Hormone Definitions
GnRH ( Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone ) : Released from the hypothalamus, stimulating LH and FSH release from the anterior pituitary.
LH ( Luteinizing Hormone ) : Triggers testosterone production in males and ovulation in females.
FSH ( Follicle-Stimulating Hormone ) : Stimulates spermatogenesis in males and follicle development in females.
Testosterone : Primary male sex hormone, crucial for sperm production and secondary sexual characteristics.
Estradiol ( Estrogen ) : Supports follicle maturation in females and prepares the uterine lining.
Progesterone : Key hormone in pregnancy maintenance, produced by the corpus luteum and later the placenta.
HCG ( Human Chorionic Gonadotropin ) : Secreted post-implantation to sustain the corpus luteum and progesterone production.
Endocrine vs. Molecular Mechanisms ( Gene Transcription )
Endocrine Regulation: Involves steroid hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone acting on distant target tissues through the bloodstream.
Molecular Mechanism : Refers to gene transcription regulated by hormone-receptor interactions, such as :
LH and FSH activating gene transcription for testosterone production, androgen-binding proteins, and enzymes for estrogen synthesis.
Molecular Mechanism : Gene Transcription Driven by Hormonal Signaling
Male System ( Spermatogenesis ) :
LH in Leydig Cells :
LH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Cholesterol ➡️ Pregnenolone ➡️ TestosteroneExplanation : LH activates cAMP and PKA , driving gene transcription of enzymes that convert cholesterol to testosterone in Leydig cells.
FSH in Sertoli Cells :
FSH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Gene Transcription ➡️ Androgen-Binding Protein (ABP)Explanation : FSH activates gene transcription for ABP , aiding sperm maturation and transport.
Female System ( Oogenesis and Follicle Development ) :
LH in Theca Cells :
LH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Cholesterol ➡️ Pregnenolone ➡️ AndrogensExplanation : LH activates gene transcription for enzymes that convert cholesterol to androgens in theca cells.
FSH in Granulosa Cells :
FSH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Gene Transcription ➡️ Aromatase ➡️ Androgens ➡️ EstrogensExplanation : FSH in granulosa cells transcribes aromatase , converting androgens ( from theca cells ) to estrogens , completing estrogen production.
Key Processes of Embryo Development
Sperm Capacitation and Acrosome Reaction ( Likely Quiz Question ) :
Capacitation: Sperm undergoes changes upon contact with the female reproductive tract
the sperm head becomes permeable to calcium ions
increases motility and the ability to swim.
Capacitation and Sperm activation occur within 1-10 hours
Acrosome Reaction: Enzymes in the sperm head ( acrosome ) are released to penetrate the egg’s outer layer
The fusion of the sperm and egg allows the release of genetic material to initiate fertilization.
Fertilization and Zygote Formation :
Fusion of Pronuclei: Male and female pronuclei fuse to create a single-cell zygote with 46 chromosomes.
Cleavage: Rapid cell divisions without growth, forming a morula (solid ball of cells).
Blastocyst Formation: Cells differentiate into trophoblasts (future placenta) and the inner cell mass (future embryo).
Implantation: Blastocyst attaches to the uterine lining within the “window of receptivity” (Days 19-23 of the menstrual cycle).
Why does only 1 sperm enter an oocyte?
2 would be bad , chromosome problems
Within minutes of sperm binding , calcium ions in the oocyte cause cortical granules to be released and remove any other sperm that may be attached
Electrical Depolarization shocks outside of ovum
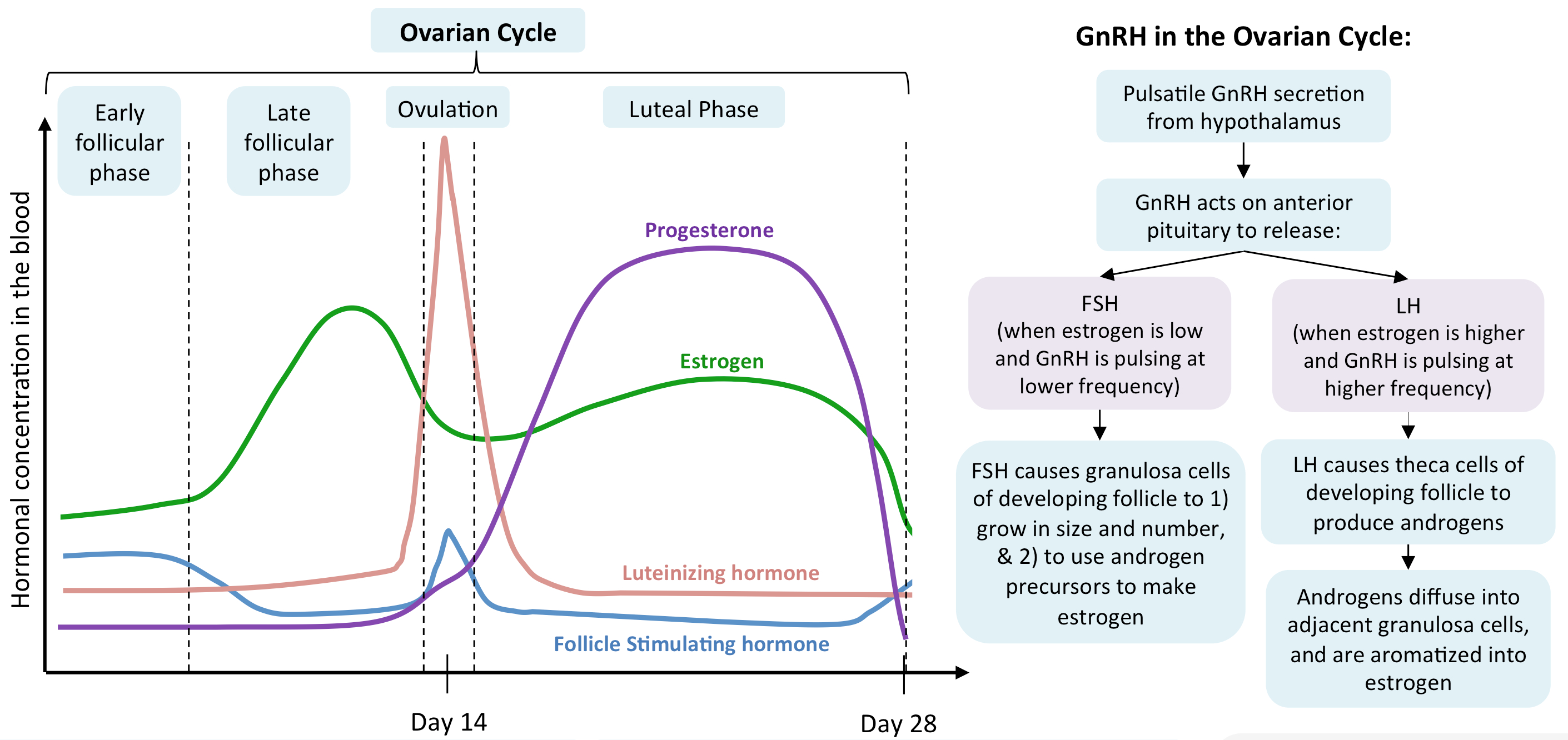
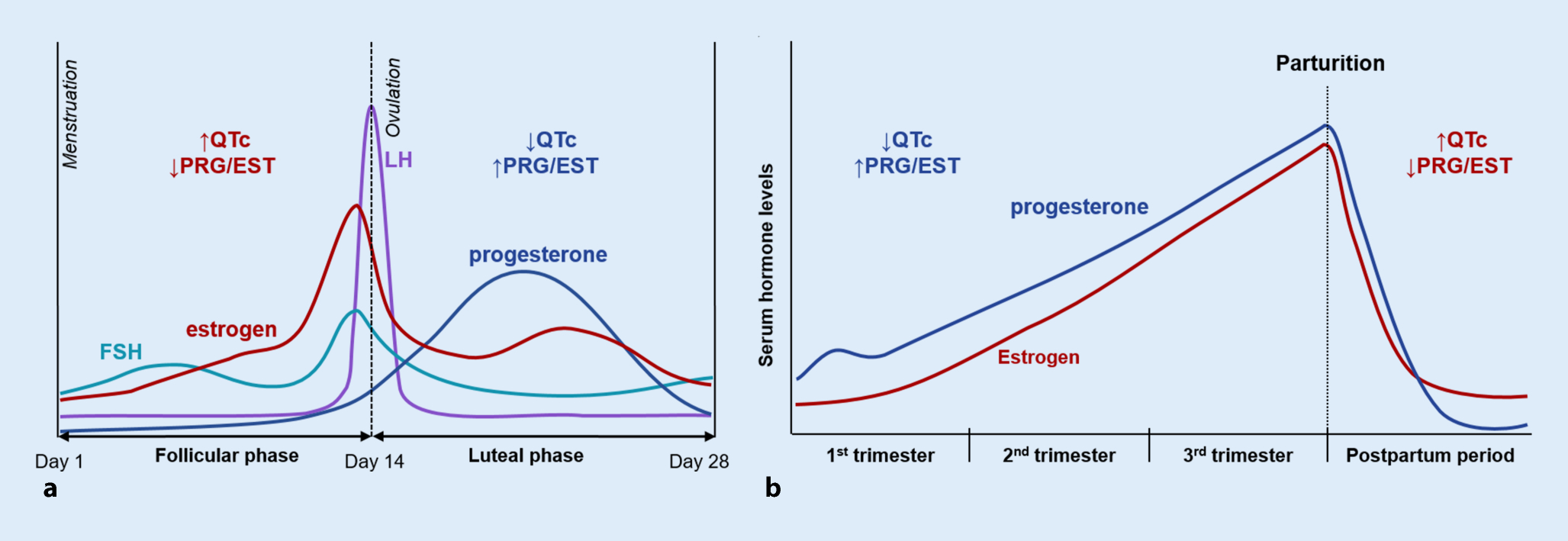
Menstrual Cycle Diagram
Hormones:
FSH ( Follicle-Stimulating Hormone ) : Stimulates follicle development in the ovaries.
LH ( Luteinizing Hormone ) : Triggers ovulation through the LH surge.
Estrogen : Rises during the follicular phase, supporting uterine lining growth; drops after ovulation.
Progesterone : Rises post-ovulation during the luteal phase to support the endometrium for potential implantation.
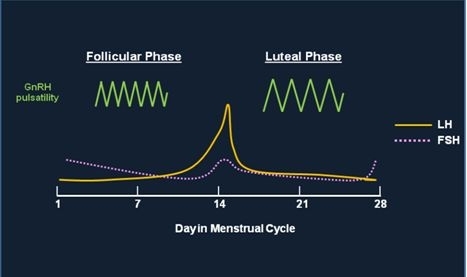
Sequence of Hormone Events:
Follicular Phase ( Days 1-14 ) : FSH and estrogen levels gradually increase , supporting follicle development.
Ovulation ( Day 14 ) : Estrogen hits a threshold, causing a positive feedback loop that triggers the LH surge. This surge leads to ovulation.
Luteal Phase ( Days 14-28 ) : Progesterone rises as the corpus luteum forms , maintaining the uterine lining. If no fertilization occurs, progesterone drops , leading to menstruation.
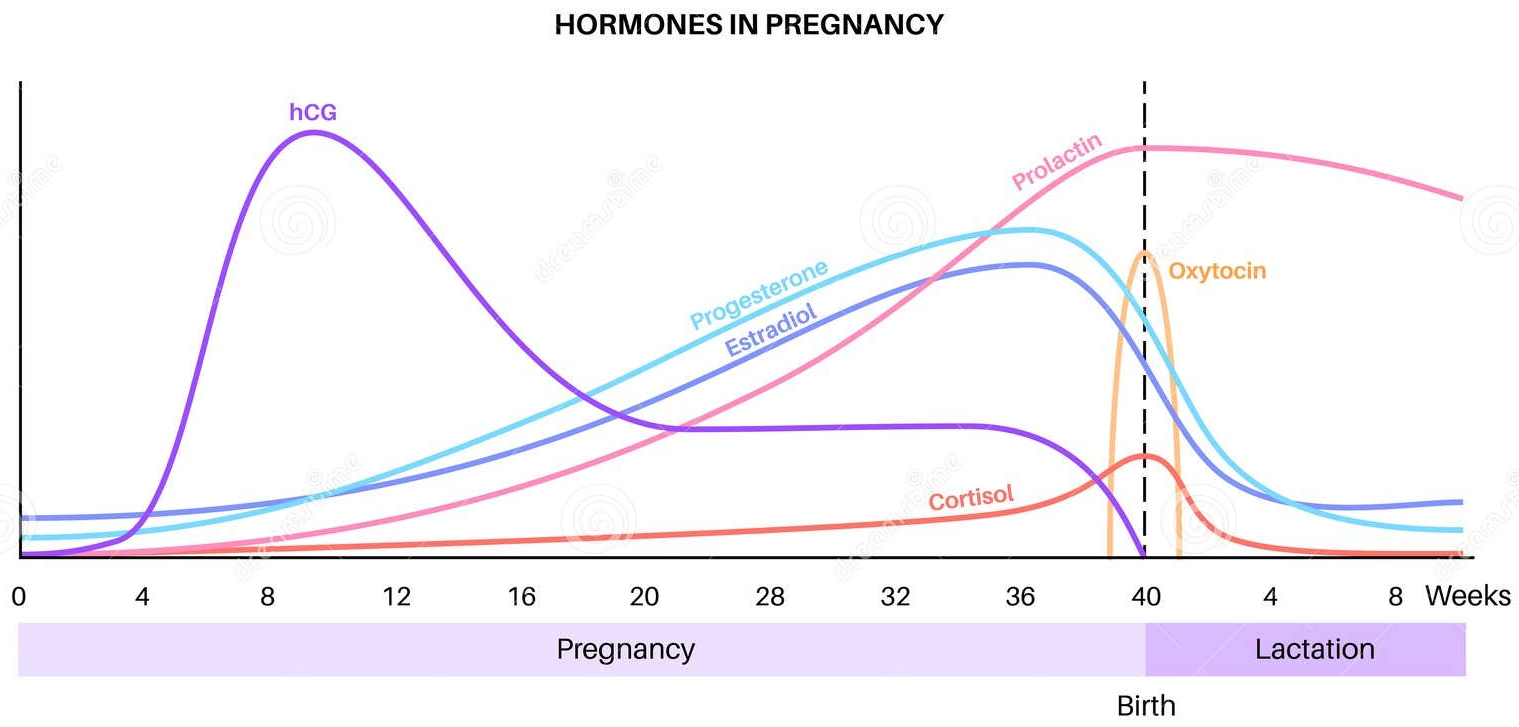
Progesterone Sources During Pregnancy
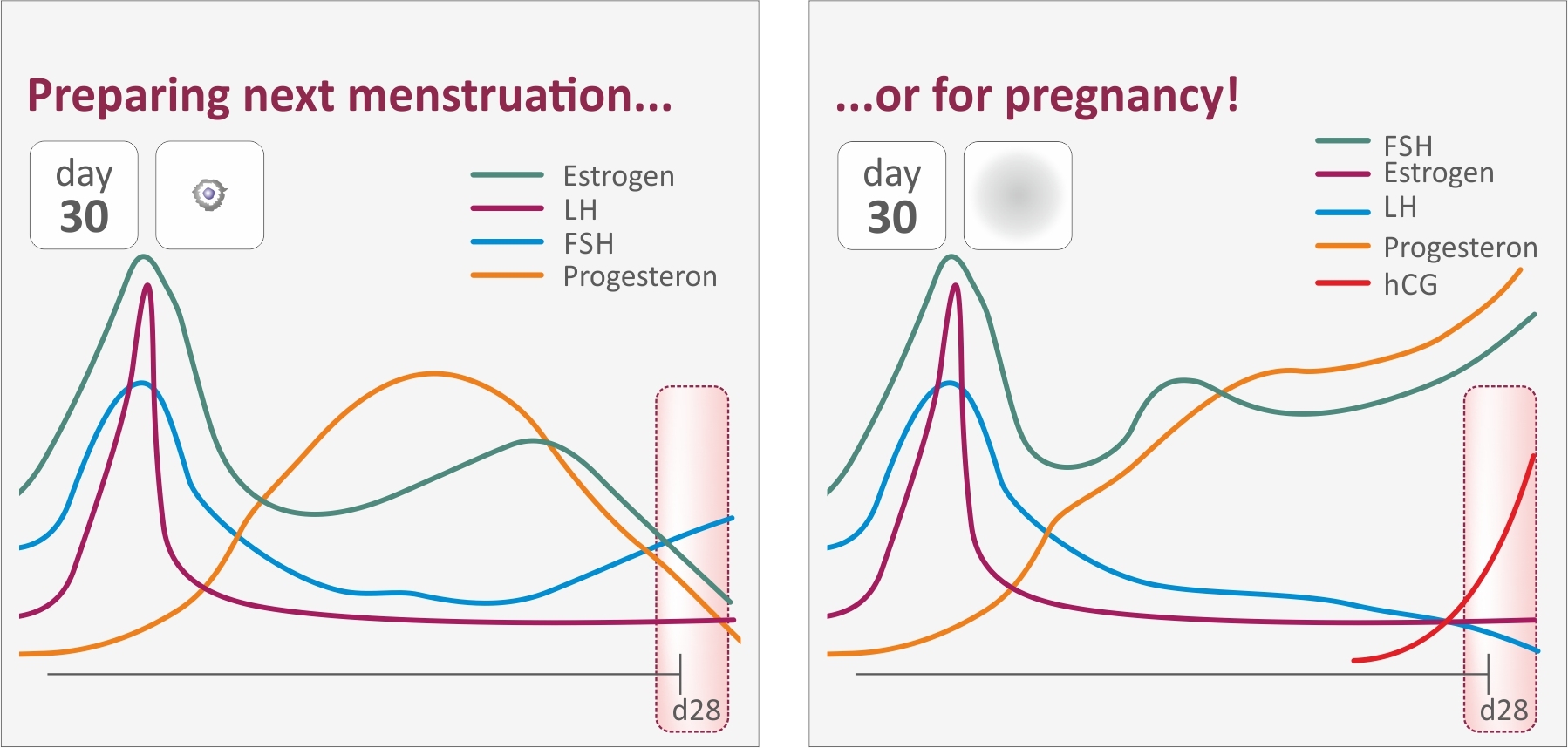
Three Sources of Progesterone ( Likely Quiz Question ) :
Corpus Luteum ( Initial Source ) : Provides progesterone immediately after ovulation to maintain the uterine lining.
HCG Signal : After implantation, the embryo secretes HCG to signal the corpus luteum to continue progesterone production.
Placental Progesterone Production : Around week 10, the placenta takes over progesterone production, sustaining pregnancy through delivery.
Regulatory Mechanisms in Reproduction
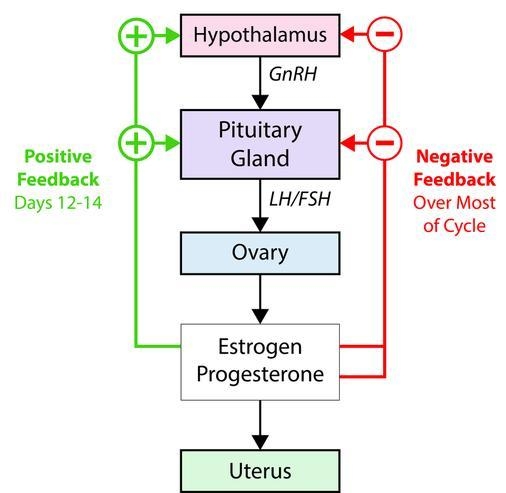
Negative Feedback :
In both males and females, high levels of testosterone or estrogen inhibit GnRH, LH, and FSH release, regulating hormone levels.
Positive Feedback Loops :
LH Surge : High estrogen levels before ovulation surpass a threshold, creating a positive feedback that causes a surge in LH, leading to ovulation.
Oxytocin in Labor : During labor, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions and cervical stretching. This stretching increases oxytocin release, amplifying contractions until birth.
Potential Quiz Questions and Answers
Describe the hormonal control of spermatogenesis.
Answer: GnRH from the hypothalamus stimulates LH and FSH release. LH acts on Leydig cells to produce testosterone, while FSH stimulates Sertoli cells to transcribe genes for ABP, promoting spermatogenesis. Testosterone provides negative feedback to regulate hormone levels.
Outline the sequence of events leading to ovulation.
Answer: During the follicular phase, rising FSH and LH stimulate estrogen production. High estrogen levels trigger a positive feedback loop, causing an LH surge. The LH surge prompts ovulation.
Explain the “molecular mechanism” involved in testosterone production in males.
Answer:
LH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Cholesterol ➡️ Pregnenolone ➡️ Testosterone– LH binds to receptors on Leydig cells, activating cAMP and PKA, which drives gene transcription for enzymes converting cholesterol to testosterone.
What is the role of HCG in pregnancy maintenance?
Answer: HCG, produced by the trophoblast post-implantation, signals the corpus luteum to continue progesterone production, which maintains the uterine lining for pregnancy.
Explain why progesterone levels must remain high during pregnancy and the effects of a drop in these levels.
Answer: High progesterone levels inhibit uterine contractions and support the endometrium for embryo survival. A drop in progesterone can trigger uterine contractions and potentially cause miscarriage.
Misc
Positive and Negative Feedback:
differentiate between positive (e.g., LH surge, oxytocin) and negative feedback mechanisms (e.g., testosterone inhibiting LH and FSH).
Capacitation and Acrosome Reaction:
“What two processes enable sperm to fertilize an egg?”
Answer: Capacitation and acrosome reaction.
Process of Fertilization :
a ligand on sperm binds to the oocyte sperm receptor ( ZP3 )
causes increase in oocyte internal calcium
triggers a cortical reaction to prevent polyspermy
this binding induces the acrosome reaction
sperm and oocyte membranes fuse
Difference Between Endocrine and Molecular Mechanisms:
Understand that “molecular mechanism” here refers to hormone-induced gene transcription
e.g., ABP production in Sertoli cells , aromatase in granulosa cells
Embryonic Development Stages :
fertilized egg ➡️ zygote ➡️ cleavage ➡️ morula ➡️ blastocyst ➡️ implantation.
Teratogens:
Critical Period : First 10 weeks ( organogenesis ) when teratogens are most harmful.
“When are teratogens most harmful?” - Answer: First 10 weeks of pregnancy.
Three Sources of Progesterone:
three stages : corpus luteum ➡️ HCG signal ➡️ placenta
Other :
Endocrine Function = Hormones
Molecular Mechanism = gene regulation
Male = LH
Anabolic steroid use in men reduces gonadal Testosterone secretion and results in a reduction in sperm
Sperm must undergo two processes to become capable of fertilizing an egg , capacitation and the acrosome reaction
female reproduction is more complex because there is a gestational phase
entirely separate function it switches to
once ovulation starts , timing order becomes constant
Window of Receptivity = after ovulation , window of time where fertilization needs to occur
70% of fertilized eggs do not develop
only the perfect embryos hopefully get selected
How does the corpus luteum know to stay around ?
it doesn't. a fertilized egg somehow releases hCG
hCG = signal to keep secreting progesterone
After you fertilize , you get rid of epigenetic marks
after 1st cell division , epigenetic marks get put back on
Ectoderm = nervous tissue
Endoderm = GI tract
Mesoderm = everything else , bones , muscle
First 10 weeks = majority of development
most dangerous time for teratogen exposure
Preeclampsia = Rapid onset high blood pressure with proteinuria or other organ involvement
Quiz :
molecular pathways of gamete production
outline implantation
diagram