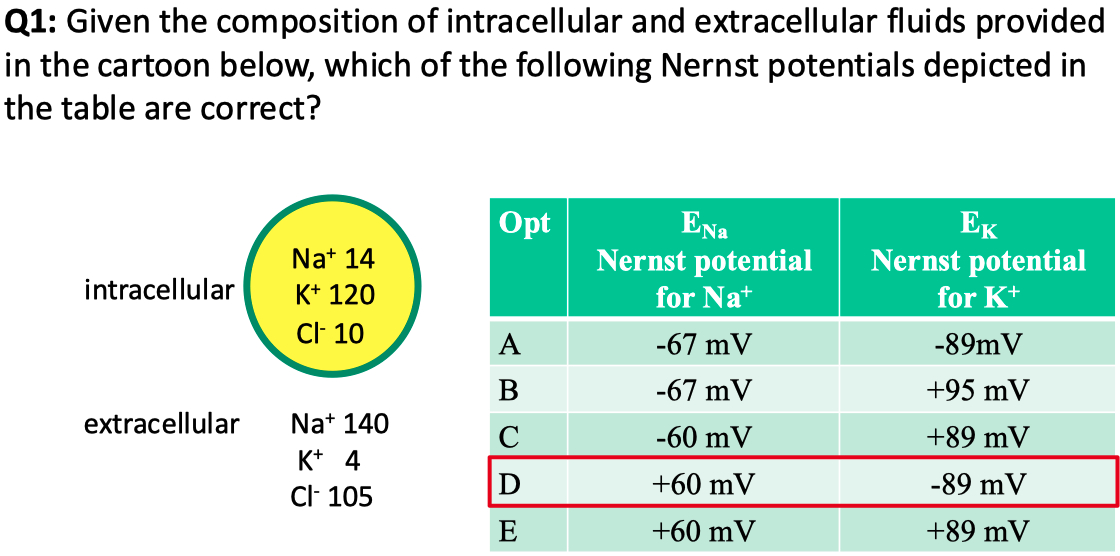
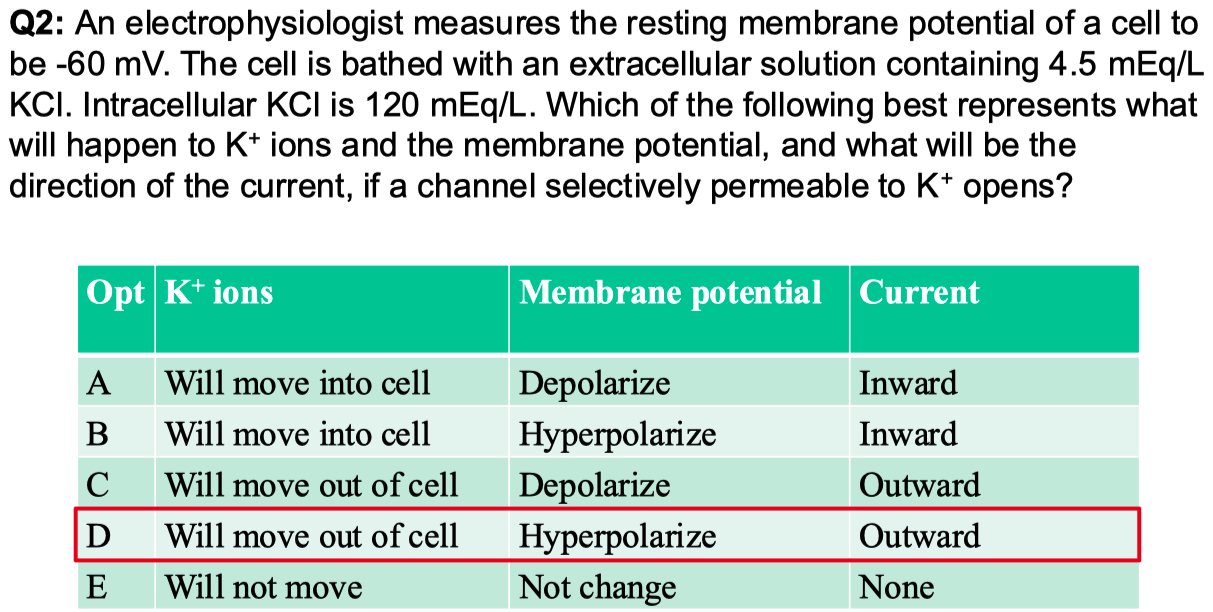
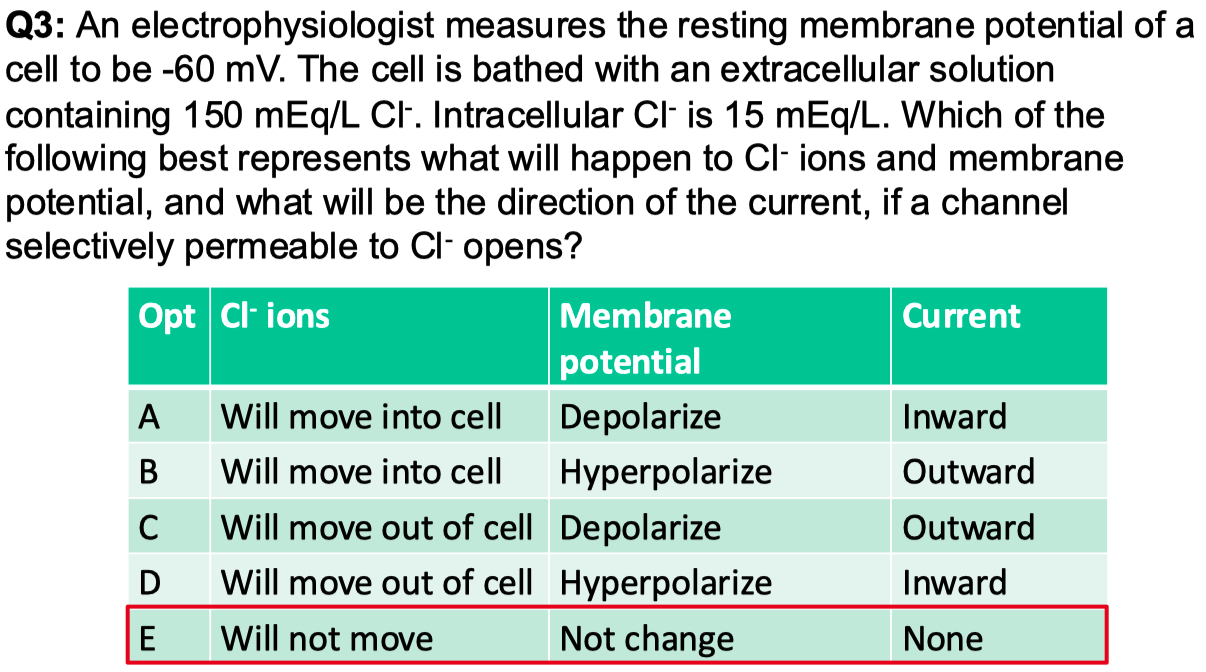
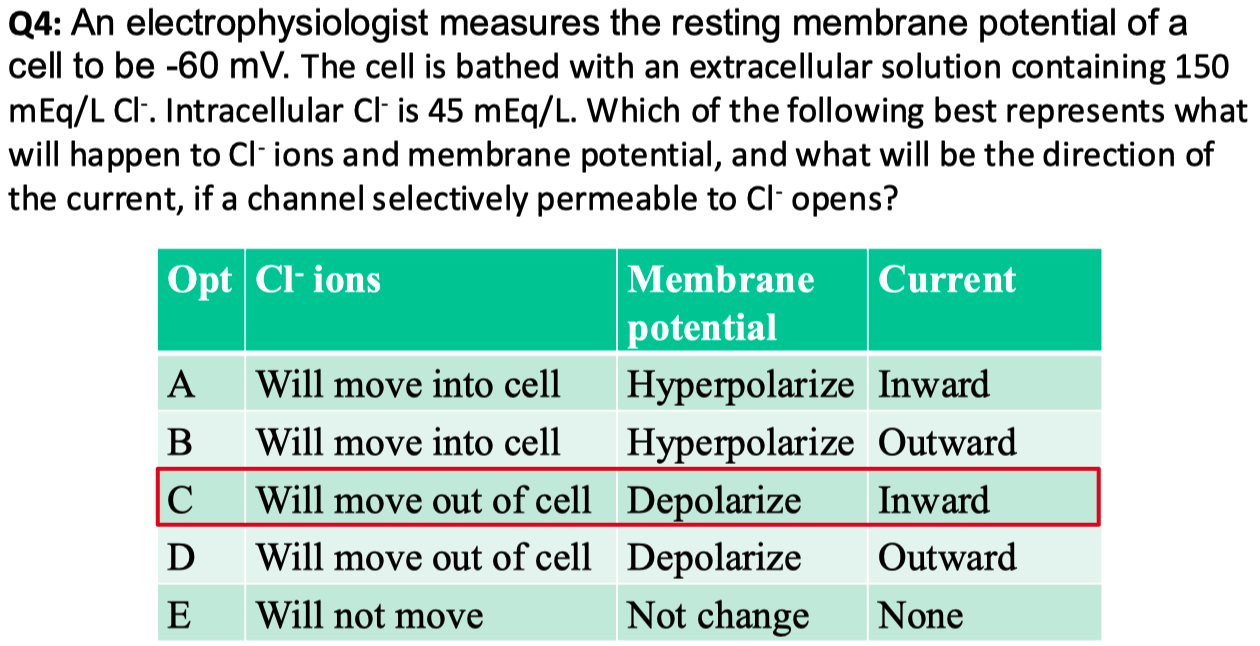
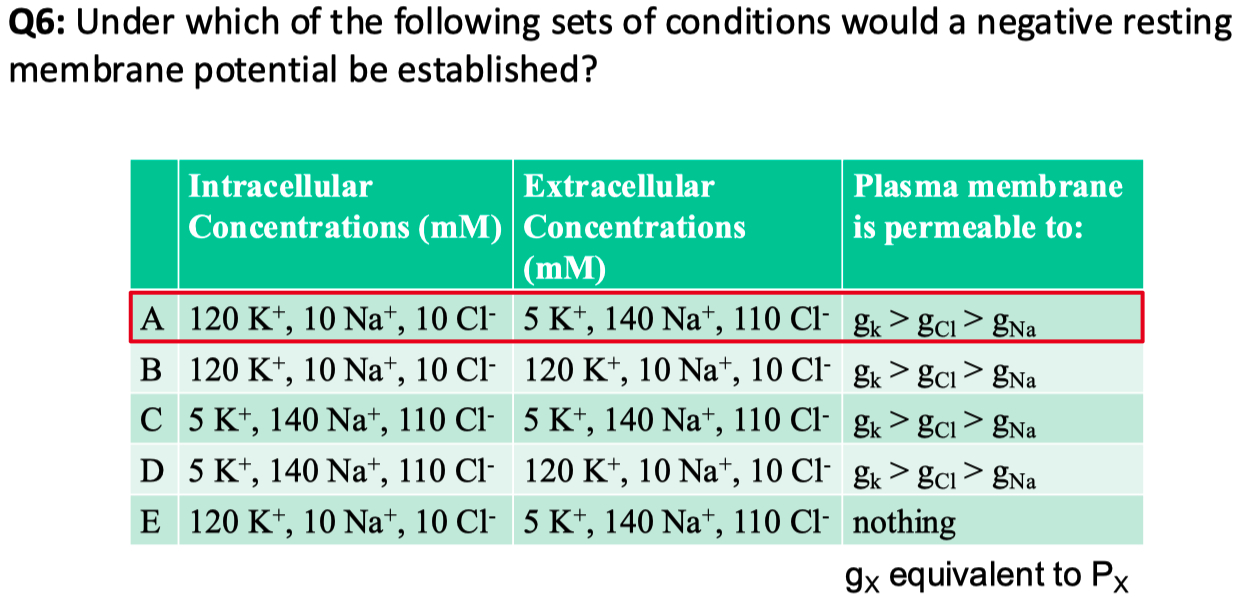



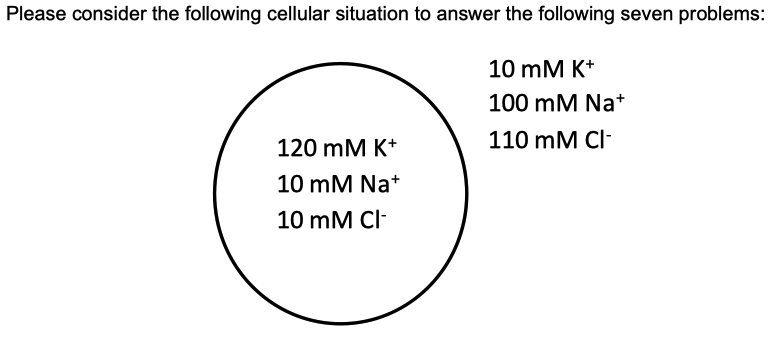
If the cell above is equally permeable to
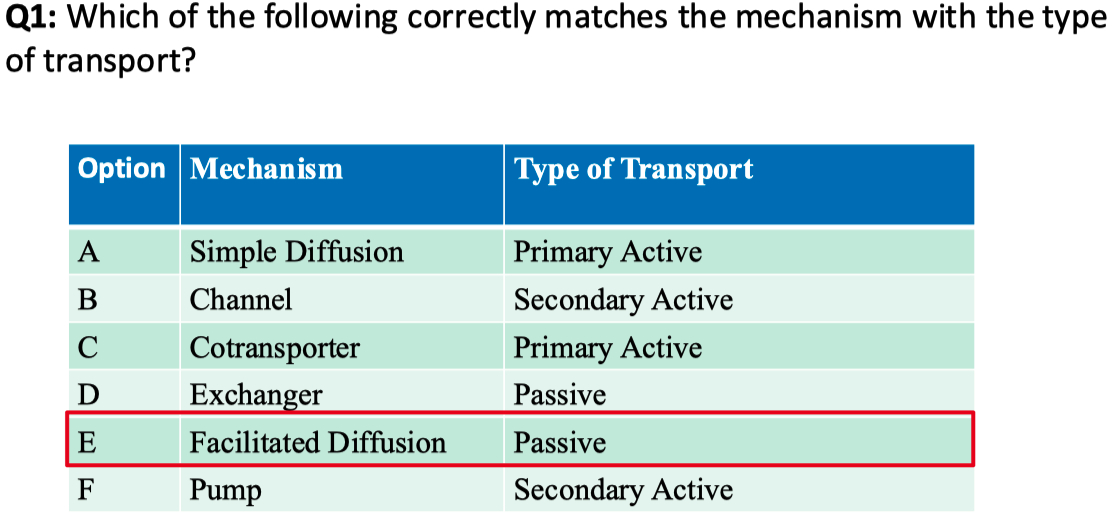
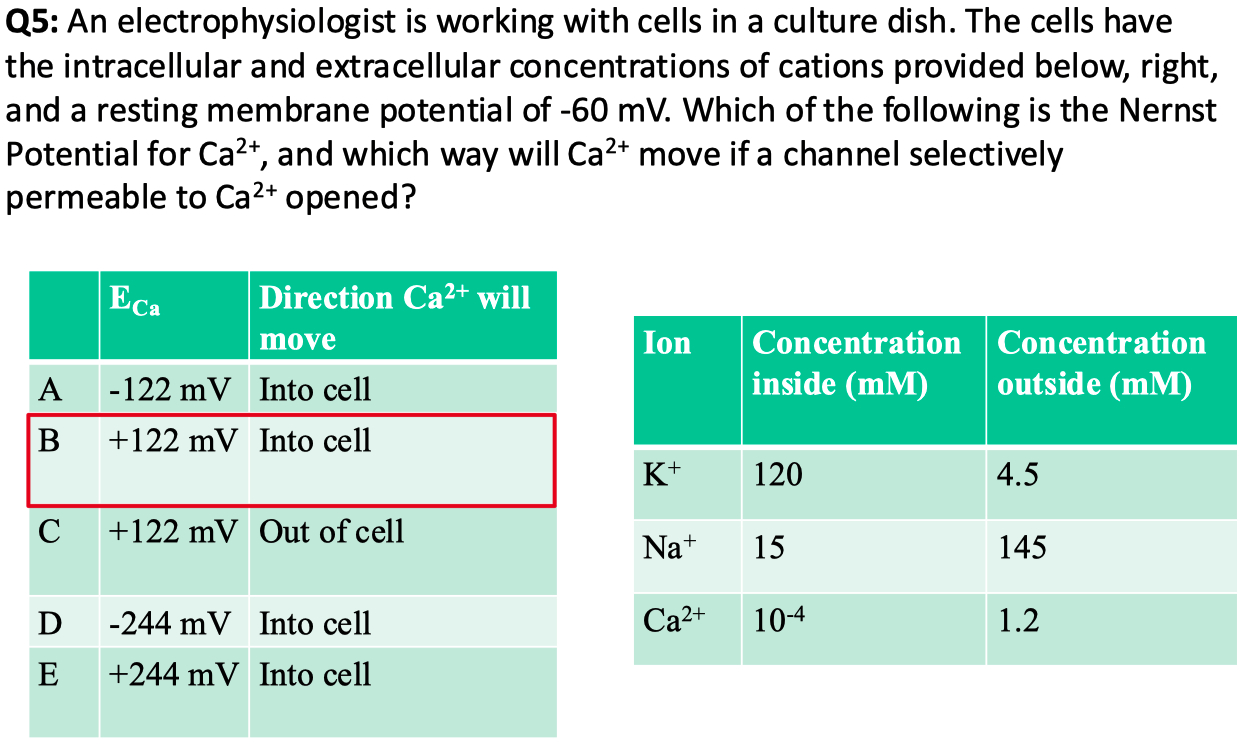
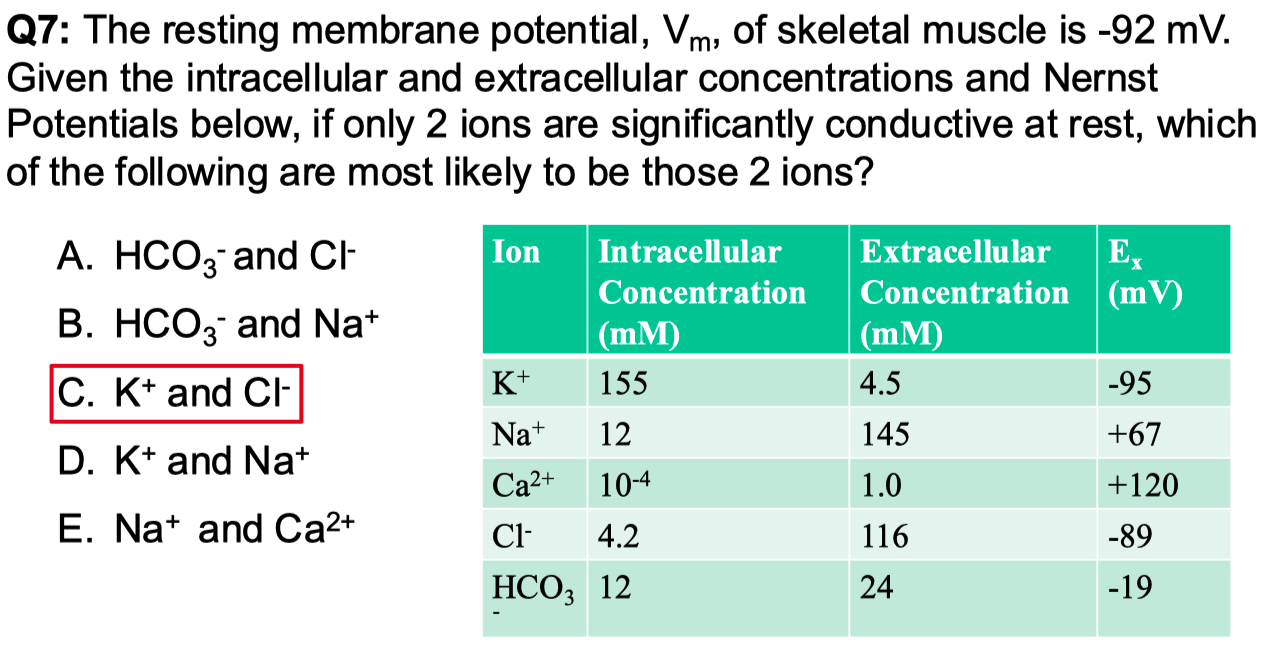
Answer = C = closest to
What direction does
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being negative
cations will want to go inside
anions will want to go outside
depolarizes the membrane
current flow = inward
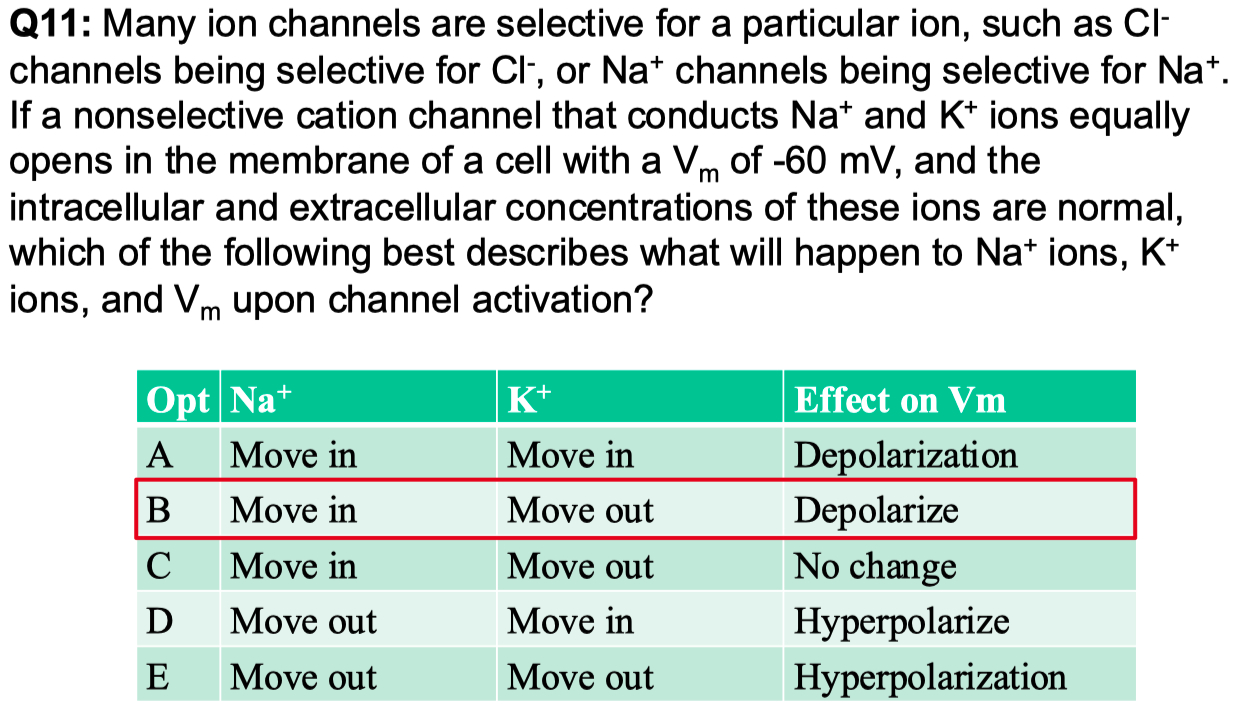
What direction does
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being positive
cations will want to go outside
anions will want to go inside
hyperpolarizes the membrane
current flow = outward
What direction does
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being positive
cations will want to go outside
anions will want to go inside
hyperpolarizes the membrane
current flow = the movement of negative charges
since negative ions moving in is the same as positive ions moving out
If
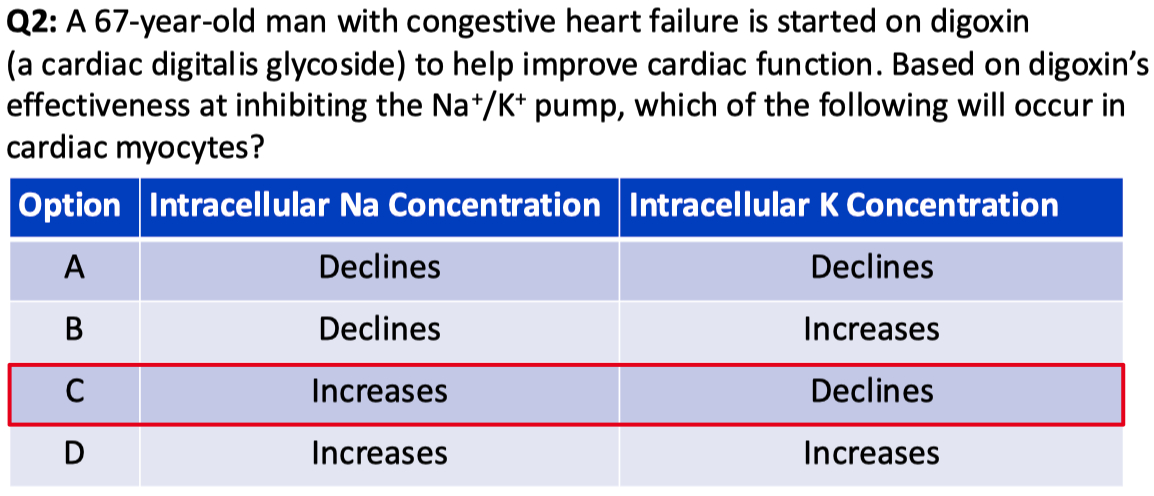
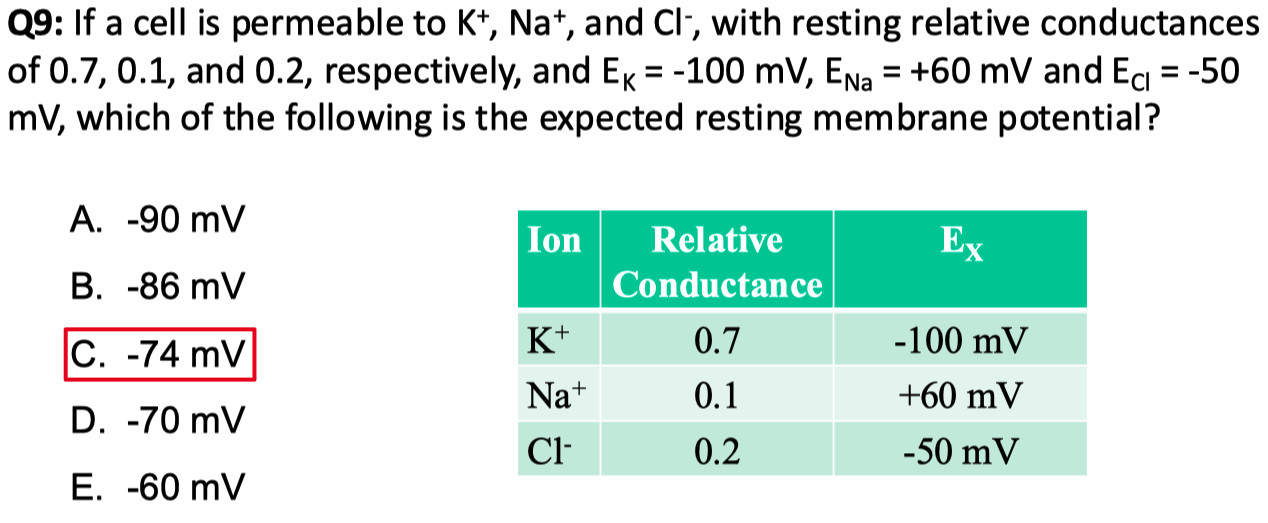
Answer = B = closest to
At this new membrane potential, what direction does
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being positive
cations will want to go outside
anions will want to go inside
hyperpolarizes the membrane
current flow = the movement of negative charges
since negative ions moving in is the same as positive ions moving out
If the serum
The cell will hyperpolarize , because the new membrane potential
Separate Problem :
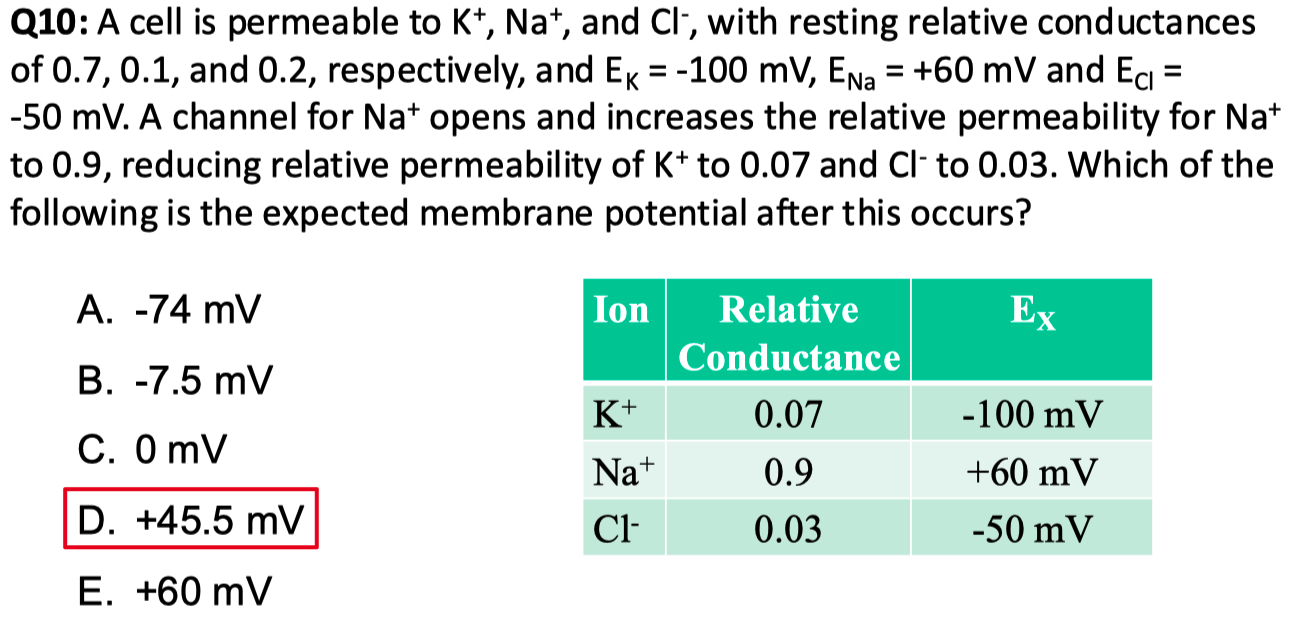
Part A : A cell is permeable to
Part B : Then, a channel for
Resting membrane potential before the change:
Membrane potential after
Ion movements:
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being negative
cations will want to go inside
anions will want to go outside
depolarizes the membrane
current flow = inward
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being negative
cations will want to go inside
anions will want to go outside
depolarizes the membrane
current flow = inward
Driving Force =
think of this as the inside of the cell being positive
cations will want to go outside
anions will want to go inside
hyperpolarizes the membrane
current flow = the movement of negative charges
since negative ions moving in is the same as positive ions moving out