Blood Flow
Resistance
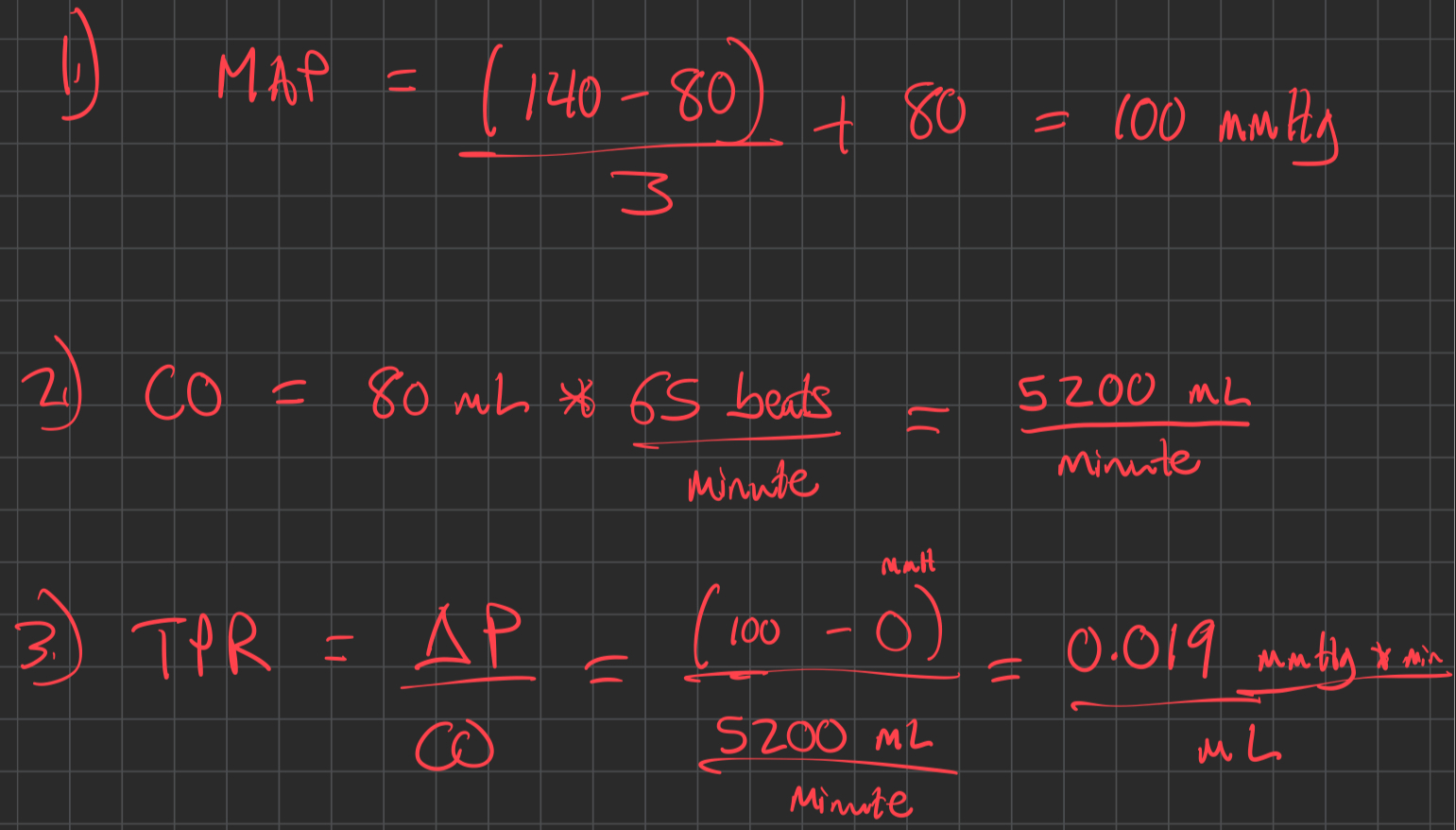
Starling Equation :
positive = efflux = filtration out of capillary into intersitium
negative = influx = absorption from interstitium into capillary
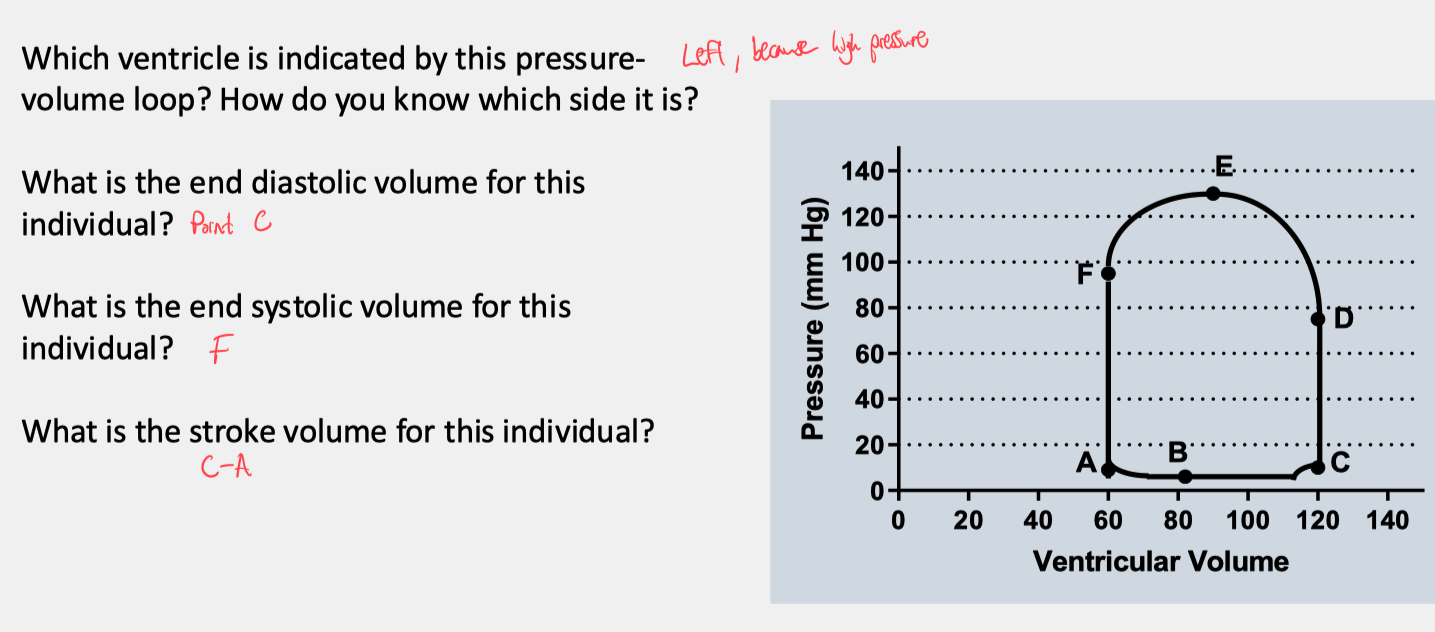
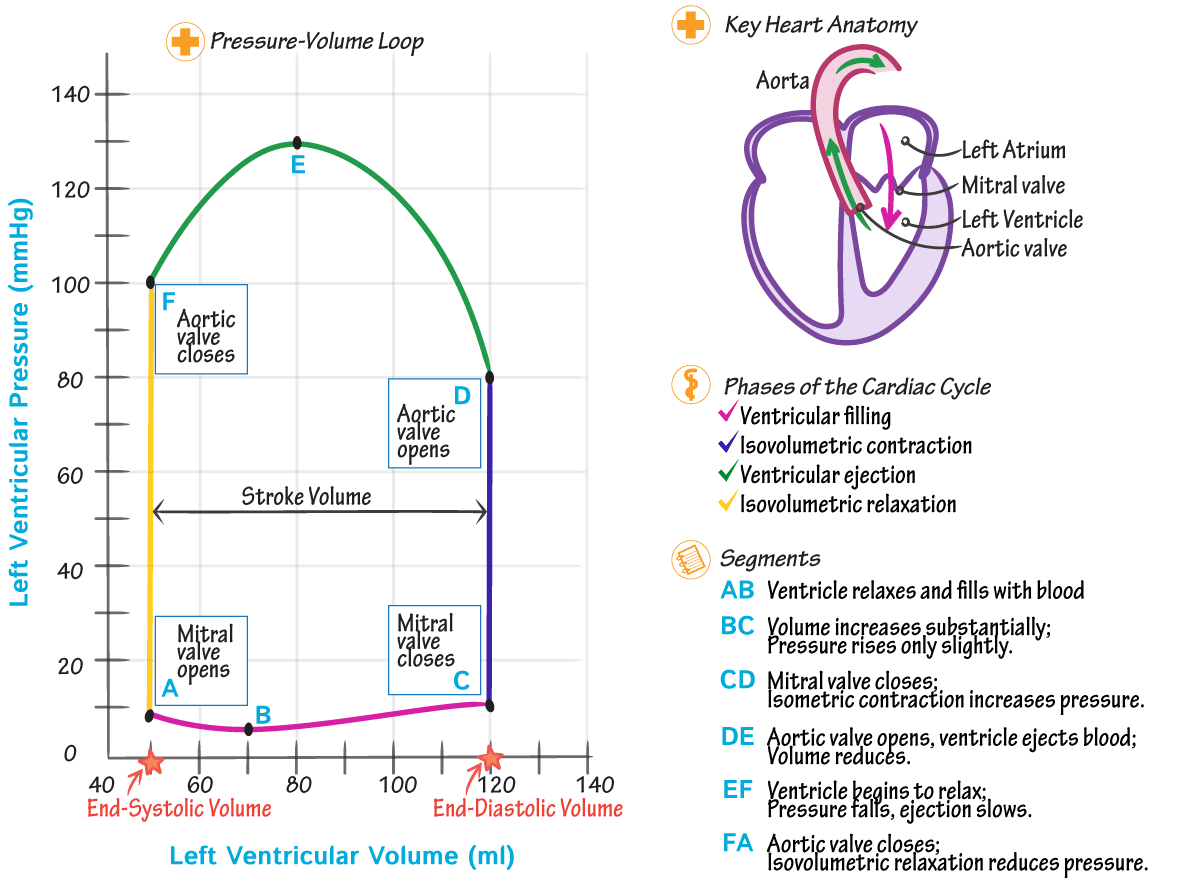
Cardiac Myocyte ECG Waveform :
P = atria contract
QRS = ventricles contract
ST = semilunar valves open
T = ventricles close
Filling
Cardio Myocyte Action Potential Waveform :
Depolarization due to sodium entering
Temporary Plateau as combination of Calcium entering and Potassium leaving
calcium enters , potassium leaves
Repolarization due to calcium channels closing , and potassium channels remaining open
NA-K-ATPase pumps re-establish resting membrane potential
Sympathetic Nervous System Control :
Baro Reflex =
Chemoreflex = carotid bodies detect high
Vasoconstrictors :
Angiotensin 2
Prostaglandins
Thromboxane
Vasodialators :
Nitric Oxide
Bradykinin
Maximize Diffusion of Oxygen in Alveoli = large surface area , low tension / thickness , strong pressure gradient , warm and moist air
Anatomic Dead Space = trachea
Functional Dead Space = collapsed bronchioles / alveoli
Respiratory System Cells :
Type 1 Pneumocytes = gas diffusion
Type 2 Pneumocytes = surfactant production
Ciliated Epithelial = debris removal
Goblet Cells = mucus production
Slow , Deep Breaths = more efficient
larger total tidal volume than fast , short breaths
you have to subtract some to dead space every breath , so you might as well make each as large as possible
Restrictive vs Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases :
Restrictive :
reduction in compliance
fibrosis , embolism
difficulty inhaling
reduced lung volumes ( all )
high
Obstructive :
inflammation
asthma , COPD , emphysema
difficulty exhaling
incomplete emptying of air from the lungs
increases reserve volume
low
Hemoglobin is needed because
Left Shift = high affinity for
Haldane Effect = hemoglobin binds
fetal hemoglobin so they can have preference over the mom's hemoglobin
Right Shift = low affinity for
Bohr Effect = Hb binds
3 Ways
Dissolved in blood plasma
Bound to hemoglobin
In bicarbonate ion form
Negative Pressure Pump :
diaphragm contraction increases thoracic volume creating sub-atomospheric pressure in the lungs to draw air in
Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction ( HPV ) = redirects bloodflow , leading to emphysema , leading to embolism , leading to pressure increases , leading to right heart failure
Control of Breathing :
pre-Botzinger = inhalation rhythm
Botzinger = exhalation rhythm
Parasympathetic = dilates , reduces mucus
Sympathetic = constricts , increases mucus
Muscle activity reduces venous pressure
Venous system has majority of capacitance
Circulatory System :
nutrient transport , waste removal , fluid balance , temperature regulation , chemical signaling , immune response
Capillaries = single cell layer
no elastin , no collagen , no smooth muscle
Arterioles = major determinant of TPR
Convection is in upper respiratory tract and in systemic circulation
Diffusion is in pulmonary alveoli and into mitochondria
Hypoxia :
systemic arteries = dilates arteries to increase perfusion
pulmonary arteries = constrict to try and shunt blood flow
Hering-Breuer Reflex = if overstretched , send signal to slow/stop breathing
Diving Reflex = cold water ➡️ vasoconstriction to prevent stuff from entering the lungs
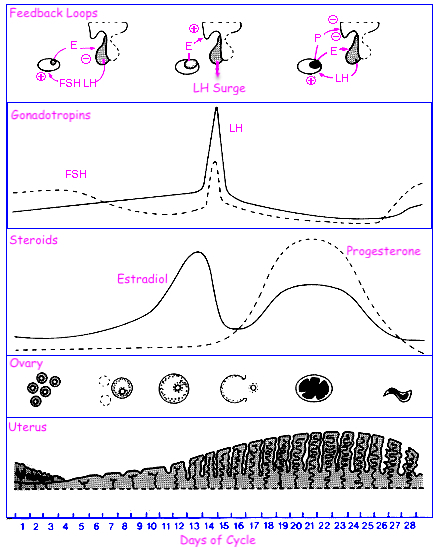
LH :
Leydig Cells = LH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Cholesterol ➡️ Pregnenolone ➡️ Testosterone
Theca Cells = LH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Cholesterol ➡️ Pregnenolone ➡️ Androgens
FSH :
Sertoli Cells = FSH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Gene Transcription ➡️ Androgen-Binding Protein ( ABP )
Granulosa Cells = FSH ➡️ cAMP ➡️ PKA ➡️ Gene Transcription ➡️ Aromatase ➡️ Androgens ➡️ Estrogens
Embryo :
zygote = fertilized egg , single diploid cell
blastocyst :
inner cell mass = forms baby / gastrulation
gastrulation @ 3rd week :
endoderm = GI tract
mesoderm = muscles
ectoderm = CNS , skin , nails
Fetus = @ 10 weeks
3 Sources of Progesterone :
Corpus Luteum , hCG , Placenta
3 Positive Feedforward Loops :
LH Surge , Oxytocin in contractions , Oxytocin in lactation