ( normoxia ) :
Prolyl hydroxylase enzymes hydroxylate HIF-α.
Hydroxylation enables binding to von Hippel-Lindau ( VHL ) protein
HIF-α is ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome.
Under low oxygen ( hypoxia ) :
Hydroxylation does not occur.
HIF-α stabilizes , binds with HIF-β , and activates gene transcription for hypoxia response.
Effect on Protein Function :
Regulates protein stability.
Hydroxylation under normoxia ensures degradation of HIF-α , preventing hypoxia response.
Lack of hydroxylation under hypoxia allows HIF-α to activate survival genes.
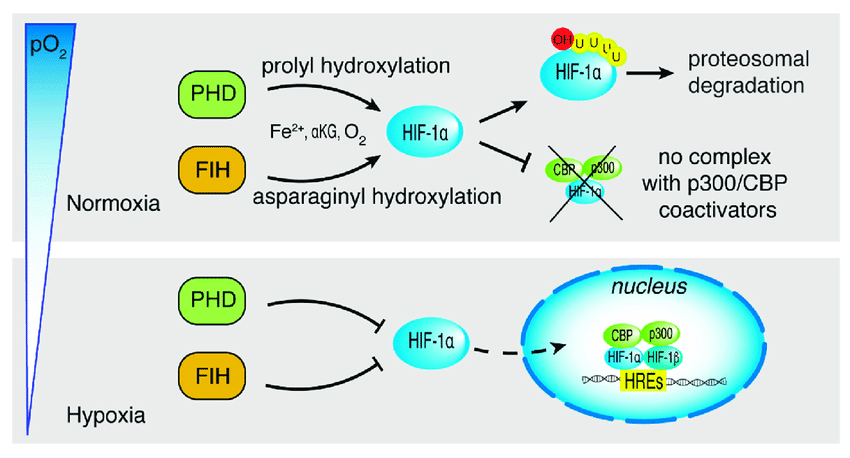
Normoxia = HIF gets hydroxylated ➡️ becomes ubiquinated ➡️ proteosomal degradation
Hypoxia = HIF doesn't get hydroxylated ➡️ becomes nuclear transcription factor ➡️ hypoxia response elements ( HREs ) are transcribed
Ubiquitination
Definition : Attaches ubiquitin proteins to lysine residues on target proteins.
What Occurs :
Marks proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome.
Example : HIF-α ubiquitination under normoxia.
Ubiquitination is triggered by hydroxylation and VHL protein binding.
Effect on Protein Function :
Regulates protein turnover by targeting them for degradation.
Maintains cellular homeostasis by removing damaged or unnecessary proteins.
Lipidation
Definition : Adds lipid groups ( e.g., palmitate, myristate ) to cysteine residues.
What Occurs :
Anchors proteins to membranes, altering localization and function.
Examples :
AMPA Receptor ( GluA1-4 ) :
Lipidation at TM2 ➡️ Golgi retention.
Lipidation at TM4 ➡️ Membrane insertion; enables PKC phosphorylation.
Potassium Channel ( Kcnma1 ) :
Lipidation at S0-S1 loop ➡️ ER and Golgi exit.
Lipidation at STREX site ➡️ Regulates kinase activity ( e.g., PKA inhibition )
Effect on Protein Function :
Alters membrane localization , which impacts protein interactions and signaling.
Specific lipidation sites determine whether proteins are retained in organelles or inserted into membranes , influencing downstream activity.
Phosphorylation
Definition : Adds phosphate groups to serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues.
What Occurs :
Carried out by kinases and reversed by phosphatases.
Example: AMP-Activated Protein Kinase ( AMPK ) :
Activated under stress ( e.g., low ATP/high AMP )
Phosphorylates glucose transporters to increase glucose uptake
Energy regulation :
AMP rises during low ATP ➡️ Activates AMPK.
Effect on Protein Function :
Alters protein activity , stability , and interactions.
Phosphorylation of glucose transporters enhances glucose uptake , helping maintain energy balance under stress.
Low ATP / High AMP ➡️ Activates AMPK ➡️ phosphorylates serine and threonine residues on glucose transporters ➡️ increases glucose import
Glycosylation
Definition : Addition of sugar groups ( glycans ) to proteins , primarily on extracellular domains.
What Occurs :
Facilitates cell-cell adhesion and protein-protein interactions.
Example - Sialic acid :
Negative charges repel but allow connections with positively charged glycans.
Example in podocytes: Glycosylation maintains podocyte-endothelial cell linkages.
Effect on Protein Function :
Enhances structural integrity and adhesion in cellular networks.
Modulates interactions with other proteins or cells , crucial for processes like immune responses and tissue stability.
Disulfide Bond Formation
Definition : Covalent linkage between two cysteine residues , forming disulfide bonds ( S-S )
What Occurs :
Stabilizes protein conformation by maintaining structural integrity.
Influenced by cellular redox states , which are regulated by reactive oxygen species ( ROS ) and antioxidants like glutathione.
Complex I and III of the mitochondrial electron transport chain can leak ROS , altering the redox environment and influencing disulfide bond formation.
This can lead to oxidative stress and misfolding if the redox balance is disrupted.
Effect on Protein Function :
Ensures correct protein folding and structural stability.
Misregulation can lead to misfolded proteins, resulting in dysfunction and disease.
Role of Glutathione : Glutathione maintains the proper redox environment for forming and breaking disulfide bonds.
It ensures that disulfide bonds are formed correctly by reducing incorrect linkages and preventing oxidative damage to cysteine residues.
SUMOylation
Definition : Addition of SUMO ( Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier ) proteins to target proteins.
What Occurs :
Modulates nuclear transport , transcriptional regulation , and DNA repair.
SUMO is attached to lysine residues , similar to ubiquitin.
Effect on Protein Function :
Alters protein localization and interactions.
Enhances or suppresses transcriptional activity , depending on the target.
Methylation
Definition: Adds methyl groups , primarily to lysine or arginine residues on histones.
What Occurs :
Regulates chromatin structure and gene expression.
Example: Histone methylation :
Specific methylation patterns can activate or repress gene transcription.
Effect on Protein Function :
Modulates gene expression by altering chromatin accessibility.
Plays a role in epigenetic regulation , influencing long-term cellular behavior.