Urea Cycle
Misc
Ways we move nitrogen around
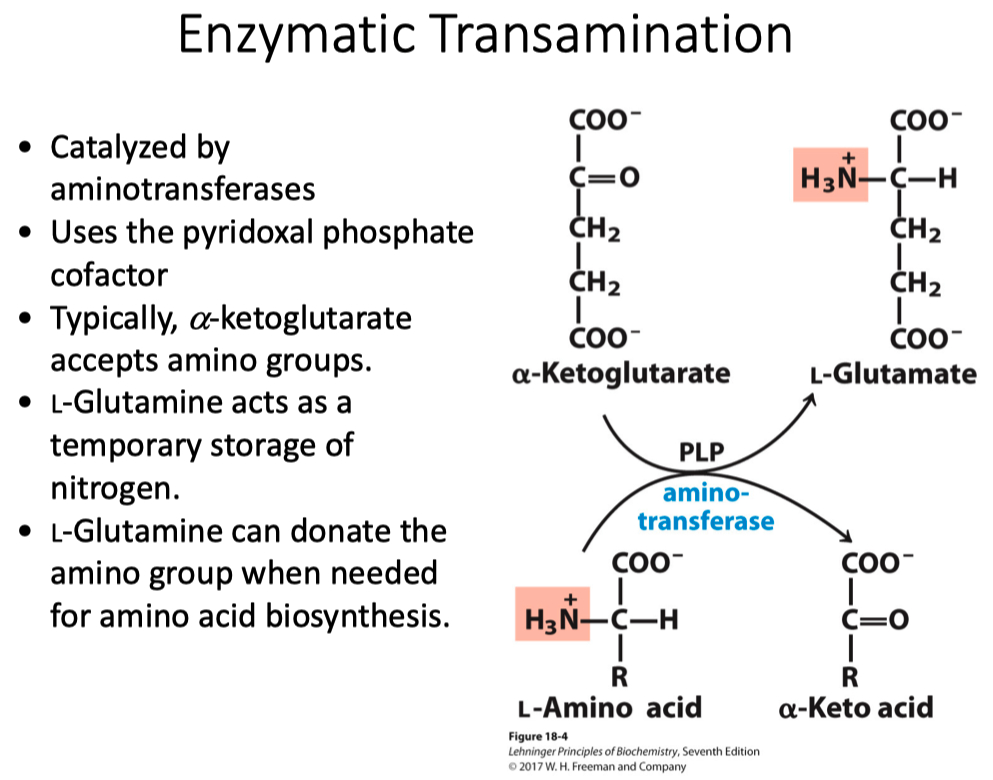
transamination pairs
nitrogen by itself is really toxic
predominant form is
transamination in most tissue is taking the amino acid through a transamination and producing an alpha-keto-acid
also at the same time taking the alpha-keto-glutarate and making glutamate
glutamate is then converted into glutamine
we do this via glutamate synthatase
this incorporates an additional
one of the few enzymes that allows nitrogen fixation in humans
ATP is used for energy
most extra-hepatic tissue , except for muscle does transamination
we transport the glutamine in the blood with 2 nitrogen’s
In muscle tissue ,
as the muscle cells are “chugging through” amino acids , we do a similar reaction to transamination
except pyruvate gets converted into alanine
alanine then goes to the liver
it then undergoes transamination to make pyruvate
we have now moved the nitrogen to the liver
most likely creating glutamate
the pyruvate most likely goes to gluconeogenesis , because if you are breaking down muscle , you are in the fasting state
that glucose can go back to the muscle cells
most likely , it goes to the brain though
this is called the glucose-alanine cycle
the carbon is really coming from stored glycogen in the muscle cell
Glycogen Storage Disease :
they can’t convert glycogen to pyruvate
starving off the carbon for the glucose-alanine cycle
decreases their ability to undergo gluconeogenesis because one of their precursors is disrupted
Lactate
Red blood cells produce a ton of lactate
Glucose-alanine cycle is not “closed”
Enzymatic Transamination
Requires PLP for amino transferase reactions
The Glucose-Alanine Cycle
Most of the time its glutamate that is made
not a “closed cycle”
Misc
We are pumping in alanine from muscle tissue
Glutamase = gets of first nitrogen
Glutamate dehydrogenase = gets off second nitrogen
Nitrogen in the blood is toxic ,
alanine and glutamine concentrations are really high because they are transporting nitrogens to the liver
First enzyme in the cycle , carbamboyl phoshpatase-1 is part of urea cycle
the “2” is part of amino acid degradation
enzymes are located in the mitochondria
citruilline is transported out of mitochondria
The Reactions in the Urea Cycle
Aspartate is the second source
arginine is a pseudo essential amino acid
anytime you have high nitrogen turn over , arginine gets stuck in the cycle
Hans Krebb discovered the TCA and urea cycle
google the “krebbs bi-cycle”
huge link between these 2 cycles
once we have arginine , we release urea through arginase
reforms arginine to complete the cycle
Remember :
what are the 2 sources of nitrogen
what is the enzyme that forms urea ?
arginase
gets rid of 2 nitrogens
how is it regulated ?
don’t want to turn off any enzymes
in the urea cycle = feed forward cycle
if the metabolites are there , it goes
we have to get rid of nitrogen
urea is really soluble , but still kind of toxic
we don’t want anything to back up
in times of high nitrogen turnover , how do we upregulate the urea cycle ?
allosterically regulate the first reaction
as glutamate is being produced , it encourages N-acetyglutamate synthase
allosterically upregulates carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
there are people deficient in urea cycle enzymes
CPS1
if you are deficient , you die very young
that nitrogen will build up as
the liver will will secrete it (
causes mental defects
Treatment :
we give them small organic compounds that the liver takes up and react with the ammonia to bind and helps get rid of it
extremely low protein diet
1 hot dog is too much
even a common cold cause spike nitrogen turnover , and send them to the hospital
Aspartate–Arginosuccinate Shunt
there are common intermediates between Urea and TCA cycle
ornithine and citrulline need to be transported across mitochondria
moving around a ton of carbon back and forth
Questions
The electron transport chain directly produces ATP ?
False , it uses indirect substrate level phosphorylation
The urea cycle is considered a feed forward cycle ?
True
Which of the following amino acids can donated a carbon to folate?
Serine
Which of the following amino acids is catabolized to acetyl-CoA?
Leucine
What are the two direct sources of nitrogen for the urea cycle?
What two molecules primarily transport nitrogen to the liver for the urea cycle?
Glutamine and Alanine
ETC
Glucose
Glucose —> 2 Pyruvate : substrate level phosphorylation
Yields a net of 2 ATP , 2 NADH
2 Pyruvate —> 2 Acetyl-CoA
Yields 2 NADH
Acetyl-CoA —>
Yields 2 ATP
2 FADH2
6 NADH
10 NADH = 25 ATP
2 FADH2 = 3 ATP
2 ATP = 2 ATp
= 32 ATP
TCA Cycle = phos
C16 —>
8 Acetyl-CoA
7 FADH2
7 NADH
8 Acetyl-CoA —>
8 ATP
24 NADH
8 FADH2
31 NADH = 77.5
investment phase happens pre oxidation , so minus 2
108 ATP - 2 = 106 ATP

These pathways energetically mean nothing unless we continue it on through the electron transport chain
31 NADH = 77.5 ATP
what is this telling us ?
its an indirect process , its not a substrate level phosphorylation
the energy we get back from NADH and FADH2 is not a direct process
Complex 5 = makes ATP
electron transport chain is raising the water behind the dam
oxidative phosphorylation
because they are indirect processes , there are caveats
something can disrupt it
with substrate level phosphorylation , you either make ATP or you don’t , nothing can really disrupt it
The numbers are averages ( 2.5 , 1.5 )
for glycolysis its 30 or 32
we have to deal with the NADH
the cytosolic NADH can not cross into the mitochondria
it uses 2 different shuttles
the malate-aspartate shuttle
inner membrane space ➡️ the matrix
outer membrane is really permeable
inner membrane is not really permeable
in the inner membrane space , you take aspartate and make oxaloacetate
the oxaloacetate can then go make malate
in this process we take NADH and move electrons onto malate , regenerating NAD+
malate is transported across the membrane
you then reform oxaloacetate , taking an NAD+ and make NADH
you reform aspartate and transport it across the membrane
oxaloacetate can’t be transported across the membrane
moved an NADH across , but nothing really happens , you reformed it
energy doesn’t change
the other way it gets across is the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle
we go from DHAP to glycerol-3-phosphate
in this case , we take the NADH and make NAD+ again
the glycerol-3-phosphate can go back to make DHAP
there’s an enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase on the mitochondrial membrane ( membrane-bound )
it uses FAD to form FADH2 to produce QH2
we lost energy because we went from NADH to FADH2
their potential energy is pretty equal
however , NADH enters through complex 1 , while FADH2 enters through complex 2. Complex 2 looses more to heat , so therefore less energy
if we do this twice , this is how we are loosing 2 ATP
if both NADH go through malate-aspartate shuttle we generate 32
if both NADH go through the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle , we generate 30 ATP
these shuttles bring up something important
things going on between cytosolic and mitochondrial matrix
Chemiosmotic Theory
we take reduced electron donors to pump protons
pumping protons back to inner membrane space
figure out experimentally how you can prove that protons are moving ?
originally we didn’t know the numbers of ATP generation
we originally thought the TCA cycle generated ATP
how do we know electron transport chain is just pumping protons , and ATP synthase is generating ATP
Chemiosmotic Theory
these reaction in the individual complexes are not a one-off reaction
not substrate = product
they happen at a large scale
electrons are getting handed off
each complex doesn’t just have one hand off
there’s a lot of reactions in glycolysis pathway that don’t do much
the same thing is happening here , its a bunch of small reactions
all of the complexes contain small molecules in them that are capable of being oxidized or reduced
example = cytochromes
small proteins that have different hemes in them that can be oxidized or reduced
multiple different subtypes of cytochromes
Structure of a Mitochondrion
snakes back and forth to increase surface area
tons and tons of enzymes bound to it
we need a ton of enzymes / proteins bound
allows more ATP to be produced
Cytochromes
by changing the ring structure , we change the reduction potential
so we have like 100 different reduction potentials
we are moving across that reduction potentials
Iron-Sulfur Clusters
these are the other way’s we move electrons around
anchored to the protein via cysteine residues
how they are anchored to the protein , the environment around it , and the complexes on top change the reduction potential
Coenzyme Q or Ubiquinone
cytochrome-c = mobile electron carrier
more hydrophilic
coenzyme Q = mobile electron carrier
more hydrophobic
anchored to the membrane
has a large hydrocarbon tail , makes it hydrophobic
acetyl-CoA = “hub”
complex 1 and complex 2 all dump into co-enzyme Q
coenzyme q = collection point , and then goes off to complex 3
NADH:Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase (Complex I)
FMN , iron sulfur clusters
on the arm , you are oxidizing the NADH to NAD+
then transferring the electrons to coenzyme Q
while doing this you pump 4 protons
the Q then goes to complex 3
electrons from NAHD : complex 1 to 3 to 4
FADH2 = 2 , 3 , 4
complexes are not linear , EVER !
Table 19-3
prosthetic groups have different reduction potentials , allowing for electrons to flow
the greater the reduction potential , the more thermodynamically favorable it is to flow electrons
these are not small , very high kilo-dalton numbers
Succinate Dehydrogenase (Complex II)
also in the TCA cycle
transferring electron from FADH to Q
but no electrons are pumped
produced more QH2 , but haven’t pumped protons
only oxidizes the FADH2 from the TCA cycle
the FADH2 from beta oxidation doesn’t happen
its only succinct to fumarate
the FADH2 from beta oxidation never really produces FADH2 , it immediately makes QH2
any time you you see FADH2 , its going to be a membrane bound enzyme that dumps it onto QH2
means there are others enzymes we haven’t talked about
Complex 1 , 2 and anything FADH2 linked , they are making QH2. That QH2 then goes off to complex 3
Ubiquinone:Cytochrome c Oxidoreductase (Complex III)
we are taking QH2 and producing cytochrome c that then goes off to complex 4
we are pumping protons here
requires multiple electron movement steps
The Q Cycle
caveat to complex 3
this is a theory still
QH2 is a 2 electron carrier
Cytochrome C is a 1 electron carrier
so we produce 2 cytochrome c for each FADH2
we don’t know how this works
through a multi-stage process we produce 2 cytochrome c that are reduced , and then we pump 4 protons
if starting at NADH , we pumped 4 for complex 1 , for 4 complex 3 = 8
FADH2 , zero protons from complex 1 , 4 from complex 3
Cytochrome Oxidase (Complex IV)
we have multiple cytochrome c coming in , but we only pump 2 protons
take oxygen and produce water
if we stop oxidizing cytochrome c , we stop oxidizing everything up the chain
NADH Protons Pumped :
Complex 1 = 4
Complex 3 = 4
Complex 4 = 2
Total = 10
FADH2 :
Complex 2 = 0
Complex 3 = 4
Complex 4 = 2
Total = 6
6 / 10 = 0.6 = 60%
1.5 / 2.5 = 0.6
NADH = 2.5
FADH2 = 1.5
this is why FADH2 produces 60 percent as NADH does
it only pumps 60% of the protons that NADH does
Electron Flow in the Respiratory Chain
complex 1 and complex 2 produce QH2
Summary of Electron Transport
at the end of the day 10 protons if you start from complex 1
6 if you start from Complex 2
FADH2 = not a mobile electron carrier
NADH = a mobile electron carrier
Reactive Oxygen Species
over nutrition / metabolic syndrome
we pull metabolism towards ATP
if we don’t need it , we stop metabolism
overnutrition is pounding it towards ATP when we don’t need to
ROS can damage proteins
we can make hydrogen peroxide
glutathione can turn it into water
if you keep “pounding” it , you run out of glutathione or the ability to take care of ROS
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ETC
Complex 5 takes protons back across
How do we know its ATP synthase and not any of the other complexes that make ATP ?
if you disrupt the membrane , there is nothing holding protons back
you can make an artificial gradient , add acid to inner membrane space
and you will make ATP
inner membrane space is more acidic
un-couplers will dispel the proton gradient
you can have an organic compound that its pKa is around the pH differences
on the inner membrane space , it will pick up the proton
it then freely diffuses through the membrane
and then gives off the proton
this is getting the proton through the membrane but circumventing ATP synthase
by doing this , you are removing the pH difference
ETC still runs , but no ATP is produced
How do we regulate ETC ?
we pull metabolism by ATP need
if ATP is high , ADP is low
shuts down the ATP synthase enzyme
It stops moving the proton across the gradient
the rest of the complexes keep building up the gradient
high concentrations of ATP cause high amount of protons in the inner membrane space
that causes the delta-G of pumping to become positive ( unfavorable )
then we can’t pump protons across in the other complexes
this shuts down the ETC
increase NADH to NAD+ ratio
this also turns off the ETC
3 dehydrogenases are sensitive to NADH / NAD+ ratio
shuts of pyruvate dehydrogenase ?
shuts off beta-oxidation , you don’t have the cofactor
glycolysis is iffy , depends on the tissue , but also shuts down probably
we turn ATP synthase back on when we need ATP again
ETC and ATP Synthase
if oxygen is being consumed we are running ETC
if we add ADP and inorganic phosphate , we don’t really do anything
if we add in succinate , we get a ton of ATP and start consuming oxygen
Cyanide is an inhibitor of complex 4
shuts everything else down
Part B :
proves you need ADP , Pi , and succinate
oligomycin is ATP synthase inhibitor
stops ETC
now add DNP ( an un-coupler ) , dispels the proton gradient
red line didn’t change
ATP produced
but the black line did
black line = oxygen consumption
tells us ETC is functioning
ETC is functioning but ATP isn’t being produced
shows they are linked , but not a direct process
If you get the proton across the membrane without going through ATP synthase
the delta-G becomes negative again
energy gets lost as heat
Russians in WW2 took DNP as a way to survive the harsh winter
DNP could also be used as a weight loss drug
you are not producing ATP , so you are pulling metabolism
so eventually you start using fat and glycogen stores to make ATP
DNP is very risky , you can kill people with it
difference between effective and lethal dose has to be huge
DNP however , there differences are very small
aka very risk
The F1 Catalyzes
how does ATP synthase actually make ATP ?
in the membrane , its oriented in a very specific way
there’s a proton channel in the portion that’s anchored to the membrane
the linkage part = the gamma subunit
rotates to change the confirmation of the alpha-beta dimers
there’s 3 alpha-beta dimers , this is where ATP is actually produced
these each have 3 different conformations
as the gamma rotates , it changes between the 3 confirmations
as the protons go through the channel , they rotate the c-subunit
they then rotate the gamma
as the gamma rotates , it interacts with the alpha-beta dimers to cause conformational change
as this happens , the alpha-beta dimers switch between open , loose, and tight
every time they switch all the way through , they produce a ATP
1 360 degree rotation produces 3 ATP
1 for each subunit
it takes 9 protons to cause a 360 degree rotation
^^ ATP Synthase
^ entire process
we have to move across other things
for every ATP produced , we have to move 1 additional proton
so it changes the 9H+ to a 12H+
now the math adds up
you need 9 protons goin through the ATP synthase channel + 1 proton going through the translocase enzyme
Evidence of Rotation
covalently attached alpha-beta subunits to a cover slip
attached actin filament to the gamma subunit
they saw the actin filament moving
different organisms have different numbers of c-subunits
if you had less c-subunits , you would make more ATP
the fewer amount of c-subunits you have the fewer amount of protons necessary to go through the channel
if you had 5 , ATP yield would double
why don’t humans have 5 then ?
less c-subunits requires more force
more c-subunits requires less force
it might not actually rotate if you get too low on c-subunits
if its too high , you make it too easy , you dispel too much of the gradient to make ATP
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle
NADH that is produced in the cytosolic , has to get to the matrix somehow
malate-aspartate shuttle
glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle
we get less ATP yield with this one
Net Production of ATP
majority is coming from NADH
we need the ETC
majority is NOT coming from direct substrate level phosphorylation
Regulation of Oxidative Phosphorylation
majority is being pulled through the respiratory chain
NADH is a huge inhibitor as we go up the chain
ATP Synthesis Can be Uncoupled
1 , 3 , 4 pump protons
complex 5 pumps it back across
Uncoupling Protein 1 is used in babies
brown adipose tissue is in babies
why is it brown ?
they have a ton of mitochondria
white has mostly fat droplets and only a few mitochondria
babies need heat production
distribution of brown adipose tissue is all in the trunk , around vital organs
uses the proton gradient not for ATP production , but to make heat
Uncouplers of Oxidative Phosphorylation
ETC , the higher the amount of uncoupled
the higher amount of electron transfer.
The regulation isn’t there.
P/O ration does down
Same thing , we are dispelling the gradient , not producing ATP , dispelled as heat. P/O ratio goes down
If P/O ratio gets too low , you don’t make ATP. Cardiac arrest , no brain function
Integration of Metabolism
Glucose-6-phosphate
involved in many different pathways
in the liver , its a switching system
all dependent on need
Hexokinase IV ( liver ) is special
not inhibited by glucose-6-phosphate
Tissue Specificity :
glucose transporters
GLUT2 = liver
high capacity for glucose
glucose can passively diffuse based on concentration
GLUT4 = muscle , insulin sensitive version
Metabolism of Amino Acids in the Liver
centralize around 1 producing the amino acids that need to be released
also gets rid of the nitrogen
dumps nitrogen into nitrogen pool , produces aspartate
glucose-alanine cycle
Fatty Acids (FA) in the Liver
main fuel source
liver produces fatty acids
we take acetyl-CoA to make many things
what directs metabolism from acetyl-CoA to Ketone bodies ?
we don't have oxaloacetate
its being pulled off for gluconeogenesis
concentration of metabolites
why in times of fasting are we not making cholesterol ?
we don't have the enzymes
we shut off the enzymes and degrade them
availability of enzymes
Ketone Bodies Are Made from Acetyl-CoA
brain relies on liver to keep producing ketone bodies
Two Types of Fat Tissue
Brown expresses the uncoupler protein
lots of mitochondria
allows ETC to function
moves protons into Inner membrane space
allows protons to make their way back into the matrix
doesn't allow proton gradient to be built
bypasses the synthase
creates heat
White is primarily fatty acids
very few mitochondria
Muscle
Difference in amount of mitochondria
Fast-Twitch have fewer mitochondria
During light activity , your lipoprotein lipase on the outside of the cell
has a really low Km
really good at getting fats out of the blood
it can also use some ketone bodies and blood glucose
blood glucose is insulin dependent
during heavy activity ,
muscle relies on glycogen
phosphocreatine helps to produce ATP
Sources of ATP for Skeletal Muscle
Energy from Phosphocreatine is slightly more thermodynamically favorable
yields more ATP because you are skipping the hexokinase step
during glycogen breakdown , how do we guarantee it doesn't leave ?
no Glucose-6-phosphatase to remove phosphate from G6P
Hormonal Control of Glycogen Mobilization
epinephrine and glucagon signal the activity
whats the difference between epinephrine and glucagon
muscle cells don't recognize glucagon , they only respond to epinephrine
epinephrine activates a bunch of things
allows muscle cells to break down glycogen
with any hormonal signaling , it is amplification
1 epinephrine releases 1000 glucose moieties
in hepatocytes , liver responds by exporting more energy into the blood
muscle responds with more mobilization
small signal , huge response
people who are fasting ( short-term )
start to release epinephrine , helps mobilize energy to get to the next meal
The Cori Cycle
isn't a closed system
blood glucose to glycogen , doesn't really enter into muscle cell
glycogen breaking down glucose
blood glucose is mostly going to be pulled off into other directions ?
Heart Muscle versus Skeletal Muscle
very similar in metabolism
heart has more mitochondria
beating all the time
heart is primarily fueled by fatty acids
why ? because it can't store glycogen
fatty acids release more energy
fatty acids are found in the blood during all stages , fasting , fed , ect
so they are always there
so the heart always has a source for energy
if O2 supply cuts off
muscle tissue will die
Mammalian Brain
Fed = glucose
Starvation = ketone bodies
If you inject too much insulin ,
insulin is an anabolic hormone
there are people that use insulin as an anabolic steroid
if someone who is not diabetic , and injects too much insulin
they can pass out
because if you inject too much insulin without eating
glucose is taken up by other tissue
muscle cells ,
there glucose transporter is insulin sensitive
the body does not have the time to respond by making ketone bodies
the brain doesn't store energy in glucose or ketones
its utilizing the glucose as fast as it can bring it in
the Km and Vmax are lined up so that glucose is always flowing into the brain at the same rate
we use it immediately to make ATP
no lag time
you pass out , because the brain doesn't have energy
Physiological Effects of Low Blood Glucose
Kept between a short range , 60 to 90
If you get too low , you release epinephrine , glucagon , cortosol
Low glucose levels are a problem
Insulin Stimulates Conversion of Excess Glucose to Glycogen and/or TAGs
Insulin is the stimulus for converting everything to storage molecules
Extra acetyl-CoA makes fatty acids --> triacylglycerol --> exported as VLDL
producing storage molecules based on insulin signal
The Well-Fed Lipogenic Liver
Intestines have carbs , proteins coming in
end up in the liver as glucose
glucose-6-phosphate can go to glycogen or pyruvate
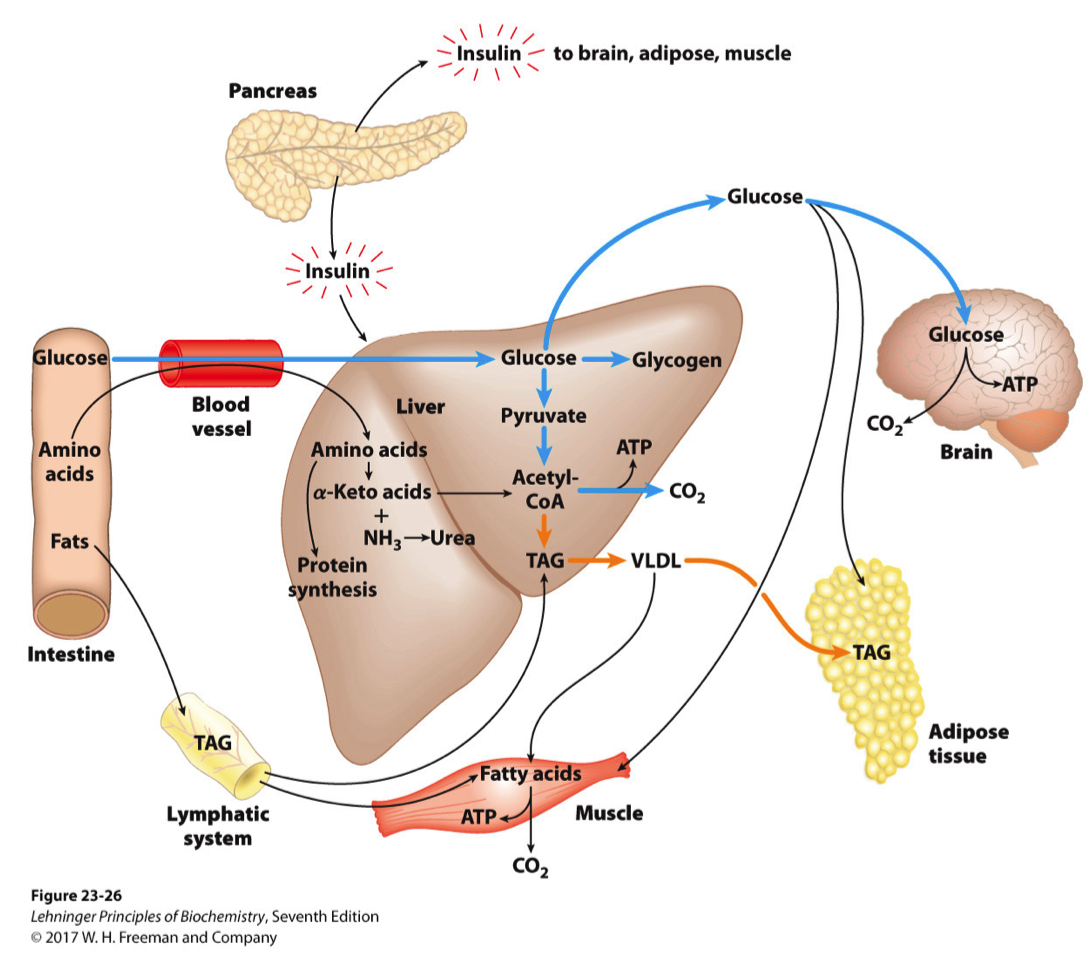
FIGURE 23–26 The well-fed state : the lipogenic liver. Immediately after a calorie-rich meal, glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids enter the liver. Insulin released in response to the high blood glucose concentration stimulates glucose uptake by the tissues. Some glucose is exported to the brain for its energy needs, and some to adipose and muscle tissue. In the liver, excess glucose is oxidized to acetyl-CoA, which is used to synthesize fatty acids for export as triacylglycerols in VLDLs to adipose and muscle tissue. The NADPH necessary for lipid synthesis is obtained by oxidation of glucose in the pentose phosphate pathway. Excess amino acids are converted to pyruvate and acetyl-CoA, which are also used for lipid synthesis. Dietary fats move via the lymphatic system, as chylomicrons, from the intestine to muscle and adipose tissues.
Pancreatic Cells
Pancreas produces the two push or pull hormones
Glucose Regulation of Insulin Secretion
what causes insulin to be secreated ?
glucose transporter into pancreatic beta cell is GLUT2
when glucose is above fasting stage , glucose enter beta cells
Hexokinase IV is also pancreatic form
pancreatic beta cells only import glucose when its high
only use when its high
after a meal , pancreatic beta cells use glucose
they undergo every pathway , to produce ATP
when ATP goes high , that inhibits the potassium channel
when its inhibited , it causes a depolarization of the membrane
stops calcium export
causes calcium influx from extracellular space
when calcium is high , causes insulin in the secretory granules to release into the cell
causes insulin secreation
Sulfonylurea Drugs
anti-diabetic drugs
inhibit the potassium channel
by causing the inhibition , causes more insulin being secreted
more insulin secretion
type 1 diabetes = not making the insulin
treatment = add insulin somehow , injections
type 2 diabetes = insulin insensitive
producing insulin , just not recognizing the signal
type 2 diabetes drugs help ramp up insulin secreation
gets high enough that receptors start to recognize it
The Fasting, Glucogenic Liver
everything is going towards glucose-6-phosphate
everything is coming towards the liver , glucose and ketones are going out
what are the major sources of carbon for gluconeogenesis ?
pyruvate
alanine = from amino acids
glycerol = from adipose tissue
NO net conversion of acetyl-CoA to glucose
Glucagon Raises Blood Glucose
helps keep it at homeostasis
all of this is coordination
Effects of Prolonged Fasting
at some point we start to use muscle protein for fuel
transamination reactions
all of the nitrogen ends up as urea
ketoacidosis , reduces blood pH
consequence of diabetes
someone who is in a prolonged fast , or keto-diet , why don't they go into ketoacidosis ?
getting the fuels , but constantly going toward keto body production
everything is going haywire , signaling is going haywire
levels are drastically different ?
Fuel Prolonged Fasting or Type 1 Diabetes
mechanisms are similar
oxaloacetate is getting pulled off
doesn't matter type 1 or type 2 ,
even if they have high blood glucose , their liver is still producing glucose and ketone bodies
not getting the signal to stop
Plasma Levels of Fatty Acids, Glucose, and Ketone Bodies During a One-Week Fast
fatty acid levels in the blood change during fasting , but relatively constant
glucose levels after about a month of fasting
beta-hydroxy-butarate goes up pretty fast
thats why heart tissue prefers fatty acids over other sources
Lipid Transport and Cholesterol
Triacylglycerol as the majors energy reserve
Fat vs Carbohydrates
Fat Advantage = always in the blood circulating
We have more fat than carbohydrate
We don’t have to hydrolyze fat , whereas you DO have to hydrolyze carbohydrate
Glycogen storage has an upper limit
No upper limit to tryacyl glycerol storage
Primary Sources of TAGs
Diet
De novo synthesis
make them to use as storage molecules
any extra carbohydrate or protein is stored as fat
Fatty Acid Synthesis Branch Point = Acetyl-CoA
Muscle , liver , heart takes first dibs , everything else stored in adipose tissue
Digestion of Lipids Overview
More simpler than carbohydrates
Starts in the mouth
Lipases are not caustic ( acidic )
Proteases are caustic , which is why they are not in the mouth
lingual lipase
affinity for short or medium chain fatty acids
gastric lipase
affinity for short or medium chain fatty acids
Dairy Products have a lot of short and medium chain fatty acids
Can’t just enter into the intestine , they have to be emulsified into bile salt
90% of bile salts get recycled
Released by cholecystokinin = signaling molecule
The other difference , is we have to modify the pH via bicarbonate
Pancreatic Lipase = affinity toward medium and long chain fatty acids.
but completely useless without co-lipase
There are fatty acids attached to other things than triacylglycerols
have to be released by other lipases
Lipases Act as Lipid-Water Interface
The lipases have to work at the lipid-water interface
Phospholipase A2-Micelle Complex
Micelles are formed with the lipid inside
bile salts inhibit the lipase from acting
Co-Lipase pokes a hole in the exterior
allows lipase to interact with the fat
Taurodeoxycholate vs Specific Activity Graph
Aka lipase activity
The circles no co-lipase
Squares = have co-lipase
Taurodeoxycholate = bile salt
as we increase concentration of bile salt ,
activity of lipase diminishes
Critical Micelle Concentration
the micelles won’t form around the fat unless they reach a certain concentration
if they get too high , they also won’t form
small window
they are active until micelles forms
once they form , there is no activity
unless you add co-lipase , then activity resumes
Bile Salts
Base = cholesterol
7-alpha-hydroylase = rate limiting step
inhibited by bile acids
just help with surface area and emulsified
if you don’t have bile salts , your digestive tract can’t digest lipids
leads to weight loss and gastric stress
some bile salts are more hydrophobic or hydrophilic than others
95% of Bile salts are reabsorbed in gallbladder
Olestra
Weight loss drug
added to food
pancreatic lipase can’t break it down ( it can’t bind )
it tastes like fat , but intestinal tract can’t break it down
they include fat soluble vitamins
people who eat a ton of these foods become vitamin D deficient
Vitamin D is fat soluble
gets removed along with drug
so they “fortify” these foods with extra vitamins
Orlistat
Compound that inhibits pancreatic lipase
dosing has to be really fine-tuned
have to restrict all fat in diet
Processing of Dietary Lipids
In the intestine , pancreatic lipase takes triacyl glycerol and breaks it down into 2 fatty acids plus a mono-acyl-glycerol
The 2 FA and MAG enter
we have no mechanism to get triacyl glycerol into dig
we reform them , because we don’t want to send out that much fat into the blood
so we take that triacyl glycerol and package it as chylomicrons
Chylomicrons = lipoprotein
on the outside its similar to micelle , but they have apoproteins
apoprotiens help with structure and solubility
FA could dissociate out ,
so we convert them back into TAG
Apoproteins are recognized by surface molecules on muscle cells and help direct them to their target
Chylomicrons
Made in intestinal cells
Starting point for lipoproteins = chylomicrons or VLDL ( very-low-density-lipoprotein )
Chylomicrons = exogenous , dietary fats
formed in the intestine
protein portion is made in rough ER
triacyl-glycerol is reformed once inside enterocytes
VLDL = fats we make from carbohydrate of protein
made in the liver
Picks up additional lipoproteins
E = helps recognized by the liver
C2 = helps activate lipoprotein lipase
Chylomicron with lots of triacyl glycerols in it
Apoproteins on the outside of Chylomicron
Cell Surface of muscle and adipose is lipoprotein lipase
C2 = goes activate
triacyl-glycerols are then broken down , and then enter into cell
Difference between lipoprotein lipase in muscle and in adipose tissue
Muscle has a very low Km
adipose has a medium Km , orders of magnitude different
Muscle obviously uses Fatty acids first before we start storing it.
It also stays active longer as fatty acids start to dissipate in the blood
Once the lipoprotein lipase on adipose tissue and muscles are being utilized , the fats get removed
Chylomicrons = even lower density than VLDL
as we remove the fats , the proteins stay , the density increases
Chylomicron Remenents are more dense
they go to the liver
apoE = gets recognized , further digested
Four Major Classes of Lipoprotein Particles
VLDL = fats from what we are producing from dietary source of carbohydrates and protein
Chylomicrons have very little protein , etc , but a ton of tryacyl glycerols
when we get to VLDL , they have more
the liver is packaging all of this up to be transported out
Free cholesterol vs cholesterol esters
cholesterol esters have a fatty acid esterified to them
much more hydrophobic
likely to stay in the core of the lipoprotein
free cholesterol is less likely to stay in the lipoprotein
How do we go from LDL to HDL ?
Liver produces VLDL
VLDL goes off to muscle and adipose
VLDL interacts with lipoprotein lipase on surface
removes fatty acids
produces IDL
IDL is somewhere between VLDL and LDL in its density
50% of IDL goes back to the liver
The other 50% goes back to another round with interaction on muscle and adipose tissue
this produces LDL
the amount of triaclyglycerides keeps decreasing
we are removing the fats
the amount isn’t higher , the percentage is higher
the majority of LDL goes to the liver
LDL = “bad” , because some cholesterol goes to peripheral tissues
but we have a limited capacity to process LDL
if you are eating too much fats , LDL percentage goes up , you have a limited capacity to uptake it
the more its circulating in the blood , the more likely it is to be oxidized
oxidized LDL starts to form plaques / lesions
old school limiting lowering drugs targeted how much LDL we have
newer ones target liver and its capacity to take up LDL
Apolipoproteins in Lipoproteins
apo = protein protion
B48 = for chylomicrons
B100 = same function as B48
transcribed form the same gene
b48 has a stop codon that gets put in , and makes only about 48%
VLDL expresses B100
Chylomicrons express B48
Electron Microscope Pictures of Lipoproteins
Chylomicrons = much bigger
VLDL smaller
keeps going down in size
Biological Roles
HDL = responsible for reverse cholesterol transport
cholesterol back to the liver
why its considered the “good” cholesterol
can be made in the blood
if we have the apo-proteins
these are the 4 main particles
changing the density comes from lipoprotein lipase activity
removing the fats from it
Cholesterol
HDL = takes cholesterol back to the liver
has a lot of cholesterol esters in it
cholesterol esters are more hydrophobic than cholesterol itself
there are two enzymes that make cholesterol esters = ACAT and LCAT , esterify
Helps keep cholesterol in the HDL molecule
hydrophobic because of the long R-group
VLDL has a lot of triacylglycerols around
cholesterol ester transfer protein
takes triacylglycerols from the VLDL and moves them to the HDL
it also moves cholesterol esters into the VLDL
makes HDL with a low concentration of esters
makes it less cardio protective protective
Cholesterol Metabolism
Synthesis = complicated process with black box enzymes
just know that all of the carbon can come from acetyl-CoA or acetate
goes to mevalonate —> isoprenes
rate limiting step is HMG-CoA synthase / reductase
also happens to be the enzyme we target with medications
eventually we form squalene , its the linear form of cholesterol
ultimately we form the steroid ring in multiple steps
Regulation :
5 different ways we regulate synthesis
1 = regulate function of regulation step ( activity )
via phosphorylation / dephosphorylation
2 = regulate amount
turn it off short term , degrade it if we don’t need it again
produce it long term if we need it
Insulin activates HMG-CoA reductase
insulin indirectly regulates through phosphorylation cascade
Glucagon is the opposite
Regulate through short term via phosphorylation / dephosphorylation
Long Term Regulation :
Transcription level control
normally , we have several things in the membrane; : Insig , SCAP are all in the membrane when cholesterol / sterols levels are high
they bind to the proteins and keep them associated
when cholesterol levels lower , SCAP and Insig separate , causes a conformational change , allows for proteases to cleave off a transcription factor from SREBP
part of SREBP is a transcription factor
HMG-CoA reductase when cholesterol levels go up
there are portions that are sterol sensing
when they start to bind the cholesterol , it causes conformational change and changes how the protein interacts
its now a target for proteolytic cleavage
when there’s no cholesterol its in the active form and functioning
2 Long term regulation :
when low = transcription level activation
when its high = we are getting rid of the protein concentration itself ( increasing proteolytic cleavage )
Regulation of HMG-CoA Reductase
LXR = transcription factor
if cholesterol levels are high , it binds to the transcription factor , changes state , allows for production of enzymes
when low , LXR binds to the repress and stops production of genes
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase = fatty acid synthesis
ABCA1 , ABCG1 = reverse cholesterol transport
others are involved in lipid synthesis
Lipoprotein Receptor
can recognize ApoE or ApoB100
when binds , it internalizes via receptor mediated endocytosis
1 in 500 have a defect in this receptor
you can’t uptake any lipoproteins , much slower at it
increases concentration in the blood
becomes oxidized , leads to atherosclerosischlerosis
Atherosclerosis
its the amount of oxidized LDL binding to other things floating around and forming plaques
forms foam cells
Drug Therapies
statins are the gold standard
research suggests it lowers cardiac diseases
its also very cheap , off-patent
they inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
limits self-synthesis of cholesterol
doesn’t help with any dietary intake
Bile Salt and Resins :
bile salts are made from cholesterol
typically 95% of bile salts are recycled
if you bind bile salts and secrete them ,
more cholesterol is delegated to re-forming bile salts
resin = surface for bile salt to bind
Naicin and Fibrates are Second line defense
Ezetimibe = reduces intestinal absorption in the gut
limits a transporter
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
aka statins
mostly competitive inhibitors
red shape of Lipitor basically matches the shape of HMG-CoA
binds to HMG-CoA reductase , and inhibits it
Disadvantage of Competitive Inhibitors :
upper threshold you can’t give past a certain point
Advantage of Competitive Inhibitor vs Co-Valent Inhibitor :
covalent inhibitor lasts so much longer
aspirin is short acting , 1 and done
Aspirin vs Ibeprophan :
aspirin is covalently inhibitor
binds to COX and inhibits it
Repatha
PCSK9 inhibitors
newest drug
in the internalization and degradation of the receptor , there is an additional protein involved
if we don’t degrade the receptor ,
we have more exceptions expressed ,
By having more receptors present , even at a reduced capacity , it’s still capable
Disadvantage = monoclonal antibody
expensive , has to be injected
reserved for people without cardiac disease
HDL
formation of cholesterol ester is really important
LCAT vs ACAT
Reverse Cholesterol Transport
HDL also can help mature lipoprotein
TAG vs CE
modifying how much is going back to the liver , and how much is being processed
Questions
What is the approximate number of protons that are transported across the mitochondrial membrane to produce 3 ATP?
12
It takes 12 protons to transport across the membrane,
9 for a complete 360 degree rotation of the gamma subunit and 3 for the phosphate transport
Oxidative phosphorylation is mainly regulation by which of the following?
Levels of NADH and ADP
Ox/Phos is mainly regulated by substrate availability
What is the main energy source for heart tissue?
Fatty Acid
Heart tissue has a high energy demand at all times.
which makes fatty acid the one fuel that would be available in both the fed and fasting state
High levels of cholesterol will alter cholesterol metabolism in which of the following ways :
Oligomerize HMG-CoA reductase increasing proteolytic cleavage
HMG-CoA has a sterol sensing domain, as cholesterol levels increase it causes the enzyme to oligomerize and degrade
Which of the following is responsible for transporting fat from dietary sources :
Chylomicrons
Chylomicrons are dietary fats
Whereas VLDL are endogenous fats
High-Level Overview
Glycerolneogenesis vs gluconeogenisis ?
Adipose tissue doesn't have glycerol kinase ?
cholesterol metabolism ( study a lot )
regulation
HMG-CoA reductase = rate limiting step
regulated via :
insulin signaling
phosph / dephosph
transcription levels ,
proteolytic cleavage = conformatonal change
as sterols in cell go higher , oligiomerzation state changes
leaves it susceptible to cleavage
production of VLDL , HDL
VLDL is produced in the liver
transported via blood
..... lots more of the story
eventually get to LDL
to LDL receptor on liver
endocytose , ......
urea cycle ( also study )
regulated
never turn it off
its a feed-forward reaction
turn it up in times of need
high nitrogen turn off
turns on CPS-1 ?
amino-acid transport ( nitrogen transport )
key sources of nitrogen
transported via ammonium (
glucose alanine shuttle
Liver and muscle
transamination pairs
oxidatative phosphorylation ( easier )
How do we go from NADH to ATP
indirect
Not substate level
atp synthase complex 5
substrate level = pyruvate kinase ?
regulation of ETC
when ATP is high , we stop producing it via complex 5
delta g becomse positive , electron transport stops
increases NADH
inhibits everything above it
uncouplers
uncoupels ETC and oxidative phosphorylation
if you add an uncoupler to mitochondria
ETC skyrockets
oxidative phosphorylation stops
Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin mediated signaling
Receptor :
type of tyrosine kinase
Alpha subunit :
localized in extracellular region
also has a transmembrane domain
contains the ligand binding site
Beta Subunit :
involved in intracellular signaling
Insulin binds
causes monomers to dimerize
tyrosine kinase regions get phosphorylated
causes the activation loop to change confirmation
opens up substrate binding site for further cellular responses / signaling
Phosphorylated tyrosine residues act as a docking site for SHC and IRC ( adaptor proteins )
Phosphorylation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase can create two signals
Shc activation = signals growth
via Grb2 recruitment
starts the MAPK signaling pathway
enhances cell growth
IRS activation = signals metabolism
"insulin receptor substrates" ( IRS )
starts the PI3-kinase signaling pathway
PIP2 ➡️ PIP3 ➡️ activates Protein Kinase B ( Akt )
regulates glucose homeostasis and a bunch of other things
aka glucose import into the cell and glycogen synthesis
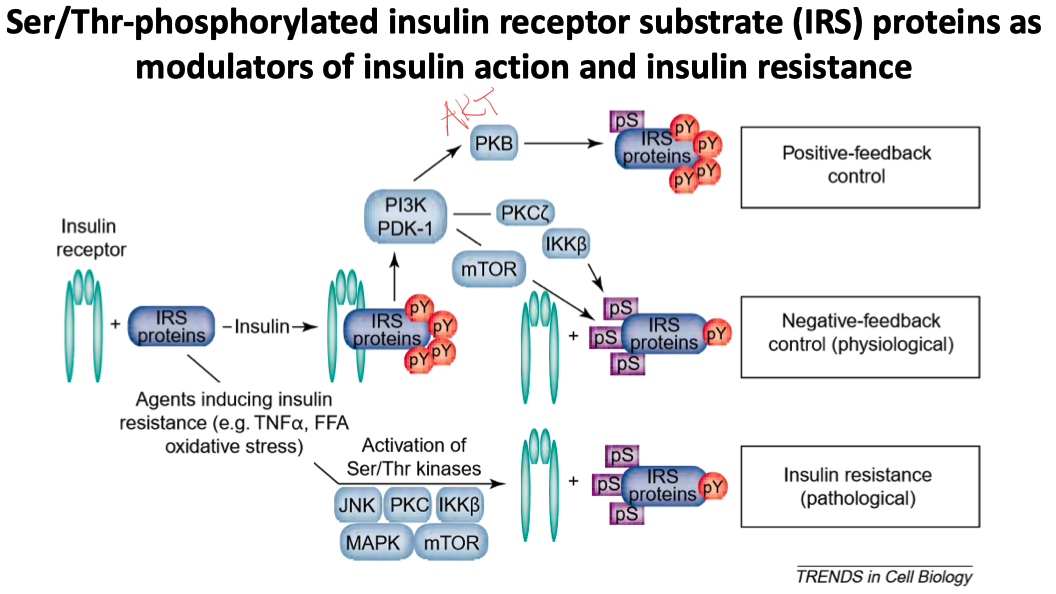
There are also serine phosphorylation sites on IRS proteins
these allow for modulation of insulin signaling
positive / negative feedback
prolonged activation of serine residues leads to insulin resistance
Insulin Resistance
defined as normal or elevated insulin causing an attenuated biological response
aka , a decreased biological response to normal concentrations of circulating insulin
aka insulin insensitivity
If those serine sites are phosphorylated on IRS proteins :
the IRS can't attract PI3K anymore
effectively , it decreases IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation
impairs its downstream targets
circulating FFA and adipokine TNF𝛼 can increase serine phosphorylation
What is metabolic syndrome
metabolic syndrome = inability to store triacylglycerides
its not a disease , but rather a cluster of metabolism disorders
high blood pressure
high insulin levels
excess body weight
abnormal cholesterol levels
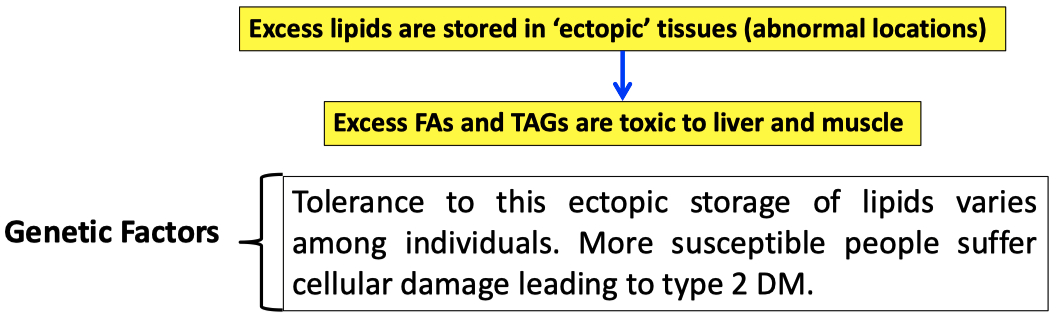
Excessive lipids are stored in abnormal ( ectopic ) places
problem / toxic
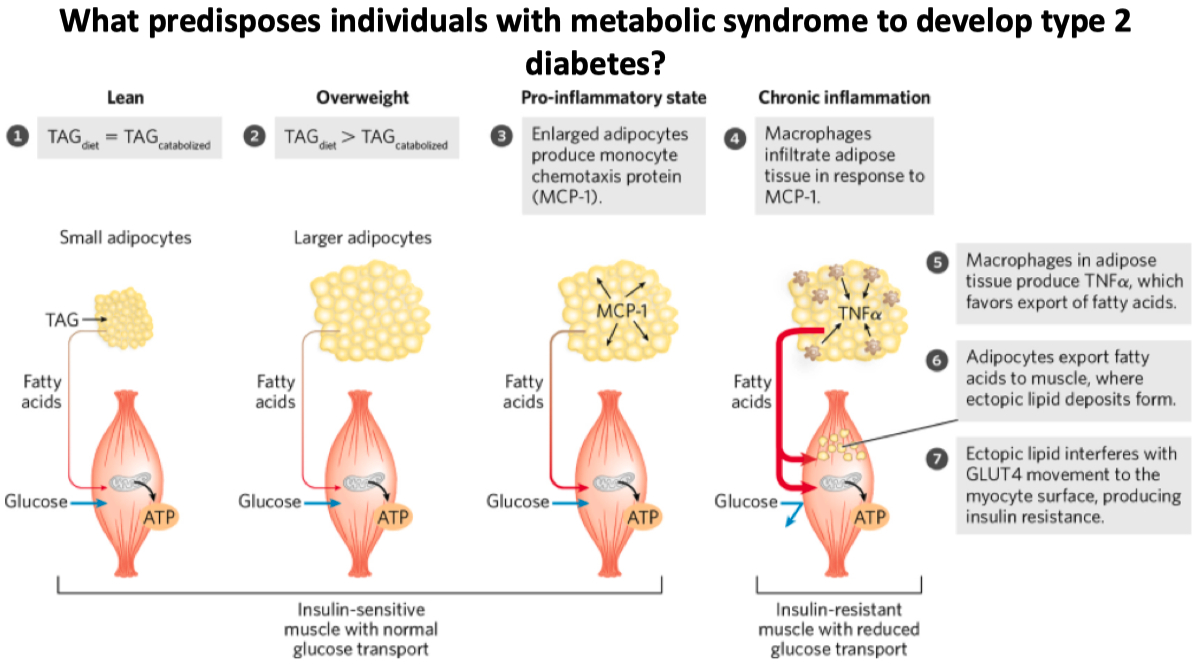
Individuals with metabolic syndrome tend to develop type 2 diabetes
MCP-1 recruited macrophages
if muscle can still store fats , it’s somewhat ok.
only if fat is being stored in like the liver or elsewhere do we consider it type II diabetes
In obesity , the capacity of adipocytes to store TAGs becomes exhausted & several changes occur :
Adipocytes become less sensitive to insulin
Gene expression associated with the development of new adipocytes is down-regulated
Expression of transcription factors in liver and skeletal muscle upregulates the lipid synthesizing machinery and increases lipid storage capacity
Drugs that increase insulin sensitivity or insulin production
Sulfonylureas :
examples = Glyburide , glipizide , and glimepiride
Blocks ATP sensitive K-channels
causes depolarization and opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
increases intracellular calcium in the beta cells
stimulates insulin release
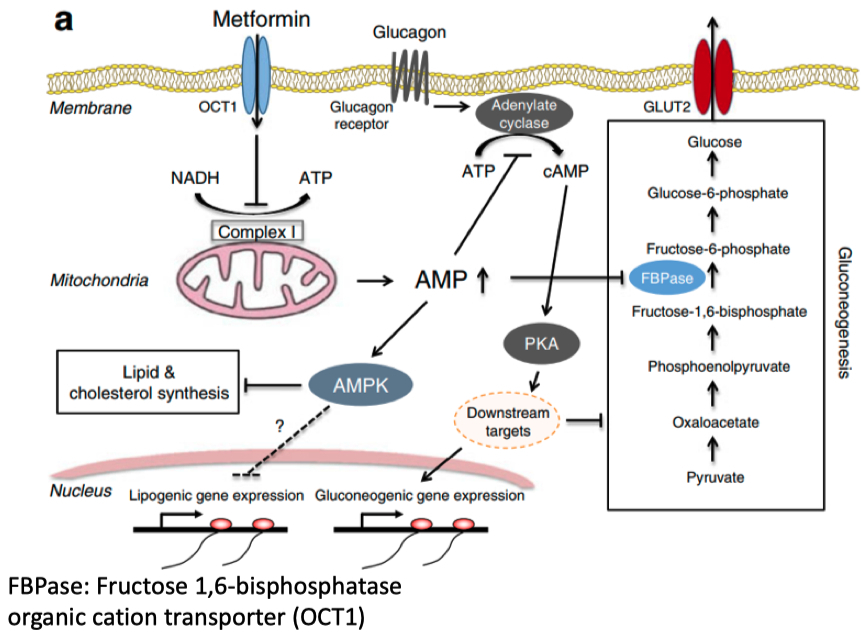
Biguanides :
example = Metformin
inhibits mitochondria complex 1
inhibits cAMP formation , aka causes high AMP concentration
activates AMPK
shifts metabolism to conserve energy
decrease in lipogenic gene expression
aka increase :
glucose uptake and oxidation
increase fatty acid mobilization and oxidation
inhibits synthesis of glucose , FA , and sterols
Thiazolidinediones ( TZDs ) :
examples = troglitazone , rosiglitazone , and pioglitazone
TZDs bind avidly to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ( PPAR𝛾 ) in adipocytes
promotes adipogenesis and fatty acid uptake
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 ( GLP-1 ) Agonists :
examples = Exenatide , Sitagliptin , and Ozempic !
GLP-1 binds to receptors on beta cells
activates adenyl cyclase to form cAMP
cAMP activates PKA and Epac2
increases intracellular calcium
promotes insulin secretion
Summary
The insulin receptor, INSR, is the prototype of receptor enzymes with Tyr kinase activity. When insulin binds, each αβ unit of INSR phosphorylates the β subunit of its partner, activating the receptor’s Tyr kinase activity.
The kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of Tyr residues on other proteins, such as IRS-1.
Phosphotyrosine residues in IRS-1 serve as binding sites for proteins with SH2 domains.
Some of these proteins, such as Grb2, have two or more protein-binding domains and can serve as adaptors that bring two proteins into proximity.
Sos bound to Grb2 catalyzes GDP-GTP exchange on Ras (a small G protein), which in turn activates a MAPK cascade that ends with the phosphorylation of target proteins in the cytosol and nucleus.
The result is specific metabolic changes and altered gene expression.
The enzyme PI3K, activated by interaction with IRS-1, converts the membrane lipid PIP2 to PIP3
which becomes the point of nucleation for proteins in a second and third branch of insulin signaling.
Metabolic syndrome, which includes obesity, hypertension, elevated blood lipids, and insulin resistance, is often the prelude to type 2 diabetes.
The insulin resistance that characterizes type 2 diabetes may be a consequence of abnormal lipid storage in muscle and liver, in response to a lipid intake that cannot be accommodated by adipose tissue.
Effective treatments for type 2 diabetes include exercise, appropriate diet, and drugs that increase insulin sensitivity or insulin production.
Surgical alteration of the digestive tract leads to weight loss and often reverses type 2 diabetes.
Complex Lipids
Lipid Storage
Double bonds create kinks
reduces the ability to compact
lipids are reduced compounds
lots of potential energy
hydrophobic in nature = good for packing
lipids are usually stored as triacylglycerols
most natural fatty acids :
between 12 and 18 carbons in length
even numbered
unbranched
chain length
chain length
number of double bonds
kinks are the enemy of compaction
to fight against becoming a solid , we introduce kinks
aka double bonds
Poly Unsaturated :
liquid at room temperature
melting temp
Trans fatty acids can pack more tightly than cis fatty acids
therefore , they have a higher melting temperature than cis
Triacylglycerols ( simplest form of a lipid ) are less soluble in water than free floating fatty acids
due to the esterification of the carboxylate group
Lipids are water-insoluble cellular components, of diverse structure, that can be extracted from tissues by nonpolar solvents.
Almost all fatty acids, the hydrocarbon components of many lipids, have an even number of carbon atoms ( usually 12 to 24 )
they are either saturated or unsaturated, with double bonds almost always in the cis configuration.
Triacylglycerols contain three fatty acid molecules esterified to the three hydroxyl groups of glycerol
simple triacylglycerols contain only one type of fatty acid
mixed triacylglycerols contain two or three types
Triacylglycerols are primarily storage fats; they are present in many foods.
Because trans fatty acids in the diet are an important risk factor for coronary heart disease, their use in prepared and processed foods has become highly regulated.
Waxes are esters of long-chain fatty acids and long-chain alcohols.
Lipid Structures
Glycerophospholipids :
main lipid type in cell membrane
mostly phosphatidylcholine
also found in mitochondrial membrane
have different head groups
they can donate protons
aka carry a negative charge
allows them to recruit proteins to bind to the lipid
Ether Lipids :
Plasmalogen :
common in heart tissue
vinyl ether analog of phosphatidylethanolamine
Platelets-Activating Factor :
aliphatic ether analog of phosphatidylcholine
first signaling lipid to be identified
Sphingolipids :
backbone is NOT a glycerol
its a long chain amino alcohol called a sphingosine
fatty acid is joined via an amide linkage instead of the usual ester bond
found mainly in the outer face ? of the plasma membrane
ceramide is the base sphingolipid , used to construct others
sphingomyelin = type found in myelin sheaths
basically the same thing as phosphatidylcholine , except it has the sphingosine backbone instead of a glycerol
blood groups are determined in part by the type of sugars on the head groups in glycosphingolipids
sugar structure is determined by which glycosyltransferase is expressed
no glycosyltransferase expressed = O group
one that transfers N-acetylgalactosamine = A group
one that transfers a galactose = B group
Sterols and Cholesterols :
steroid nucleus = 4 fused rings
the fused rings make it almost planer ( basically rigid )
modulate membrane fluidity and permeability
thicken the plasma membrane
most bacteria do NOT have sterol / cholesterol
mammals get cholesterol from diet , or the liver can synthesize it
cholesterol is transported to tissues via blood stream
must be bound to a protein
most hormones are derivatives of sterols
steroids :
oxidized derivatives of sterols
have the sterol nucleus , but don't have the alkyl chain like cholesterol does
more polar than cholesterol
steroid hormones are synthezied in the gonads or adrenal glands from a cholesterol base
The polar lipids, with polar heads and nonpolar tails, are major components of membranes. The most abundant are the glycerophospholipids, which contain fatty acids esterified to two of the hydroxyl groups of glycerol, and a second alcohol, the head group, esterified to the third hydroxyl of glycerol via a phosphodiester bond. Other polar lipids are the sterols.
Glycerophospholipids differ in the structure of their head group; common glycerophospholipids are phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. The polar heads of the glycerophospholipids are charged at pH near 7.
Some archaea have unique membrane lipids, with long-chain alkyl groups ether-linked to glycerol at each end and with sugar residues and/or phosphate joined to the glycerol to provide a polar or charged head group. These lipids are stable under the harsh conditions in which these archaea live.
The sphingolipids contain sphingosine, a long-chain aliphatic amino alcohol, but no glycerol. Sphingomyelin has, in addition to phosphoric acid and choline, two long hydrocarbon chains, one contributed by a fatty acid and the other by sphingosine. Three other classes of sphingolipids are cerebrosides, and gangliosides, which contain sugar components.
The Sterols have four fused rings and a hydroxyl group. Cholesterol, the major sterol in animals, is both a structural component of membranes and precursor to a wide variety of steroids.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
K - A - D - E
K :
cofactor for a carboxylase in the coagulation pathway
if deficient , it leads to bleeding problems
warfarin blocks this pathway
A :
Involved in visual pigment
isoprene units allow electron delocalization / movement
Precursor for other hormones involved in signaling
D :
forms in the skin by a reaction driven by sunlight; in the liver/kidney
converted to a biologically-active hormone that regulates calcium uptake
E :
antioxidant
Arachidonic Acid ( AA ) Derivatives
Phospholipases can breakdown / cleave different membrane phospholipids into Arachidonic Acid + LPC
Arachidonic Acid can go through different enzymes to turn into different derivatives
AA + COX = Prostaglandin , prostacyclin , thromboxane
AA + LOX = Leukotrienes , HETEs , HPETEs
AA + CYP2C = EETs
Prostaglandins = anti-inflammatory , anti-fever
Thromboxanes = form blood clots
Leukotrienes = smooth muscle contraction in lungs
Fatty Acid Nomenclature
Delta vs Omega Nomenclature
Common Names :
Palmitic Acid ( 16:0 )
Stearic Acid ( 18:0 )
Palmitoleic Acid ( 16:1n-9 )
Oleic Acid ( 18:1n-9 )
Linoleic Acid ( 18:2n-6 )
Arachidonic Acid
EPA
DHA
Essential Fatty Acids
NOT produced in the human body
must be obtained in diet
Linoleic Acid , aka Omega-6 =
base for making arachidonic acid
eicosanoids
base for making eicosapentaenoic acid ( EPA ) and docosahexaenoic acid ( DHA )
anti-inflammatory
Summary
Some types of lipids, although present in relatively small quantities, play critical roles as cofactors or signals.
Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate is hydrolyzed to yield two intracellular messengers, diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate is a nucleation point for supramolecular protein complexes involved in biological signaling.
Prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, and lipoxins, all of which are eicosanoids derived from arachidonate, are extremely potent hormones.
Steroid hormones, such as the sex hormones, are derived from sterols. They serve as powerful biological signals, altering gene expression in target cells.
Vitamins D, A, E, and K are fat-soluble compounds made up of isoprene units. All play essential roles in the metabolism or physiology of animals. Vitamin D is precursor to a hormone that regulates calcium metabolism. Vitamin A furnishes the visual pigment of the vertebrate eye and is a regulator of gene expression during epithelial cell growth. Vitamin E functions in the protection of membrane lipids from oxidative damage, and vitamin K is essential in the blood-clotting process.
Lipidic conjugated dienes serve as pigments in flowers and fruits and give bird feathers their striking colors.
Polyketides are natural products widely used in medicine.
Working With Lipids
Reagents to Extract Neutral and Membrane Lipids
Neutral ( TG , Waxes ) :
use hydrophobic solvents
Ethyl ether , chloroforms , benzene
Membrane :
use more polar solvents
Ethanol , methanol
Basic Principles of TLC , GC , HPLC , MS
TLC :
involves a stationary phase (usually a thin layer of adsorbent material like silica gel or alumina coated onto a glass or plastic plate) and a mobile phase (solvent or solvent mixture). A small amount of sample is applied near the bottom of the plate, which is then placed vertically in a developing chamber containing the mobile phase. As the mobile phase moves up the plate, different compounds in the sample migrate at different rates due to their varying interactions with the stationary phase. The separation is visualized as spots on the plate, and the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and identify compounds.
GC :
GC is a separation technique used for volatile compounds. It consists of a stationary phase (a solid support with a liquid or solid coating) and a mobile phase (an inert gas like helium, nitrogen, or hydrogen). The sample is vaporized and carried through a long column by the mobile phase. Compounds in the sample interact with the stationary phase and are separated based on their differing boiling points and affinity for the stationary phase. As the compounds exit the column, they are detected by a detector (e.g., flame ionization detector or mass spectrometer), and the retention time is used to identify and quantify the compounds.
HPLC :
HPLC is a widely used separation technique for a broad range of compounds. It uses high pressure to force the mobile phase (a liquid solvent or solvent mixture) through a column packed with a solid stationary phase (e.g., silica or polymer-based particles). The sample is injected into the mobile phase, and compounds in the sample interact with the stationary phase, resulting in separation based on their polarity, size, or other properties. The compounds are detected as they elute from the column, and the retention time is used for identification and quantification. Different types of HPLC include reversed-phase, normal-phase, size-exclusion, and ion-exchange chromatography.
MS :
MS is an analytical technique used to identify and quantify compounds based on their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). The sample is ionized by an ionization source (e.g., electron impact or electrospray), and the ions are separated by a mass analyzer (e.g., quadrupole, time-of-flight, or orbitrap) according to their m/z. The ions are then detected, and the resulting mass spectrum provides information about the molecular mass, elemental composition, and structure of the compounds. MS can be used as a standalone technique or coupled with other separation methods like GC or HPLC for more comprehensive analysis.
Summary
In the determination of lipid composition, the lipids are first extracted from tissues with organic solvents and separated by thin-layer, gas, or high-performance liquid chromatography.
Phospholipases specific for one of the bonds in a phospholipid can be used to generate simpler compounds for subsequent analysis.
Individual lipids are identified by their chromatographic behavior, their susceptibility to hydrolysis by specific enzymes, or mass spectrometry.
High-resolution mass spectrometry allows the analysis of crude mixtures of lipids without prefractionation—the “shotgun” approach.
Lipidomics combines powerful analytical techniques to determine the full complement of lipids in a cell or tissue (the lipidome) and to assemble annotated databases that allow comparisons between lipids of different cell types and under different conditions.
Questions
The action of metformin is to increase ATP production ?
False
The glycerophospholipids are composed of two fatty acids attached to glycerol and threonine ?
False
The main difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids is :
the presence of double bonds
How do free fatty acids contribute to impaired insulin signaling response ?
Free fatty acids activate IRS-1 serine phosphorylation
Name the two essential fatty acids
Linoleate and Linolenate
The melting point of fatty acids depends upon chain length and _______ ?
Degree of unsaturation
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
Enzymes involved in Synthesis
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase :
Bi-Functional enzyme with 3 active domains
Biotin carrier protein = swing arm
transfers activated CO2 from biotin carboxylase domain to the transcarboxylase active site
Biotin Carboxylase = carboxylates biotin
Transcarboxylase = transfers activated CO2 from biotin to acetyl-CoA , forming malonyl-CoA
Fatty Acid Synthase :
2 major isoforms
FAS 1 = found in vertebrates and fungi
single multifunctional polypeptide chain that catalyzes 7 different reactions
a dimer of two identical monomers
each monomer has 7 active sites in 7 different domains :
5 of those are actual catalysis enzymes
1 is an acyl carrier protein ( ACP ) = swing arm
Flexible arm to carry intermediates from one enzyme subunit to the next
1 is a thioesterase that releases the palmitate product from ACP
FAS 2 = found in plants and bacteria
Advantages of Multi-Enzyme Complex :
active sites are all centralized
higher efficiency
all 7 enzymes are encoded by a single gene
Reactions for Fatty Acid Synthesis
acetyl and malonyl group activation
acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is first transferred to the –SH group of the b-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (KS)
in a reaction catalyzed by acetyl-CoAACP transacetylase (AT)
The malonyl group is transferred from malonyl-CoA to the –SH group of acyl carrier protein (ACP)
4 step elongation reaction
Acetyl-CoA is the priming group only in the first cycle
after that, only malonyl-CoA is added to the ACP each time
After activation , there is a four-step process
Condensation : of the growing chain with activated acetate
Reduction : of carbonyl to hydroxyl
Dehydration : of alcohol to trans-alkene
Reduction : of alkene to alkane
Each cycle results in the net addition of two carbons to the growing fatty acid chain.
These steps are repeated till a fatty acid with 16 carbon atoms is synthesized.
termination reaction
Seven rounds of the four-step lengthening reactions produces palmitoyl-ACP
Palmitoyl-ACP is hydrolyzed by a thioesterase to release a free palmitate
This is why it there are only 6 net H2O molecules.
one gets "burnt" here to hydrolyze free palmitate
Why are there only 6 net
Overall, the biosynthesis of FA requires acetyl-CoA and the input of energy in the form of ATP and reducing power of NADPH.
What is the Function of ATP ?
used to synthesize malonyl-CoA
What is the function of NADPH ?
used in the 2nd and 4th steps as the electron donor
Locations of Fatty Acid Synthesis
acetyl-CoA Shuttle :
citrate shuttle on inner mitochondrial membrane
shuttles acetyl-CoA out of the membrane as citrate
acetyl-CoA is made from glucose and amino acids in mitochondria
Intramitochondrial acetyl-CoA first reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate
in the TCA cycle catalyzed by citrate synthase.
Citrate then passes into the cytosol through the mitochondrial inner membrane on the citrate transporter
Acetyl-CoA is regenerated by the action of ATP-dependent citrate lyase in the cytosol
Oxaloacetate is shuttled back into the mitochondria as malate or pyruvate
Elongation = mitochondria
Desaturation = endoplasmic reticulum
Factors Involved in the Process of Fatty Acid Synthesis
NADPH is used as a reducing agent / electron donor
synthesized in :
pentose phosphate pathway
from malic enzyme
Regulation of Fatty Acid Synthesis
what is the rate limiting step?
converting the phosphorylated / inactive version of the promotors into the dephosphorylated / active / polymer form
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase regulates rate-limiting step of fatty acid synthesis
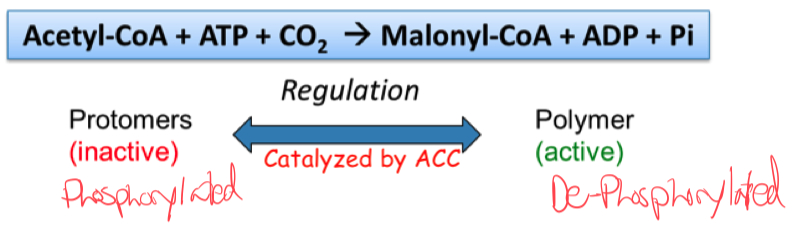
How is acetyl-CoA carboxylase regulated ?
ACC is regulated by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation and protein polymerization
ACC forms long , active filamentous polymers from inactive protomers
Palmitoyl-CoA = allosteric inhibitor ( feedback inhibition )
Citrate = allosteric activator ( ATP and acetyl-CoA high in mitochondria )
When we have enough FA ( palmitoyl-CoA ) , we inhibit malonyl-CoA
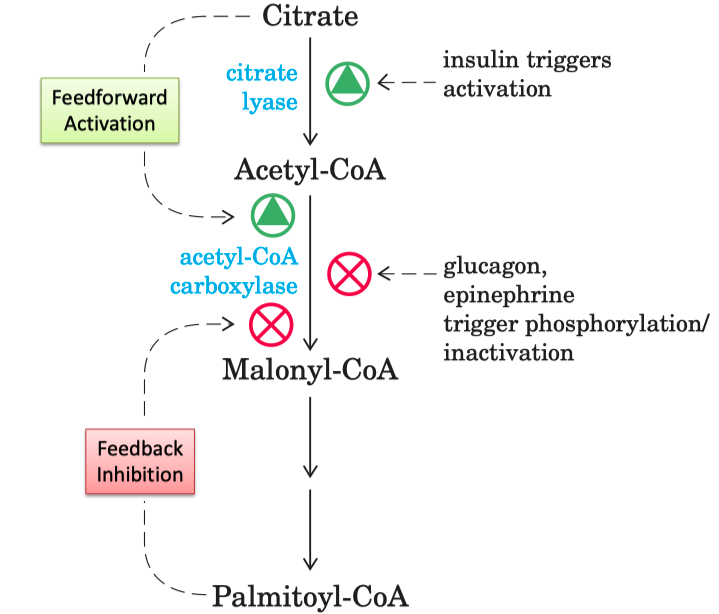
Insulin signaling leads to dephosphorylation of ACC
activates ACC activity to ensure that excess glucose will be rapidly converted to fatty acid for long term energy storage
Glucagon and epinephrine triggers phosphorylation
inactivates acetyl CoA carboxylase
Fatty Acid Elongation and Desaturation
Understand the location
palmitate ( C16 - saturated ) is the final product
anything longer or anything with double bonds has to be transported to the smooth E.R.
Understand electron transfer
The double bonds are introduced by the catalysis of fatty acyl-CoA desaturase (a mixed-function oxidase)
where both the fatty acyl group and NADPH are oxidized by O2 .
The electrons of NADPH are transferred to O2 via Cyt b5 reductase and cytochrome b5
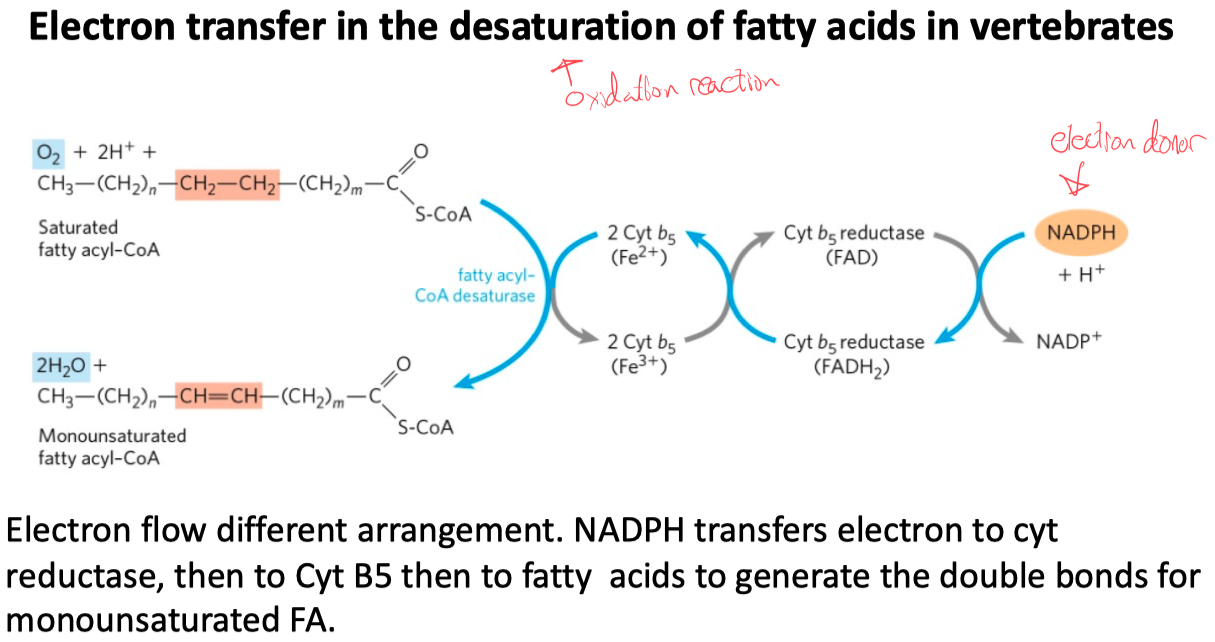
Biosynthesis of Eicosanoids
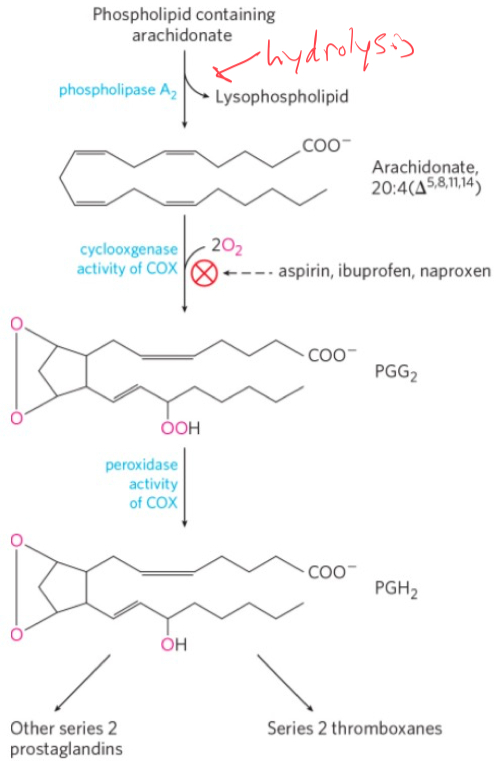
Prostanoid Biosynthesis
COX is an enzyme that catalyzes the rate determining step in the conversion of AA to prostanoids by a 2-step process involving oxygen.
Cyclooxygenase adds two molecules of O2 to AA to form the endoperoxide PGG2
PGH2 serves as a “branch point” for specific enzymes leading to the formation of prostacyclin, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes.
NSAIDs action of Mechanism
Aspirin inhibits the first reaction by acetylating an essential Ser residue on the enzyme.
Ibuprofen and naproxen inhibit the same step, probably by mimicking the structure of the substrate or an intermediate in the reaction.
Slide 40 on Lecture 02 and 03
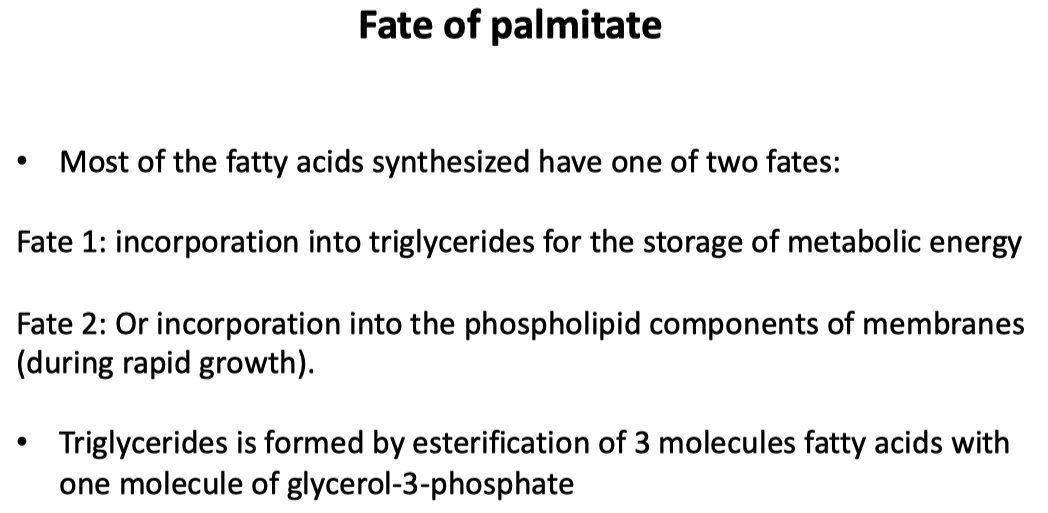
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerols
The Precursor
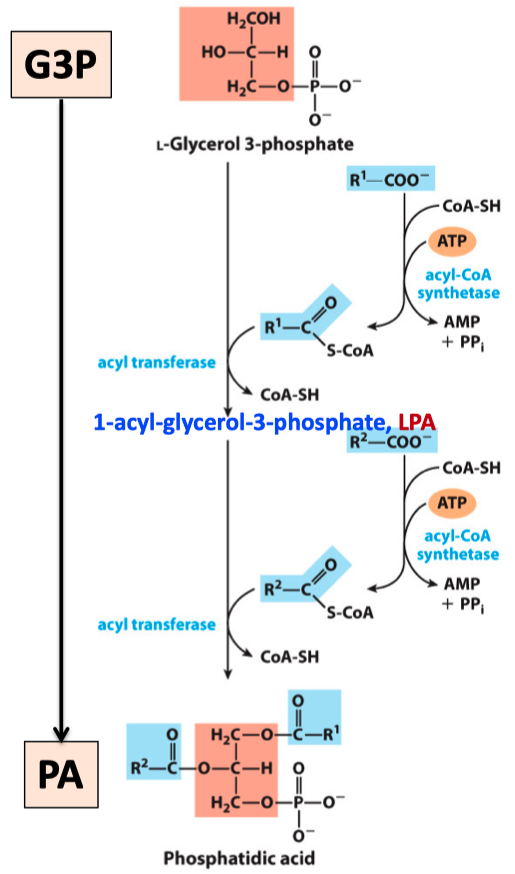
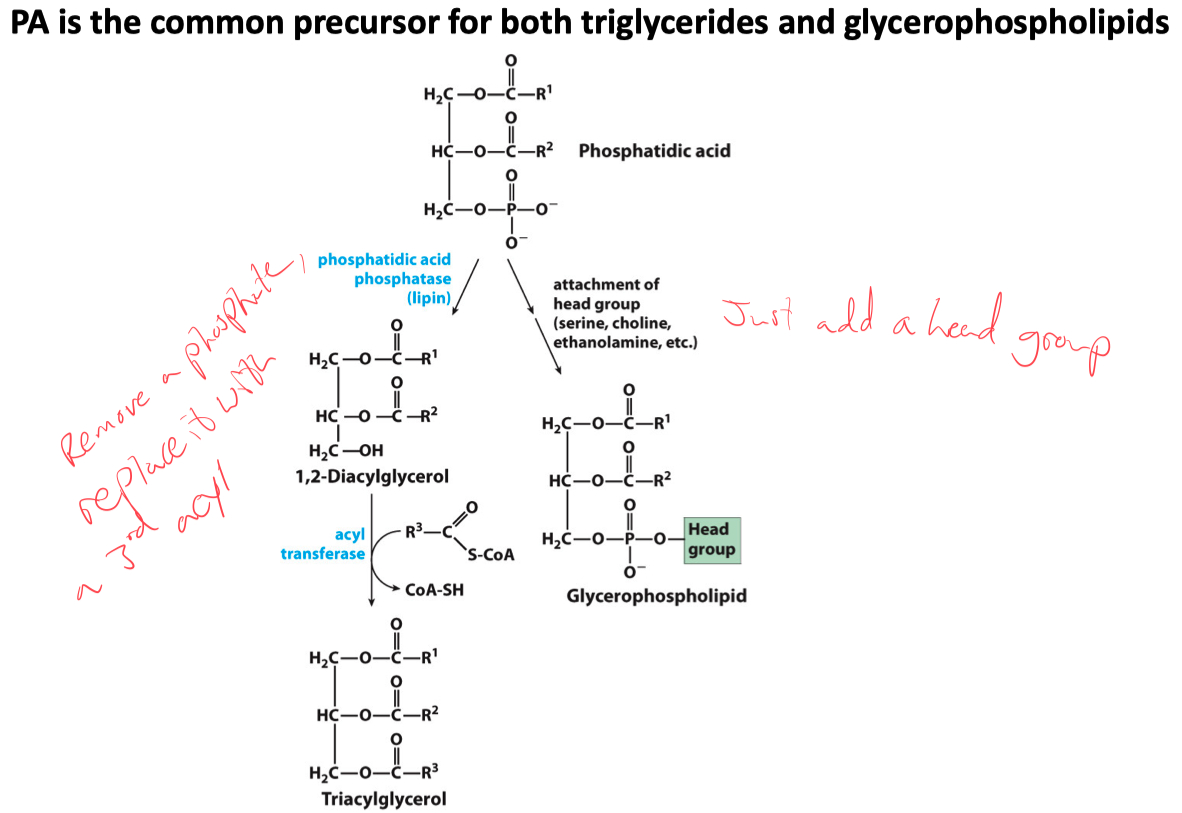
Phosphatidic Acid is the common precursor for the synthesis of both triglycerides and glycerophospholipids
PA synthesis and Conversion of PA to TG
Phosphatidic acid is made by transferring two acyl groups from two acyl-CoAs to L-glycerol 3-phosphate
L-glycerol 3-phosphate is derived from either glycerol or dihydroxyacetone phosphate
A phosphatidic acid is converted to a triglyceride via a dephosphorylation reaction
catalyzed by phosphatidic acid phosphatase and an acyl transferring reaction
The vast majority of the glycerol 3-phosphate is derived from the glycolytic intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
In liver, a small amount of glycerol 3-phosphate is also formed from glycerol by the action of glycerol kinase.
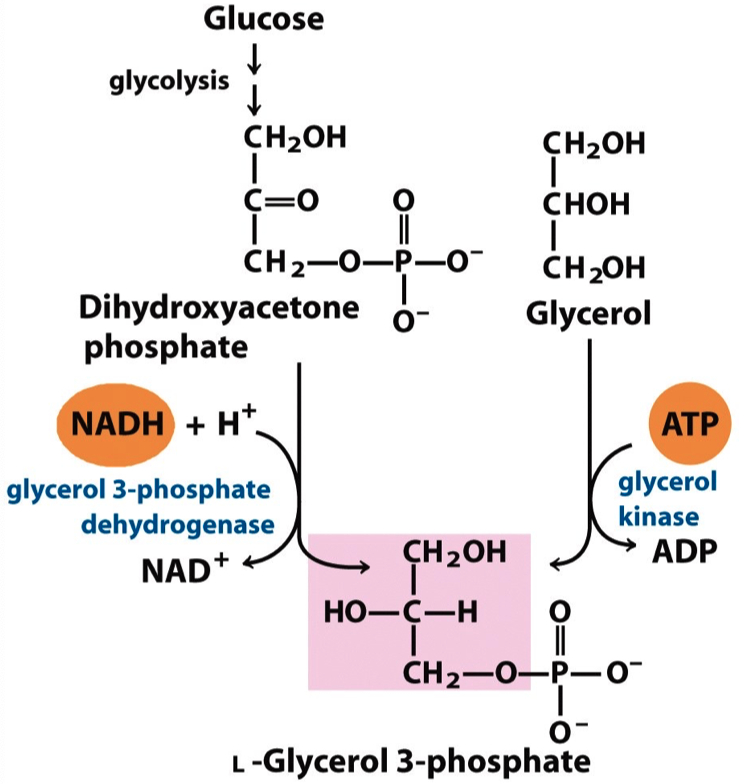
Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) catalyzes the ATP-dependent formation of a thioester bond between a fatty acid and coenzyme A.
One mole of L-glycerophosphate acylated with 2 mol of CoA–fatty acids yields PA.
Re-Esterification and Action of Mechanisms of Dexamethasone and Thiazolidinediones
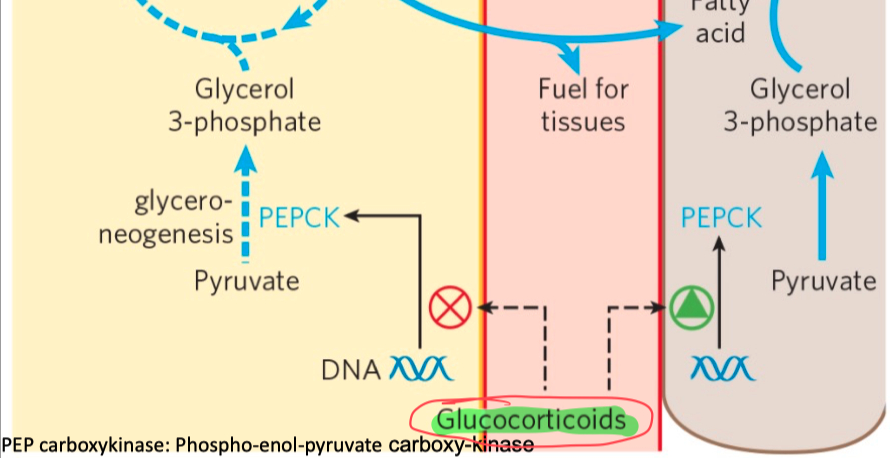
Glucocorticoid hormones stimulate glyceroneogenesis in the liver
while suppressing glyceroneogenesis in adipose tissue which is controlled by the activity of PEPCK
Dexamethasone = corticosteroid
in adipose tissue :
decreases transcription of PEPCK
inhibits glyceroneogenesis
in liver tissue :
increases transcription of PEPCK
stimulates glyceroneogenesis
Thiazolidinediones :
reduces the levels of fatty acid in the blood and increase sensitivity to insulin
activate PPAR𝛾
induces the activity of PEP carboxykinase
increase the rate of glyceroneogenesis
thus increasing the resynthesis of triacylglycerol in adipose tissue
and reducing the amount of free fatty acid in the blood
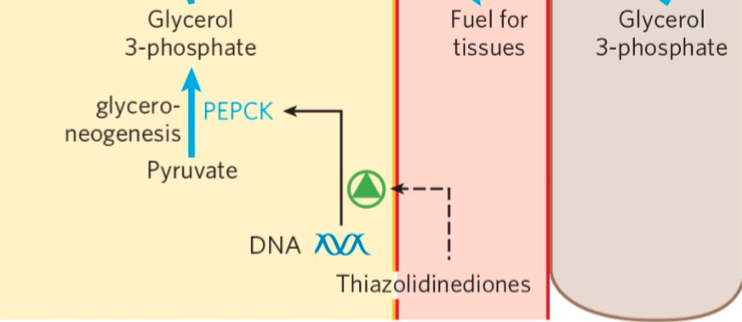
Summary
Triacylglycerols are formed by reaction of two molecules of fatty acyl–CoA with glycerol 3-phosphate to form phosphatidic acid
this product is dephosphorylated to a diacylglycerol
then acylated by a third molecule of fatty acyl–CoA to yield a triacylglycerol
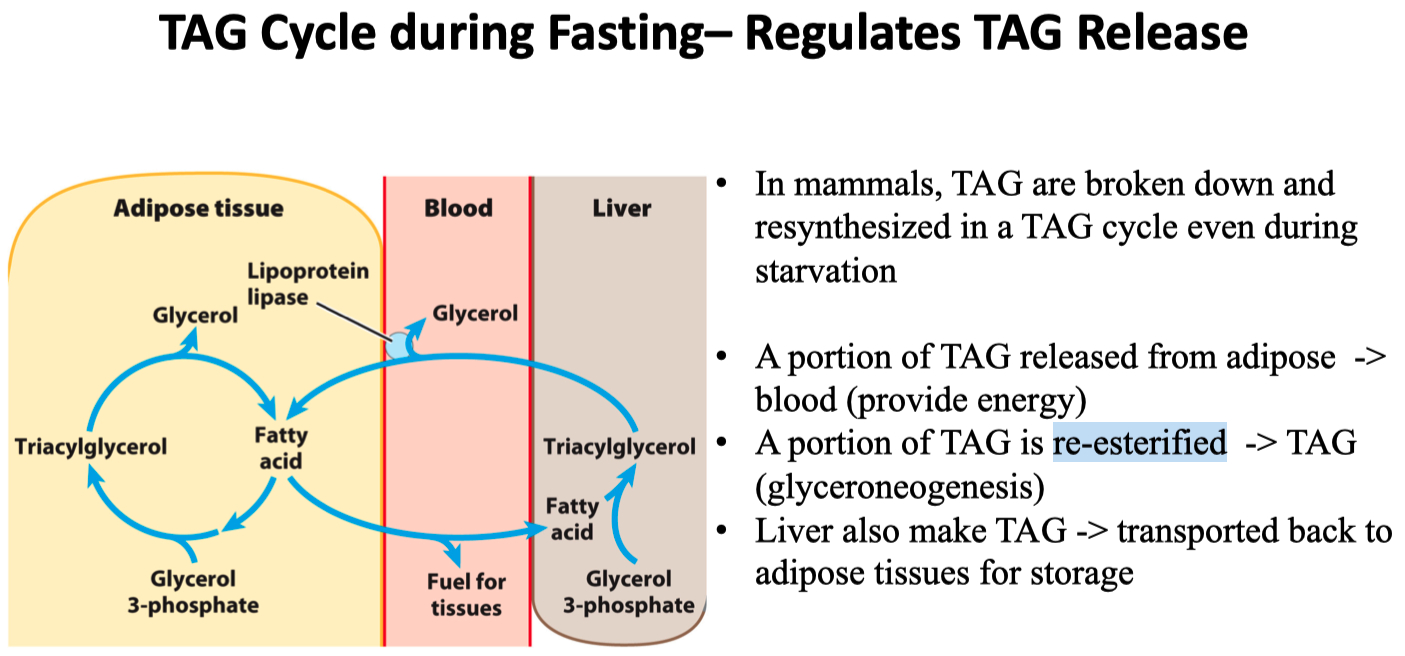
The synthesis and degradation of triacylglycerols are hormonally regulated.
Mobilization and recycling of triacylglycerol molecules result in a triacylglycerol cycle. Triacylglycerols are resynthesized from free fatty acids and glycerol 3-phosphate even during starvation. The dihydroxyacetone phosphate precursor of glycerol 3-phosphate is derived from pyruvate via glyceroneogenesis.
Biosynthesis of Phospholipids
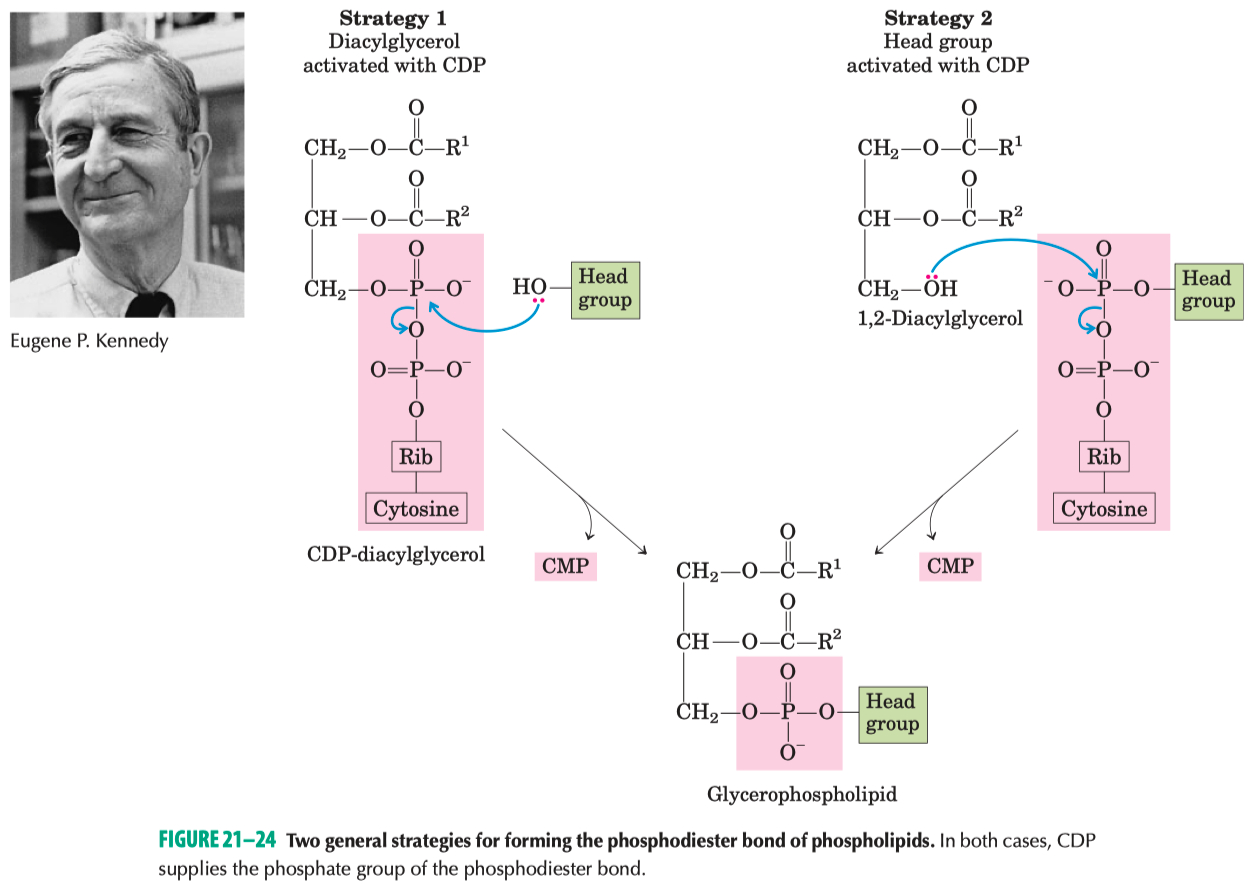
Two Strategies for Phospholipid Biosynthesis
CDP is attached to Diacylglycerol forming CDP-DAG
used to make Phosphatidylglycerol , cardiolipin , inositol
CDP is attached to the headgroup forming CDP-Headgroup
used to make phosphatidylcholine , phosphatidylethanolamine
Kennedy Pathway
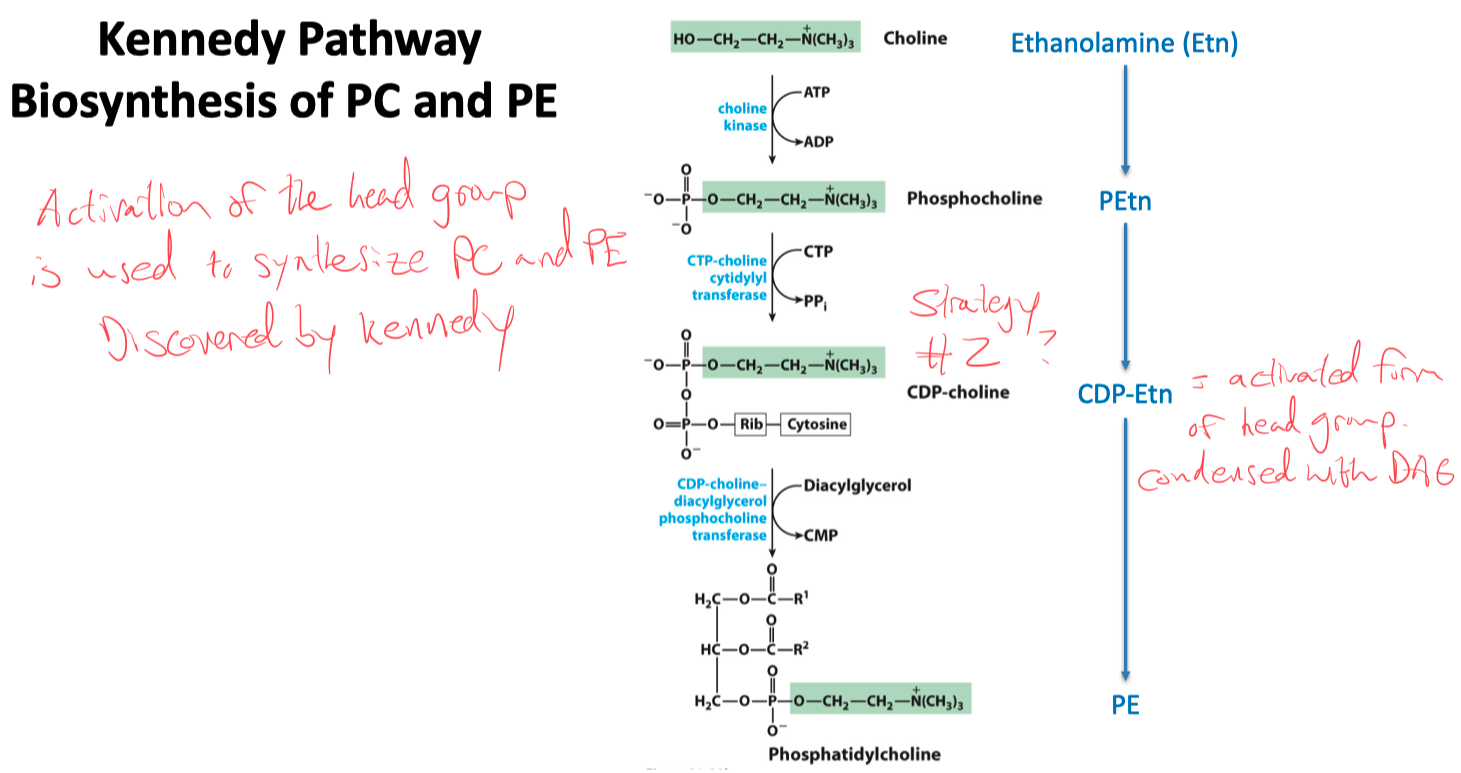
PC and PE
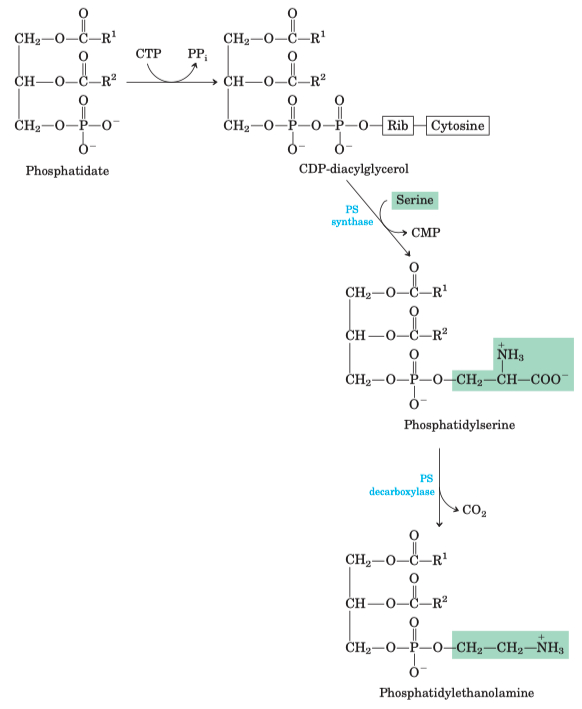
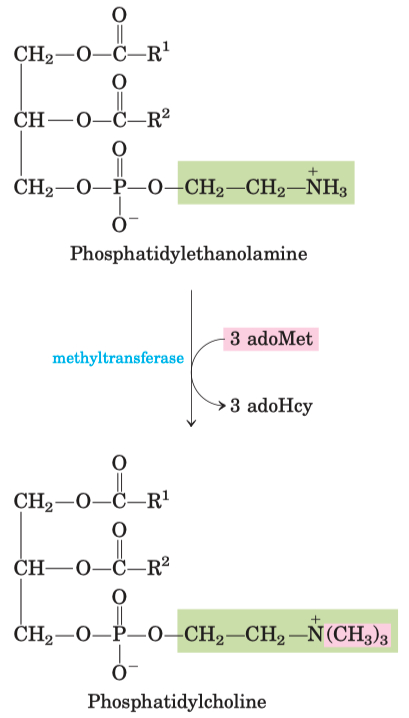
PE :
CDP-DAG ➡️ swap cytosine for serine ➡️ burn off a CO2 = Phosphatidylethanolamine
PC :
PE ➡️ attach 3 carbons using 3 adoMet ➡️ Phosphatidylcholine
Interconversion of PS , PC , and PE
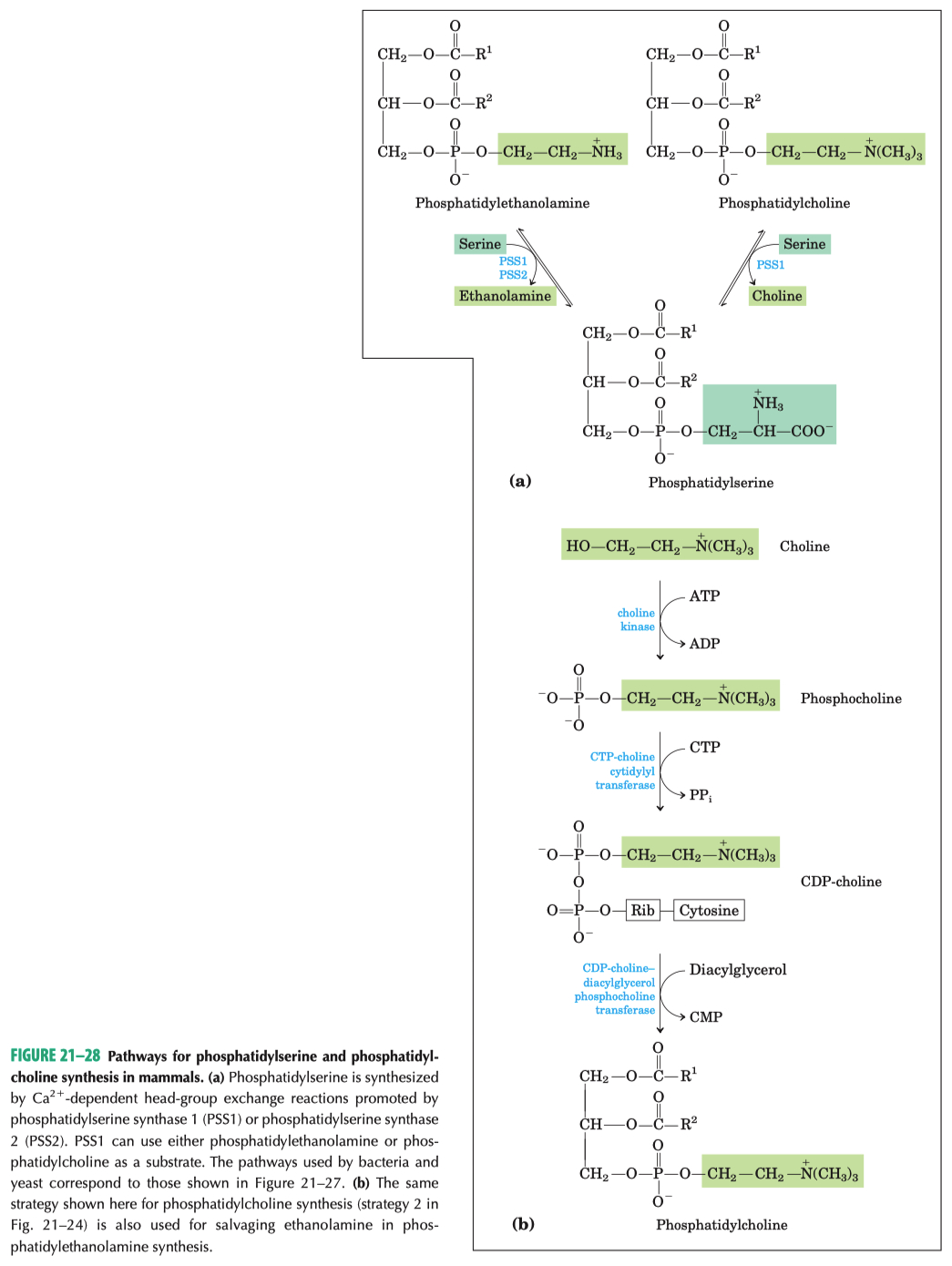
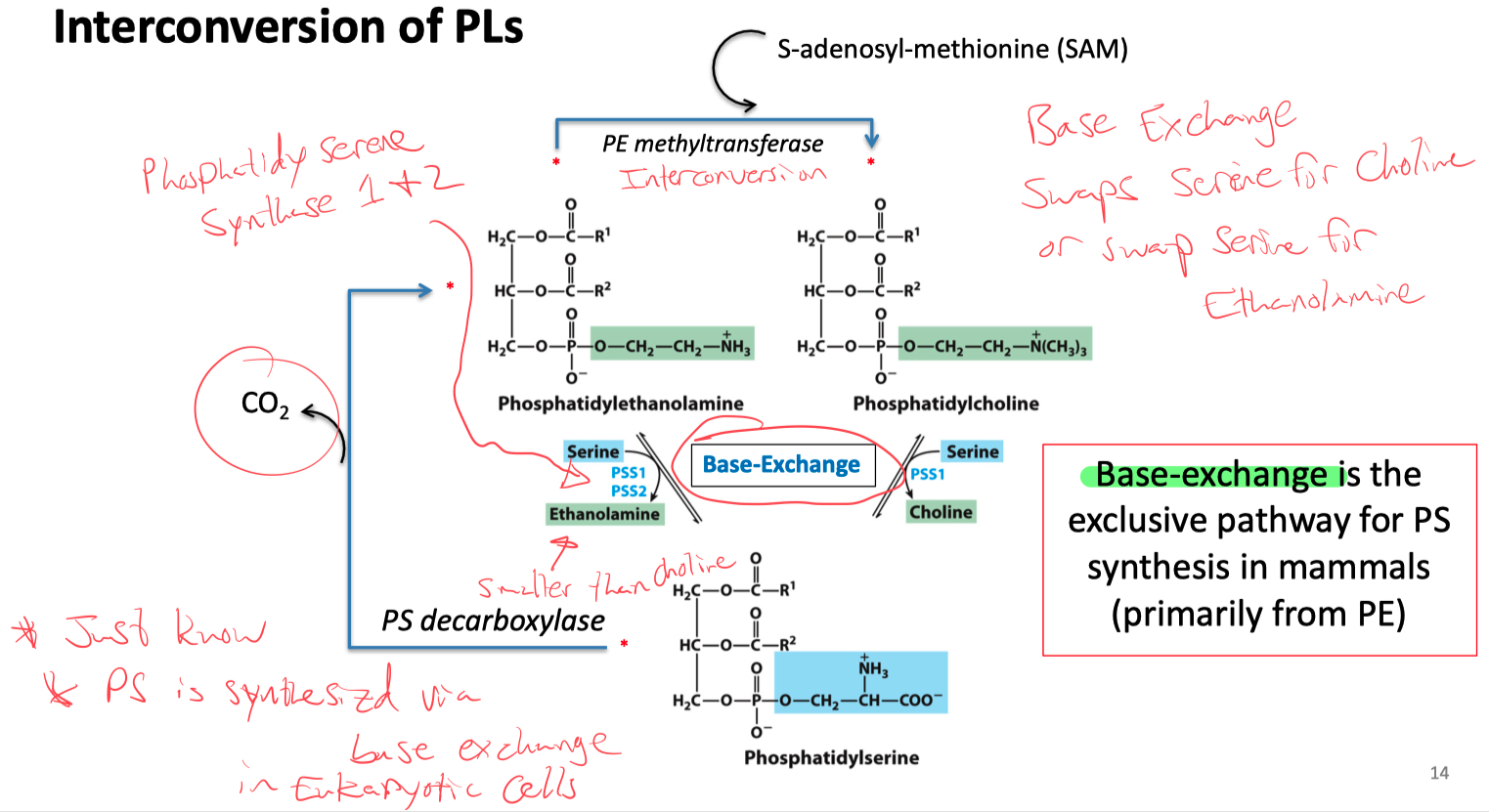
Base exchange :
swaps serine for choline
swaps serine for ethanolamine
PS is synthesized via base exchange in eukaryotic cells
What is the precursor for glycerophospholipids and triacylglycerol ?
Phosphatidic Acid !!!
Review Questions
How does FFA or DG contribute to impaired insulin signaling response?
circulating FFA & adipokine TNFα may ↑ serine phosphorylation of IRS proteins, causing impaired insulin signal transduction.
What predisposes individuals with metabolic syndrome to develop type 2 diabetes?
obesity , insulin resistance
What is the action of mechanism of metformin?
Inhibits mitochondrial Complex 1 ➡️ increases AMP ➡️ activates AMPK
AMPK ➡️
activates lipogenic gene expression ➡️
increases fatty acid mobilization and oxidation
inhibits synthesis of glucose , FA , and sterols
inhibits lipid and cholesterol synthesis
increases the translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4 to the cell surface
What is metabolic syndrome?
cluster of metabolic disorders
obesity , high blood pressure , elevated blood sugar levels , high triglyceride levels , low HDL
leads to high risk of heart disease , etc
How is acetyl-CoA transported out of mitochondria? Explain the shuttle system
must be converted to citrate to exit mitochondria. Then in cytosol citrate can be lysed to convert back.
In fatty acid synthesis , there are 7 dehydration steps required for palmitate , why only 6 net
Seven rounds of the 4-step lengthening reactions produces palmitoyl-ACP
In the termination Reaction :
Palmitoyl-ACP is hydrolyzed by a thioesterase to release a free palmitate
This is why it there are only 6 net H2O molecules.
one gets "burnt" here to hydrolyzes free palmitate
What is the rate-limiting step of fatty acid synthesis ?
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase step
How is acetyl-CoA carboxylase regulated ?
Inhibitor = palmitoyl-CoA
Activator = Citrate
What is the primary metabolic source of the reducing power required for fatty acid synthesis and desaturation ?
NADPH = reducing agent / electron donor
Synthesized in pentose phosphate pathway and also from malic enzyme
What are the precursors shared by triaclyglycerols and glycerophospholipids ?
Phosphatidic Acid
What are the mechanisms of action of dexamethasone and thiazolidinediones on triacylglycerol levels?
Dexamethasone = corticosteroid
in adipose tissue :
decreases transcription of PEPCK
inhibits glyceroneogenesis
in liver tissue :
increases transcription of PEPCK
stimulates glyceroneogenesis
Thiazolidinediones :
reduces the levels of fatty acid in the blood and increase sensitivity to insulin
activate PPAR𝛾
induces the activity of PEP carboxykinase
increase the rate of glyceroneogenesis
thus increasing the resynthesis of triacylglycerol in adipose tissue
and reducing the amount of free fatty acid in the blood
What are the strategies to synthesize membrane phospholipids?
CDP is attached to Diacylglycerol forming CDP-DAG
used to make Phosphatidylglycerol , cardiolipin , inositol
CDP is attached to the headgroup forming CDP-Headgroup
used to make phosphatidylcholine , phosphatidylethanolamine










