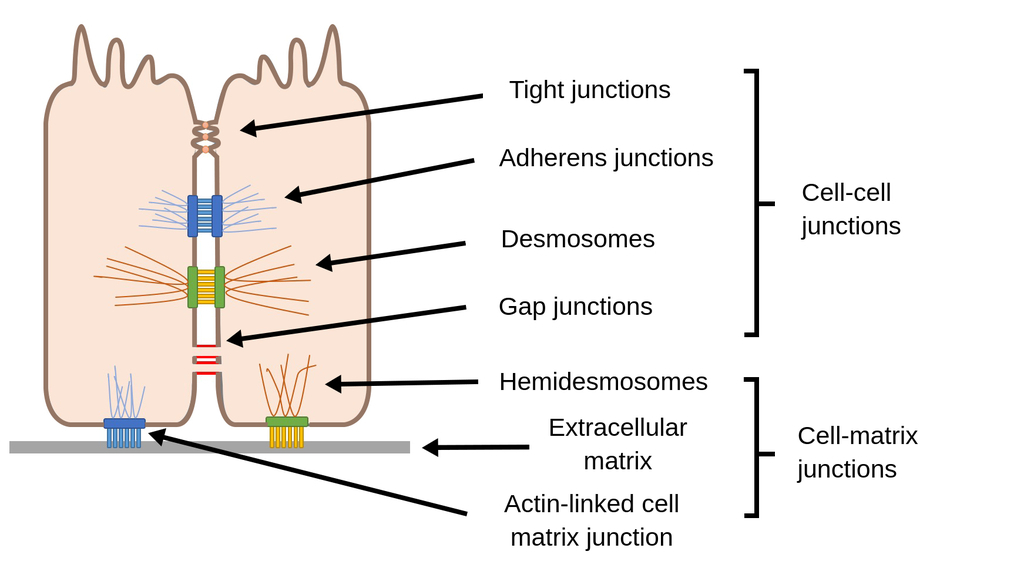
Cell Junctions
Tight Junctions :
contain strands of cloudin and occludin
example = blood-brain-barrier
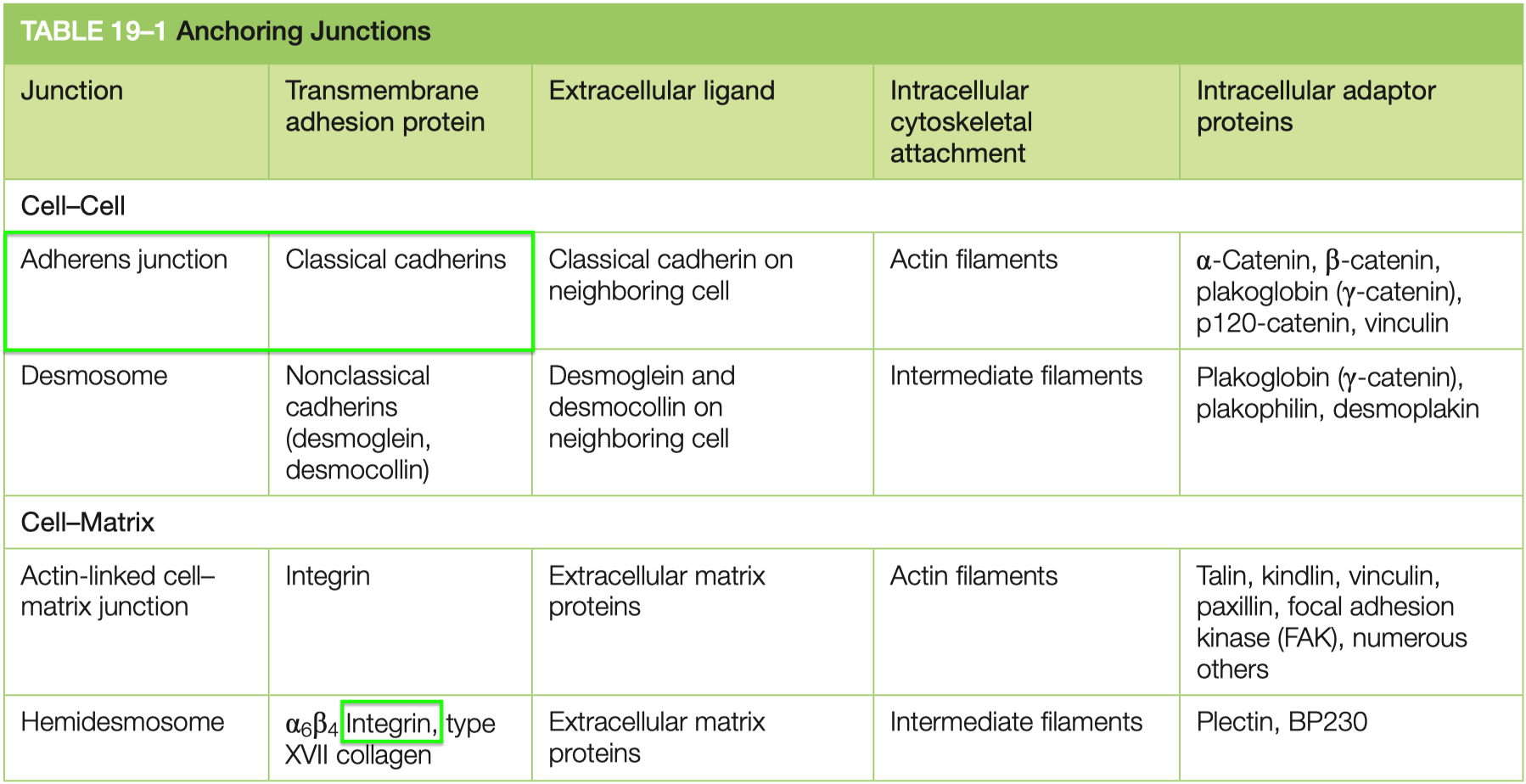
Adherens :
strong mechanical
peristalsis
uses classical cadherins to link cytoskeleton ➡️ actin
Desmosomes :
stronger than adherens
tissue rigidity
uses non-classical cadherins to link cytoskeleton ➡️ intermediate filaments
cardiac muscle , skin
Hemidesmosomes :
uses integrins to link cytoskeleton ➡️ basal lamina intermediate filaments
Gap Junctions :
facillitate communication
synchronized heart beat
allow electricity , ATP , misc things to pass
6 trans membrane domains
connected by connexins
GPCR
Signal Molecule binds and Activates GPCR (
binds and inhibits adenylyl cyclase
reduces PKA activation
reduces cell response ( gene transcription )
Signal Molecule binds and Activates GPCR (
binds and stimulates adenylyl cyclase
increases PKA activation
increases cell response ( gene transcription )
Signal Molecule binds and Activates GPCR (
this depletes levels of PIP2 in the membrane
but voltage gated M-channels ( potassium channels ) need PIP2 in order to open
so M-channels close
this is a SIGNALING event !
the removal of PIP2 closed potassium channels , depolarizes the membrane ,
makes it very easy to fire action potential now
only a little bit of sodium is need to reach the action potential threshold
DAG then activates PKC
IP3 causes calcium to be released from endoplasmic reticulum
the calcium can also reinforce / enhance signaling of PKC
3 Different Ways
Depletion of
Liberation of
Libration of DAG and hence activation of PKC
Describe one alternative pathway that G-protein activation may signal via
Conventional Way = producing signaling molecules
Alternative Way = reduction ! of
Misc
Cadherins = used in adherins and desmosomes
calcium dependent
Catenins = link cadherins ➡️ actin skeleton
Integrins = link cytoskeleton ( actin ) ➡️ ECM
Extracellular Matrix Compounds
Proteoglycans
Fibrinectin
Integrins
Glycoproteins