Mitotic Lineage vs Self-Regulation
Fate = the particular structure and function that a given cell takes on in the course of cellular differentiation
Mosaic Specification of Cell Fate = every cell follows its particular destiny no matter what its neighboring cells are up to
Mitotic Lineage :
C. elegans's body is mostly transparent
you can make a "map" that shows every cell division that takes place in the transition from zygote to adult ,
including the final differentiation of every cell
this means that, by keeping track of the mitotic lineage of each cell, you can perfectly predict what any particular cell will become neuron, skin cell, or gut or mouth cell
with enough persistence, you can trace the mitotic lineage of all 959 cells, including the 302 neurons
mitotic lineage specifies each cell's fate
Self-Regulation :
Also known simply as regulation.
the process by which embryos manage to compensate for missing or damaged cells and nevertheless produce an entire individual.
no other cell changes its fate to take the place of the fallen comrade
the animal simply goes on without whatever the destroyed cell would have become
C. elegan's does NOT use self-regulation
just as the brain exhibits less plasticity as we grow older, the ability of embryos to self-regulate becomes more limited as the embryo grows
the later in development you look, the less self-regulation you see. It is as if each cell narrows in on its eventual fate, differentiating in a particular way, and becomes unable to broaden the range of possible cell fates again.
The only explanation for self-regulation, this ability of remaining cells to ''pitch in'' and compensate for missing cells, is that the surviving cells somehow are able to "sense" a loss of comrades and then change their fates. In other words, the cells must be communicating with one another to know what structure each should form.
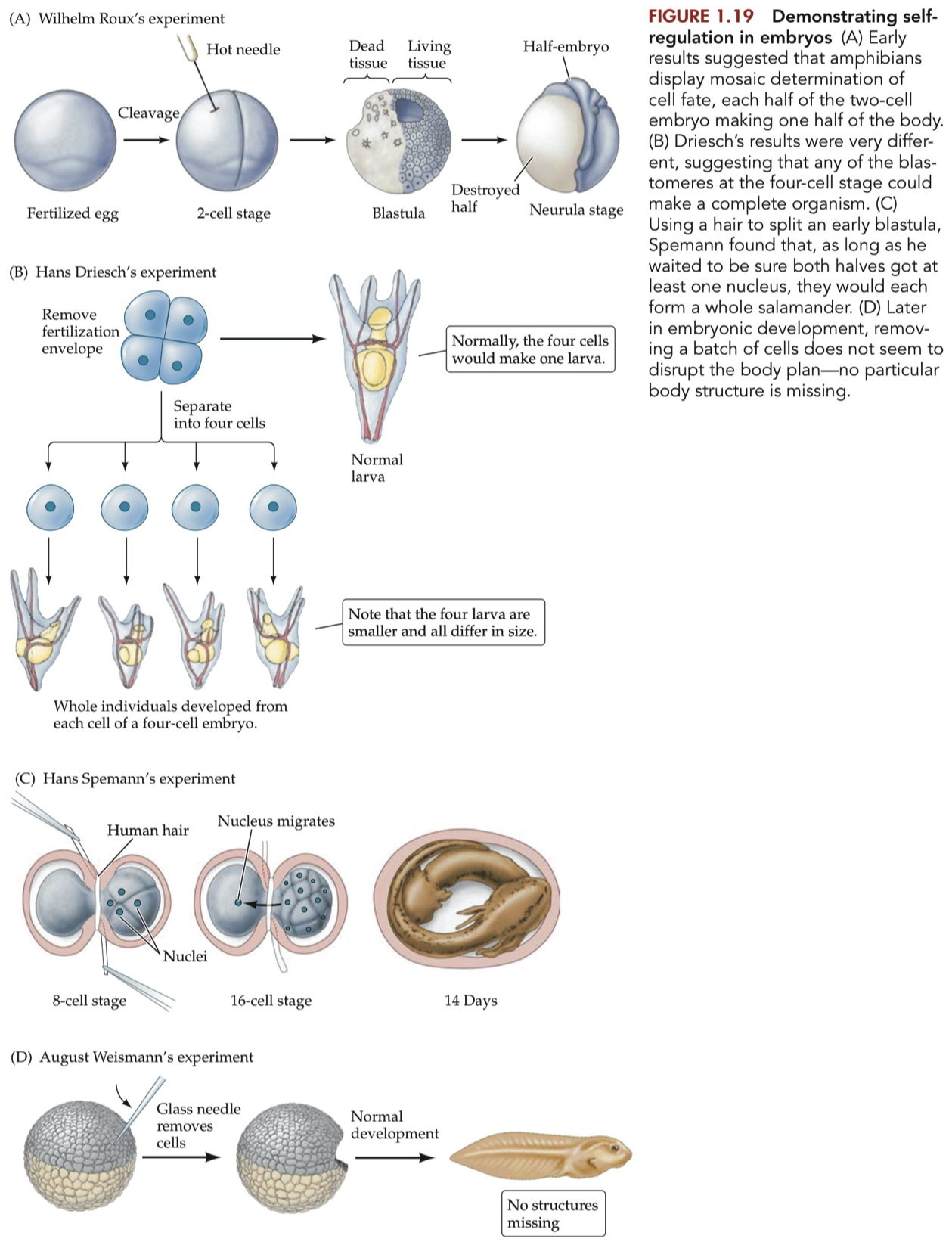
Mosaic versus Cell-Cell Interactions
The nineteenth-century and early twentieth-century results are the opposite of those later reports we described for the worm C.elegans.
We described worm development as mosaic specification of cell fate, each cell going on to follow the fate predestined by its mitotic lineage, no matter what neighboring cells do.
The development seen in these experiments with hydras and amphibians and mammals,
in contrast, can be described as conditional specification of cell fate,
in which cell fate depends on environmental conditions.
Cells take on a fate that is appropriate for their location in the body,
which is determined by the type of cells that surround them.
In other words, cellular differentiation is guided by cell-cell interactions, the communication and influence between developing cells.
Sydney Brenner, who pioneered work on C.elegans, has characterized the difference between the worm strategy of mosaic cell differentiation and the more common, cell-cell interaction strategy for determining cell fate as the "European plan" versus the "American plan"
European Plan :
emphasizes "who is your ancestor?"
each cell uses this information to decide whether to become a neuron or a skin cell , to live or to die.
American Plan :
emphasizes "who is your neighbor?"
each cell uses this information ( what sort of cells are around me ) to decide which cell fate to take on.
a person from any station in life can work to take on any role in society
it's a matter of being in the right place at the right time.
What is self-regulation, and why does it argue against mitotic lineage-directed cell differentiation?
Self-Regulation = the ability of cells to autonomously adjust their fate and function in response to environmental cues
cells adapt to microenvironmental factors without predetermined lineages.
Mitotic Lineage-Directed Cell Differentiation = a deterministic model where cells follow a predefined path of specialization post-mitosis.
Blueprint: Cells have an 'instruction manual' guiding their differentiation.
Restrictions: Once committed, cell fate is hard to alter.
Argument Against Mitotic Lineage-Directed Differentiation :
Plasticity :
Self-regulation: Cells demonstrate flexibility in fate decisions.
Lineage-directed: Presumes limited flexibility.
Context Sensitivity :
Self-regulation: Cells respond to immediate environmental cues.
Lineage-directed: Environment often considered a secondary influence.
Homeostasis :
Self-regulation: Supports dynamic equilibrium in tissues.
Lineage-directed: Can result in imbalance due to predetermined paths.
Efficiency
Self-regulation: Resource-efficient adaptation.
Lineage-directed: Could waste resources by forcing cells into unnecessary roles.
In summary, the inherent adaptability suggested by self-regulation stands in contrast to the deterministic nature of mitotic lineage-directed cell differentiation.
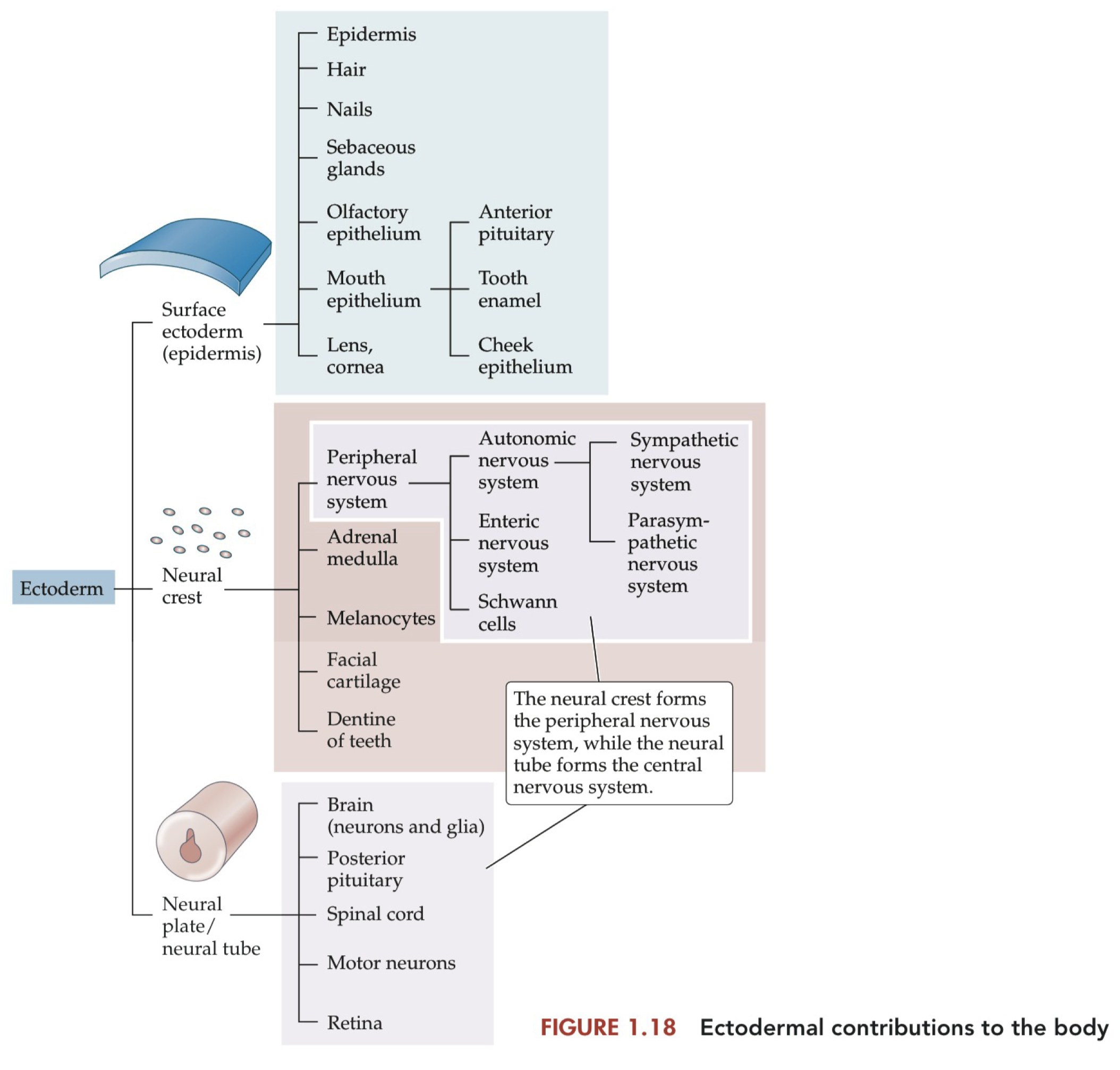
Structures Derived from the Neural Crest and Neural Tube
Ectoderm :
surface = skin , exterior cells
neural crest = peripheral nervous system
melanocytes , adrenal medulla
neural plate / tube = central nervous system
spinal cord , motor neurons


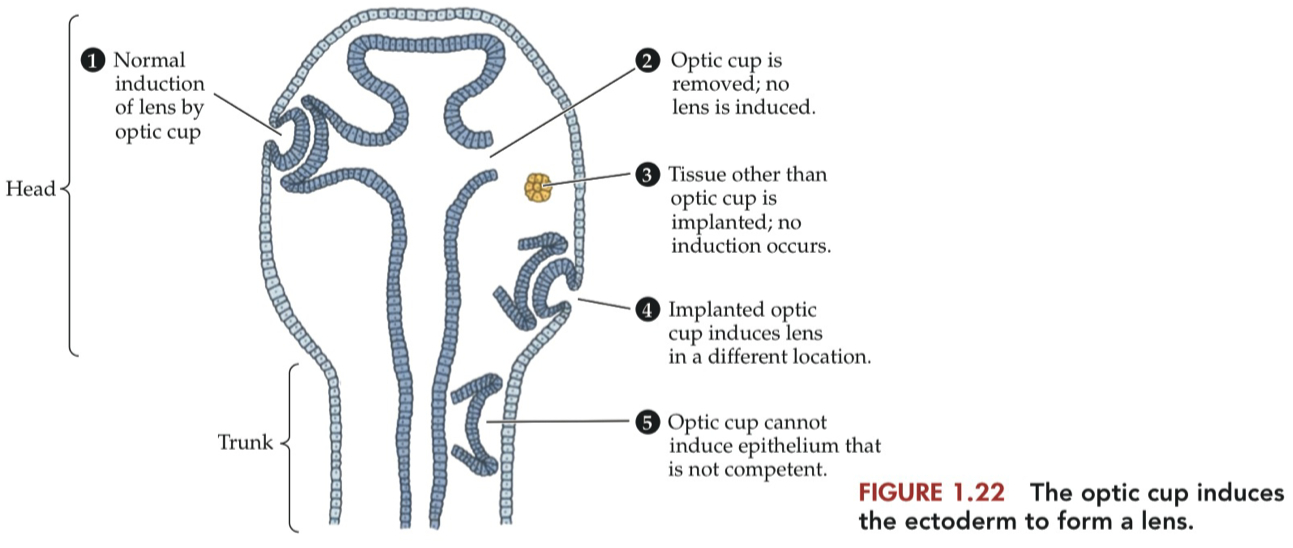
Induction
the process by which one group of cells directs the differentiation of other, nearby cells.
There were two possible explanations for how the epithelium in front of the optic cup differentiated to form the cornea and lens.
One possibility was that this particular stretch of epithelium was always fated to produce cornea and lens, and the optic cup always managed to encounter the epithelium in that particular spot.
An alternative possibility, suggested by the many instances of embryonic self-regulation, was that the optic cup instructed whatever epithelium it encountered to produce the tissue needed to complete the front half of the eye.
the optic cup releases signals to cause the epithelium to change its fate, differentiating into cornea and lens rather than skin.
this process, when one tissue directs the differentiation of some other tissue, is called induction.
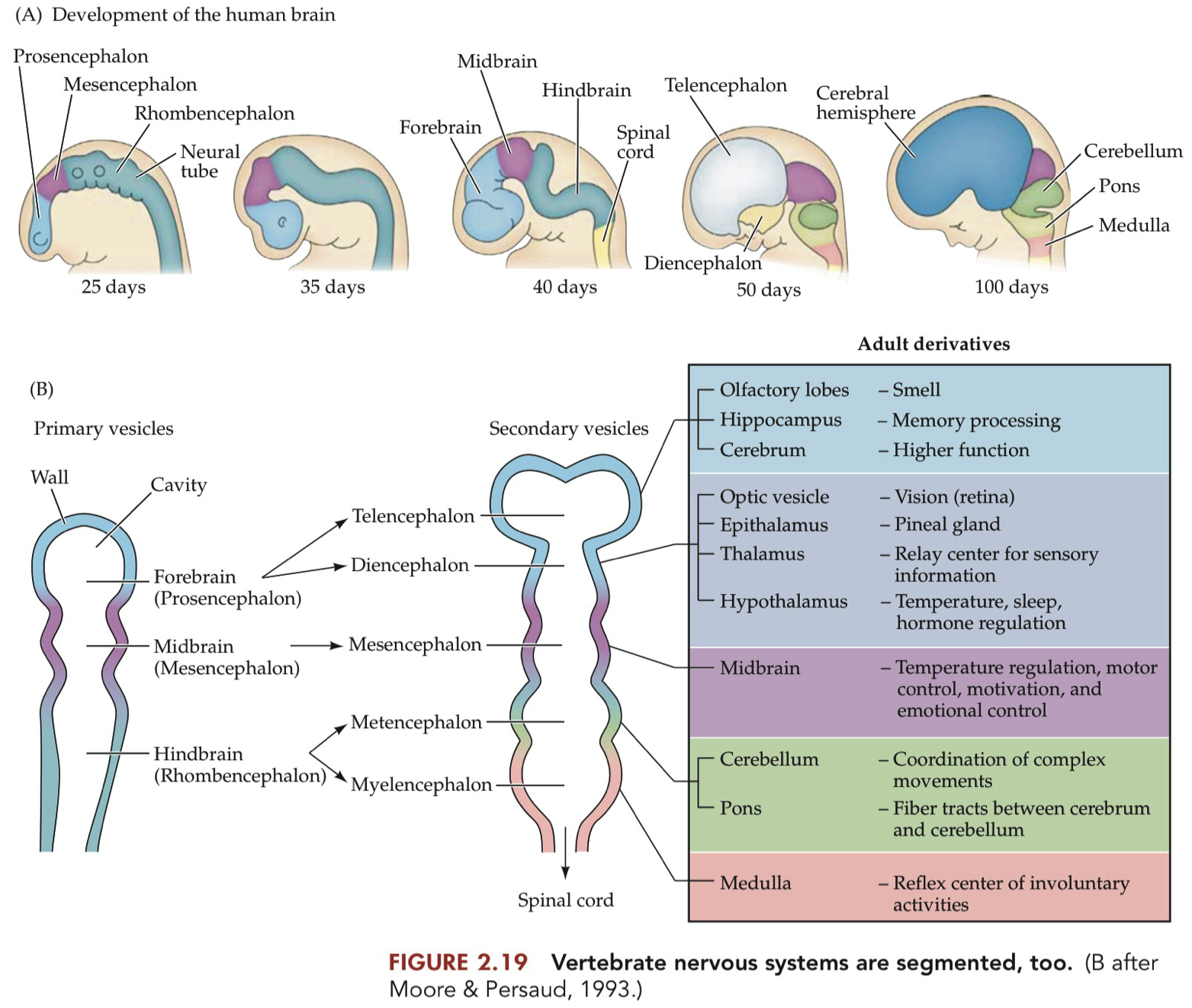
The 3 Primitive Vesicles
neural tube = earliest progenitor of the nervous system
over time , it divides into different sub regions
eventually we get these mature nervous system structures
Forebrain = prosencephalon = the most anterior aspect of the embryonic vertebrate brain.
develop into the telencephalon and diencephalon
Midbrain = mesencephalon = the middle segment of the embryonic vertebrate brain.
develops into the adult midbrain
does not further divide into secondary vesicles
Hindbrain = rhombencephalon = the caudal-most segment of the embryonic vertebrate brain.
develops into the metencephalon ( pons and cerebellum ) and myelencephalon ( medulla )
these divisions of the brain are directed toward their different fates by the action of Hox genes and other homeobox genes during development.
the genes also set up ''inducing zones'' that direct the fates of their neighbors, much the way the dorsal lip of the blastopore induces formation of the neural plate
Transcription Factors vs Homeobox Genes vs Hox Genes
Transcription Factors = proteins that regulate gene expression
Homeotic Selector Genes = Hox Genes = Homeotic Genes = a class of genes in which mutations tend to result in swapping out one body part for another.
example = when mutation of antennapedia results in the formation of legs where antennae normally form
hox genes direct segmentation in the mammalian brain
Homeobox = a nucleotide sequence that produces a DNA-binding domain in many transcription factor proteins.
it is found in Hox genes and many transcription factors
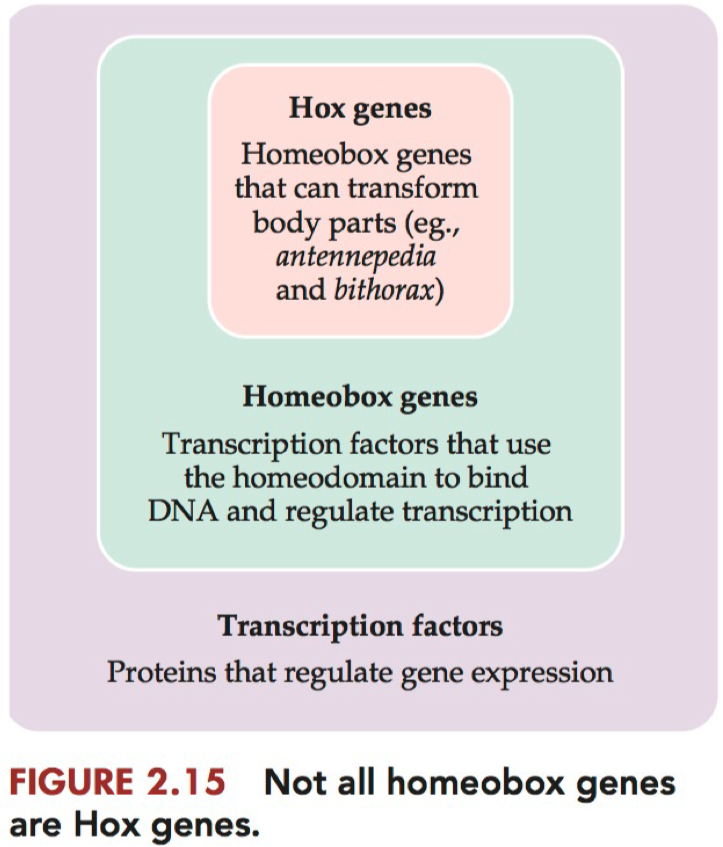
not all homeobox genes are Hox genes
discovered these mutations in forward genetic screens
all on same chromosome
arranged head to tail
in mammals they are called Hox genes
in flys they are called homeotic genes
homeotic genes
subset of transcription factors , that when expressed have the power to transform body parts
bind DNA through Homeo domain ( consensus binding sequence )
there are other genes that have a home
Homeobox vs Hox Genes
Lets just use the fruit fly , Drosophila
It has 8 Hox genes distributed along a single chromosome
side note , they are distributed "colinearly"
such that their order on the chromosome matches the order in which they are expressed along the anterior-posterior axis of the body.
These 8 Hox genes are DNA sequences that are transcribed into RNA , and then translated into special proteins
Each of the 8 proteins has a special area on its 3D structure called the "homeodomain"
The homeodomain areas can be used as transcription factors.
they bind to enhancer or promoter regions on other parts of the chromosome to help express proteins critical for building body parts
legs, wings, and antennae , etc
Ok , we got the 8 special genes out of the way which deal with body part development.
Now , there are other genes ( DNA sequences ) distributed amongst the chromosomes which when transcribed into RNA , and then translated into protein also contain a "homeodomain" in their 3D structure
however these are NOT involved in building body parts
so we just refer to these other genes as "Homeobox genes"
Their translated proteins , which do contain homeodomains , still act as transcription factors , binding to enhancer and promoter regions ,
but instead of regulating body part development , they regulate other special developmental processes
such as segment polarity , eye development , cell differentiation / patterning , and other morphological features.
we just delineate these as a special class of transcription factors only because they do in fact contain that same conserved 3D area on their protein , the homeodomain.
but they don't regulate body part development , so they are NOT hox genes.
Otx2 = a homeobox gene required for development of the vertebrate midbrain and forebrain
Otx2 knockout animals fail to develop any head at all
gene expressed in the most rostral part to the nervous system
not a Hox gene , but it is a homeobox gene
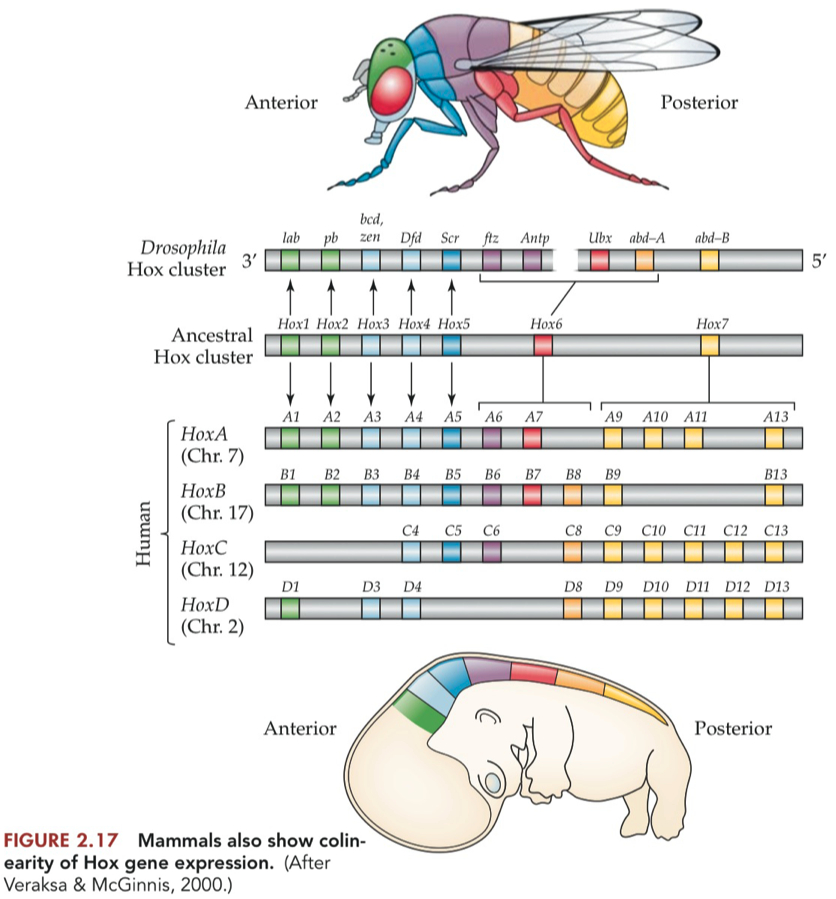
Just as Drosophila Hox genes show colinearity, expressed across the anteriorposterior axis in the same order as the genes appear on the chromosome,
vertebrate Hox genes were found to be expressed in a co linear order, for all 4 chromosomes
This colinear expression was most obvious in the spinal column, where the Hox genes are expressed in, and direct the fate of, cells forming the bony vertebrae protecting the spinal cord
The duplication of the Hox genes in vertebrates seems to have retained some redundancy in the system. Typically, a single mutation in a Hox gene in mammals may have a relatively subtle effect, so it may take deletion of more than one Hox gene to have a noticeable effect
What is meant by the colinearity of Hox gene expression in flies and mammals?
Genes are activated in a spatial order that matches their arrangement on the chromosome.
Genes are activated in a temporal sequence that corresponds to their physical order.
The concept of colinearity is conserved between flies and mammals, despite evolutionary distance.
In summary, the colinearity of Hox gene expression refers to the ordered expression of Hox genes in both spatial and temporal dimensions, consistent with their arrangement on the chromosome. This phenomenon is observed in both flies and mammals, highlighting a conserved regulatory principle in anterior-posterior axis development.
Definitions
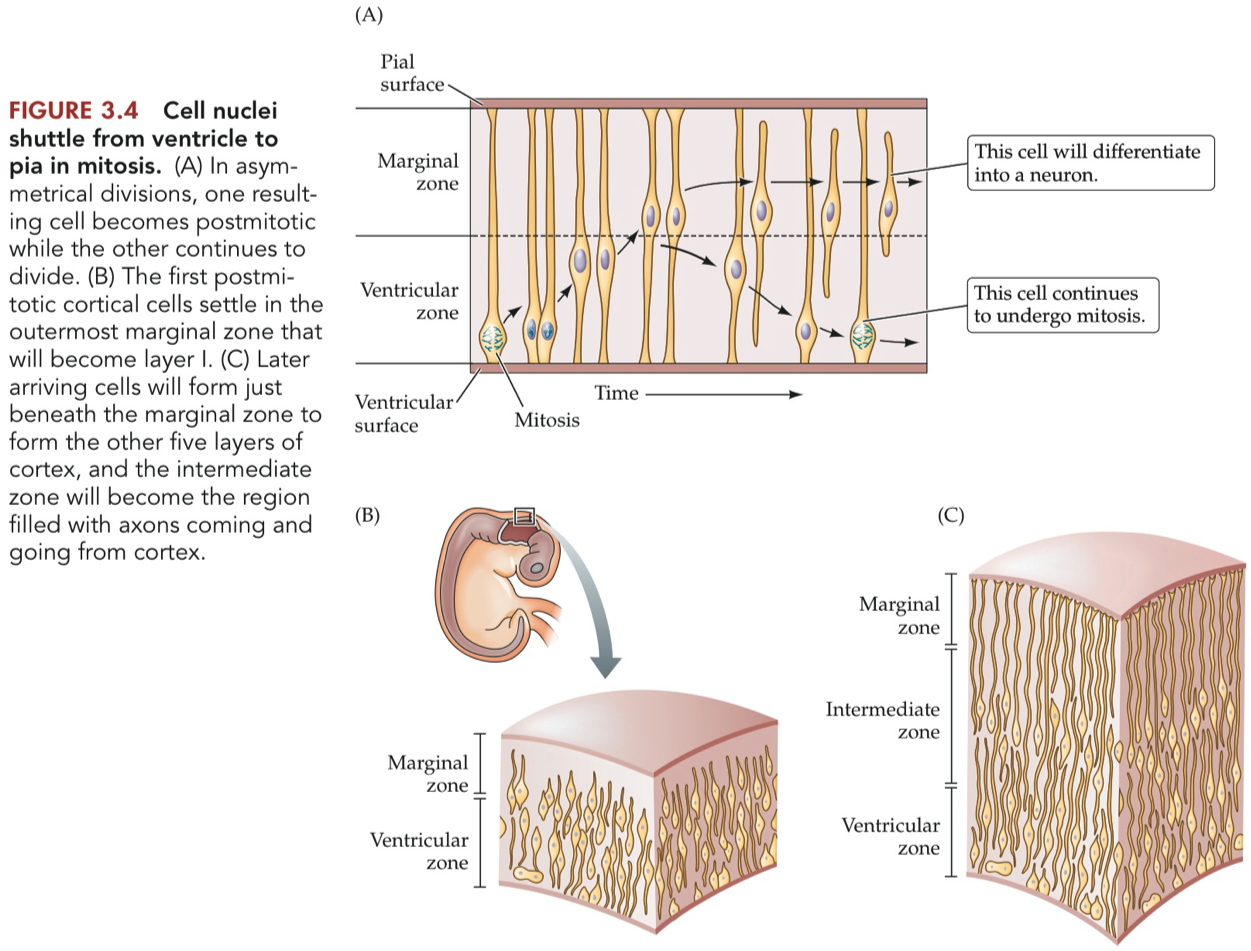
Symmetrical Cell Division :
both cells becoming postmitotic or both dividing
a neuroblast divides to produce two neuroblasts
Asymmetrical Cell Division :
on daughter cell becoming postmitotic while the other divides again
a neuroblasts divides such that :
one daughter cell remains attached to both the ventricular and pial surfaces and prepares to divide again ,
while the other daughter cell has no attachment to either surface and migrates away from the ventricular zone.
this postmitotic daughter cell will populate the width of the neural tube , differentiating into a neuron or glia
Ventricular Zone :
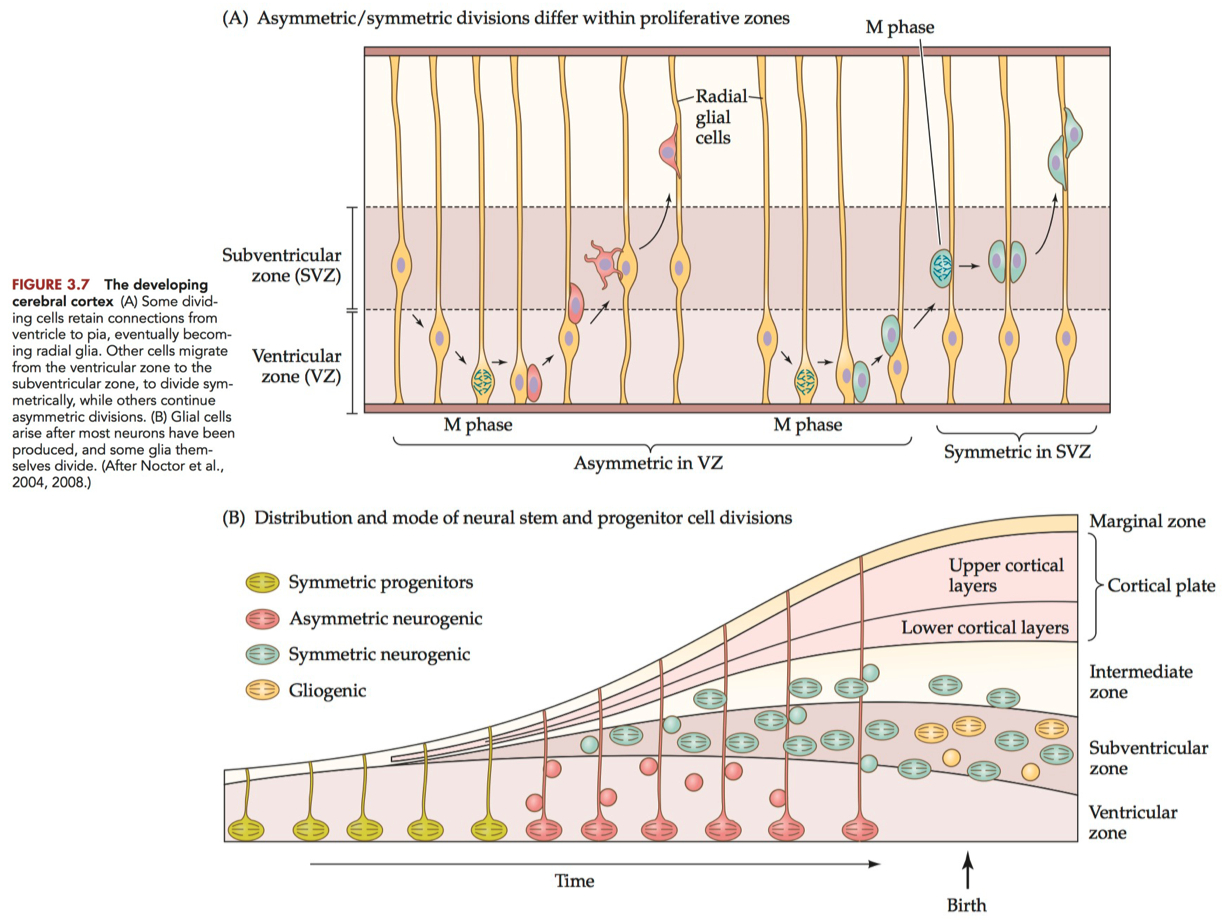
the regions adjacent to the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord, where cell division continues throughout life.
initially favors symmetric divisions for expansion
transitions to more asymmetric divisions as differentiation needs increase.
Subventricular Zone ( SVZ ) :
the region just next to the ventricular zone , where many cells divide
to provide neurons and glia to the developing vertebrate brain ,
and in at least some brain regions , new neurons in adulthood.
during cortical development, primarily experiences symmetric divisions for the rapid production of neurons.
in the adulthood , there's a mix, with both symmetric and asymmetric divisions
Intermediate Zone :
the layer between the ventricular zone and marginal zone of the developing vertebrate brain.
Cortical Plate :
in developing cortex , the expanding layer of post mitotic cells that settle beneath the marginal zone and above the intermediate zone.
It will form layers II-VI.
Marginal Zone :
the outermost layer of the developing vertebrate brain.
by adulthood it will form the molecular layer of the cerebral cortex.
also sometimes called the mantle zone
Molecular Layer :
the outermost layer of the vertebrate cerebral cortex, consisting primarily of dendrites and axons with relatively few cell bodies.
Meninges :
Three protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Pia Matter :
innermost layer of the meninges.
directly adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord.
Pial Surface :
the outer surface of the pia mater that is in contact with the cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space.
Neocortex :
the six-layered outer region of the mammalian cerebral cortex.
Radial Glia :
long, slender glial cells that stretch from the ventricular surface to the pial surface in the vertebrate cerebral cortex.
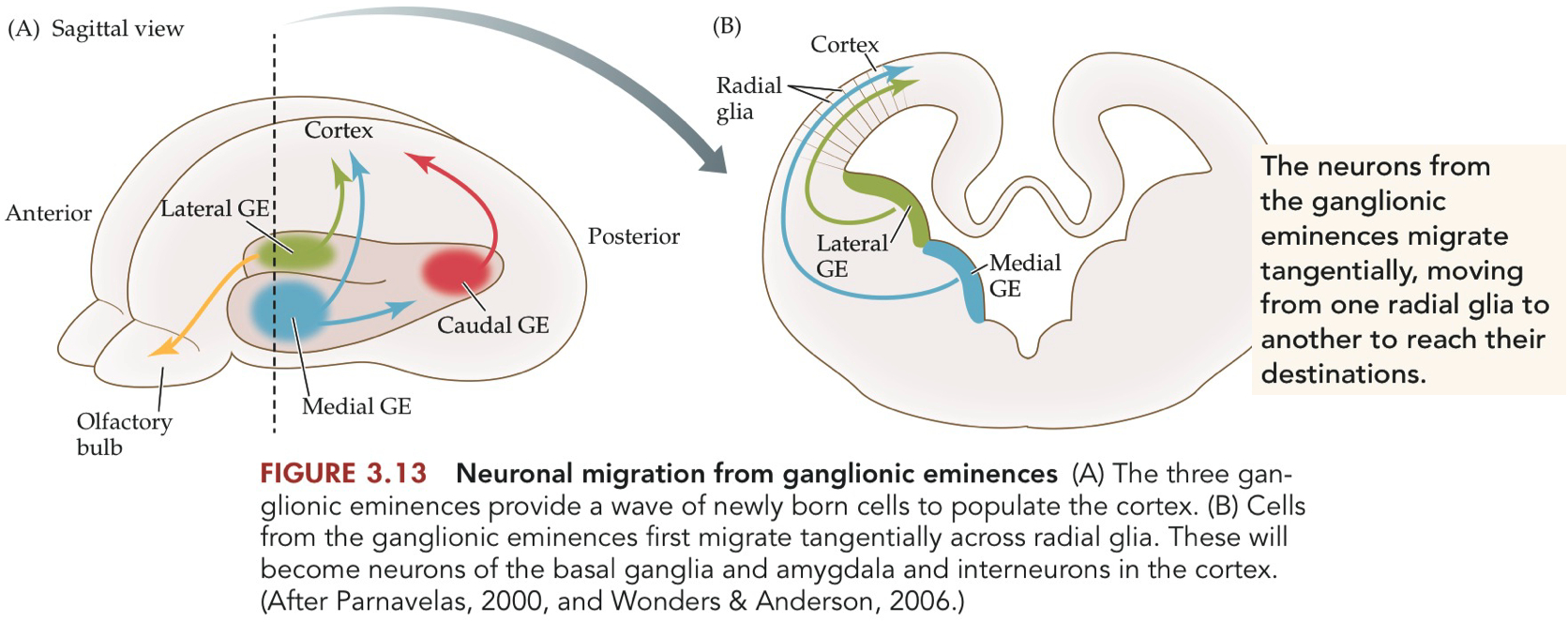
Ganglionic Eminences ( GE ) :
transient structures in the ventral telencephalon.
raised areas in the developing brain.
produce neurons, especially cortical interneurons, which later migrate to other brain regions.
there are three GEs :
medial and lateral GE are seen in rostral telencephalon
a caudal GE in posterior telencephalon
Brain Regions where Neurons are Born
Neurogenesis = the mitosis of cells that will give rise to neurons
process of dividing to produce cells that differentiate into neurons
neurogenesis is NOT neurons dividing to form new neurons
neurons do not normally divide
neurogenesis IS the process of nonneuronal cells in a germinal zone dividing to produce daughter cells that leave the germinal zone and change into neurons.
Subventricular Zone ( SVZ )
Location: Lining of lateral ventricles.
Produces: Interneurons for the olfactory bulb.
Dentate Gyrus of the Hippocampus
Location: Within the hippocampus.
Produces: Granule cells involved in learning and memory.
Subgranular Zone ( SGZ )
Location: Part of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus.
Produces: Similar to Dentate Gyrus; more specific region.
Striatal Matrix
Location: In the striatum.
Produces: Medium spiny neurons.
Cerebellum
Location: Specifically, in the external granule layer during development.
Produces: Granule cells.
Reticular Formation
Location: Brainstem.
Produces: Various types of neurons for autonomic and motor control.
Spinal Cord
Location: Ependymal layer around the central canal.
Produces: Limited neurogenesis, mostly glial cells.
Other Developmental Zones
Location: During development, several transient zones exist.
Produces: Different types of neurons, later migrating to their mature locations.
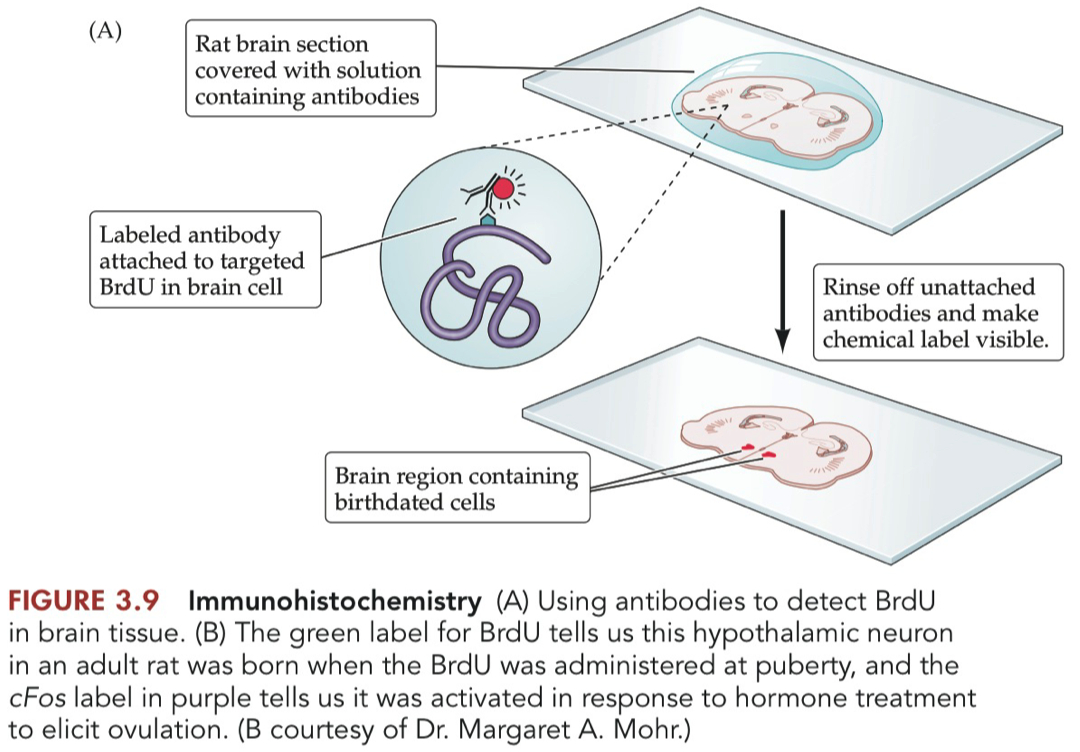
Birthdating Neurons - Radiolabeled Thymidine vs BrdU
Birthdate = the time during development when a given cell underwent its final mitosis before differentiating into a neuron or glial cell
Thymidine = a nucleotide used in the synthesis of DNA.
Because thymidine is not used in RNA , it can serve as a DNA-specific marker.
Radiolabeled thymidine ( [ 3H ]Thymidine ) is incorporated into the DNA during the S-phase of the cell cycle.
Marker = radioactive decay
BrDU = 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine = a synthetic nucleotide that can serve as a substitute for thymidine in the synthesis of DNA but can be readily distinguished from thymidine by the use of antibodies.
BrdU substitutes for thymidine and integrates into newly synthesized DNA.
Marker = Non-radioactive, detected by antibody staining
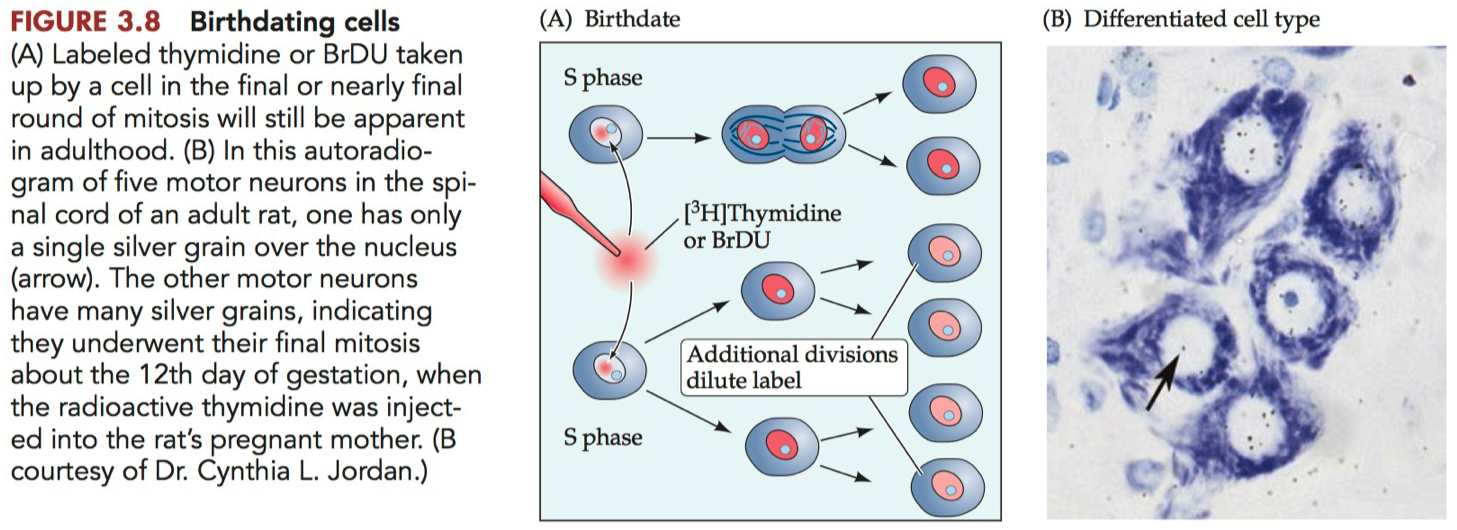
More dots ( more labeling ) = more mature neuron when injected
Indicates that the neuron was in a dividing state when the label was introduced.
If you see more dots later on, it suggests that those neurons have ceased division and matured without further diluting the label.
Less dots ( less labeling ) = less mature neuron when injected
Suggests that the neuron has undergone further divisions after the label was introduced, diluting the label among its progeny.
Indicates less mature neuron at the time of injection as it continued to divide.
Sensitivity
Radiolabeled Thymidine: Lower due to radioactive decay.
BrdU: Higher due to antibody-based detection.
Long-term Studies
Radiolabeled Thymidine: Suitable for long-term due to long half-life.
BrdU: Limited by its chemical stability.
Detection Technique
Radiolabeled Thymidine: Requires specialized autoradiography equipment.
BrdU: Requires immunohistochemical techniques.
In summary, radiolabeled thymidine is older and less safe but allows for long-term studies ,
whereas BrdU offers higher resolution and is safer, albeit less stable for long-term tracking.
Birthdating Cells
any relationship between when a cell is born and where it ends up in the mature cortex
if you want to understand when a cell is born ,
treat the mom with Tridiated thymidine
can tell where that DNA has been incorporated
whenever they are in the S-phase , some will be incorporated
early in development you have a lot of cell division
it keeps dividing , and that radioactivity gets diluted
when you give the radioactive thymidine , you give one shot , and it lasts about 10 hours , and then gets flushed out
transfers to the embryo
barely labeled = post mitotic many cell division after you gave the injection
developed later
heavily labeled
developed earlier
Now we use BRDU
use an antibody to detect it
Radial Glial Cells - Radial vs Tangential Neuron Migration
Role of Glial Cells :
Radial Migration :
Provide structural pathways for neurons to migrate along
Originate from ventricular zone
Direct scaffolding and guidance
Tangential Migration :
radial glia are less involved
more indirect, less structural support
Cell Types
Radial Glial Cells :
excitatory neurons
originate from ventricular zone
Tangential Migration :
inhibitory neurons
originate from ganglionic eminences
Contributions to Cortical Circuits :
Radial Glial Cells :
main building blocks of cortical layers
excitatory circuits
Tangential Migration :
provide inhibitory components
regulatory elements in circuitry
Adult Neurogenesis
adult neurons are continually generated in the olfactory system and the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation
very few new neurons are added to the adult neocortex
Adult-born neurons originate in three germinal zones
olfactory neuroepithelium
subventricular zone
subgranular zone
Box 3.1 = The Controversy of Neurogenesis in Adulthood
Initial Skepticism
Pasko Rakic: Reported in 1985 that neurogenesis in monkeys, including in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb, ceased by puberty.
Reaffirmation of Adult Neurogenesis
Other Researchers: Rediscovered and expanded upon findings of adult neurogenesis in rats, mice, and even primates.
Human Evidence: Cancer patients treated with BrdU showed evidence of new neurons in the dentate gyrus.
Rakic's Re-examination
Methodology: Used BrdU instead of thymidine for better sensitivity.
Revised Claims: Acknowledged the occurrence of adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb in monkeys.
Neocortex Neurogenesis
New Findings: Reports surfaced about neurogenesis in the neocortex in monkeys.
Rakic's Second Rebuttal: Maintained that no neurogenesis occurs in the monkey neocortex, despite earlier findings in rats.
Continued Discoveries
Other Regions: Additional reports indicate adult neurogenesis in the neocortex, amygdala, and striatum.
Problem with Negative Findings
Absence of Proof: Failing to detect something doesn't mean it doesn't exist.
In essence, the field has evolved from skepticism to a broader acceptance of adult neurogenesis, not just in rodents but also in primates, including humans.
However, the controversy highlights the challenges in interpreting negative findings and the importance of methodology in scientific investigations.
Research Papers
Kempermann
hypothesis = they want to see if they enrich the environment does it increase the number of new neurons born ?
BrDU = chemical analogue of uridine , used to visualize DNA
strong in cells that divided the last time they divided
if its in stem cells which are constantly dividing , the signal will be diluted
more labled cells in enriched case than the control
21 day old mice , randomly distributed into 2 groups
21 days is the day in which they can wheen
then they put them in a cage with toys or just empty cage
let them sit for 40 days
during the last 12 days , they give BrDU injection
no difference in the rate at which cells are born
so the enriched environment just promotes cell survival
Figure 2 , Panel A = take home message
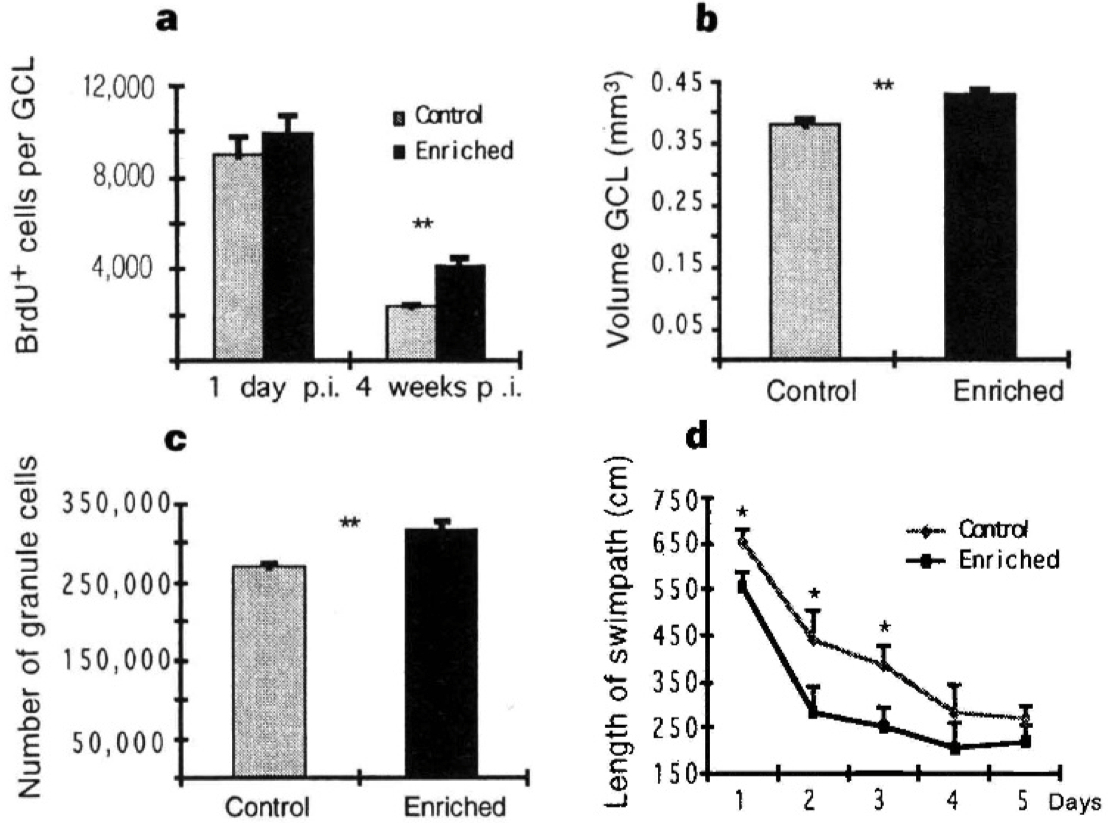
Figure 2 a-d, Four parameters in which enriched mice differ from their control littermates. a, Number of BrdU-positive cells per hippocampal granule cell layer (GCL). The density of BrdU-positive cells was determined stereologically (cells per mm3 ) and multiplied by the absolute volume ofthe dentate gyrus. Significance level is P < 0.005 (t-test). b, Volume of the dentate gyrus. At 4 weeks p.i., the volume of the hippocampal dentate gyrus was significantly (P < 0.005, t-test) increased in the enriched group. c, Absolute granule cell number in the dentate gyrus. At 4weeks p.i., enriched mice had significantly more granule cell neurons (P < 0.01 ). The underlying neuronal density was 6.47 ± 0.25 per sample volume in controls and 6.56 ± 0.14 in enriched mice and thus not influenced by environmental enrichment. All data are given as mean ± standard error. N was 5 per group at 1 day p.i., and 7 per group at 4 weeks p.i. d, In the spatial learning task (Morris water maze), enriched mice (lower curve) have a significantly shorter swim path (P < 0.05, t-test) on days 1 to 3 of testing. On day 1 there was no significant difference between the groups in the first two trials, indicating equal baselines. The time to reach the platform (latency) paralleled this curve and reached the significance level on day 2. At all time points, no difference in the average swim speed could be found, and on a transfer test without a platform on day 6 no differences between groups were detected (data not shown).
Anderson
interneuron migration
DiI = marker , label , integrates into cell membranes
sticks with the cell wherever it migrates
marks the cell , and you are able to watch it
LGE = lateral ganglionic eminence
another place where a lot of neurons are born
its where they migrate from to the cortex
calbindin over laps with
couple different proofs these are neurons and not glial cells
transected side
not a lot of neurons get to migrate from LGE
pathway = tangential migration
if they cut the bridge the cells are not able to migrate
they go around the edges
how these cells get to where they are supposed to go
lot of cells in LGE that express Dlx-1
if you leave the brain intact , you see postive cells in the cortex
GABA cells start from Dlx-1
Dlx-1 positive cells are also GABA positive cells
Figure 3 :
In the mutant , they show you two different
what do we see in terms of migration patterns between control and knock-out ?
in wild-type , the labeled cell are able to migrate out
in the mutant , they don't migrate
they are missing Dlx-1 and 2
so they can't migrate
Figure 4 :
does it influence migration of pyramidal cells ?
no , they are present in layer 5
not affected by Dlx-1 and 2 knockout
you are just missing the interneurons
migration of interneurons goes through lateral pathway
pyramidal cells = excitatory neurons
this paper confirms interneurons migrate through a different strategy than pyramidal neurons do
Dlx-1 and 2 = homeobox transcription factor
NOT a hox gene
controls genes that are critical for migration
Required for migration of interneurons
tangential migration = string to string
The 6 Layers of the Neocortex
Cortex has 6 layers
if you are in the brain stem , it doesn’t have 6 layers
no layered structures
Thalamus , basal ganglia , etc don’t have layers
Cerebral Cortex was developed to have vertical groups of cells that are interconnected with each other
they each have different jobs
You can identify the different layers based on cell types
3 different stains
golgi stain = entire morphology of individual neurons, including the soma, dendrites, and, often, the full extent of the axon.
nissle stain = cell body
Weigert stain = meyelin sheaths
Big cells = pyramidal cells ( triangular shape cell body ) , really long dendrites that extend up into other layers
Processing that happens , happens vertically
information usually comes into layer 4
and then its processed either vertically up , or vertically down
There are places in the brain of rodents that are called barrel cortex
Neuron Types in Cerebral Cortex
Projection Neurons vs Local Interneurons
Appearance of Cortical Layers can Differ Between Regions
Size and thickness can vary between layers
some parts of the brain have a very thick layer 4 , some have a very thin layer 4
Subtle Differences in Cytoarchitecture of cortex can be useful in delineating cortical regions
can identify brain areas based on thickness patterns
Layers in Cerebral Cortex have their origins in the zone so early neural tube
ventricular zone = where cells divide
sub-ventricular ( deep with respect to the ventricle ) = still cell division
once they stop dividing , they migrate along radial glial cells into the various parts of the cortex
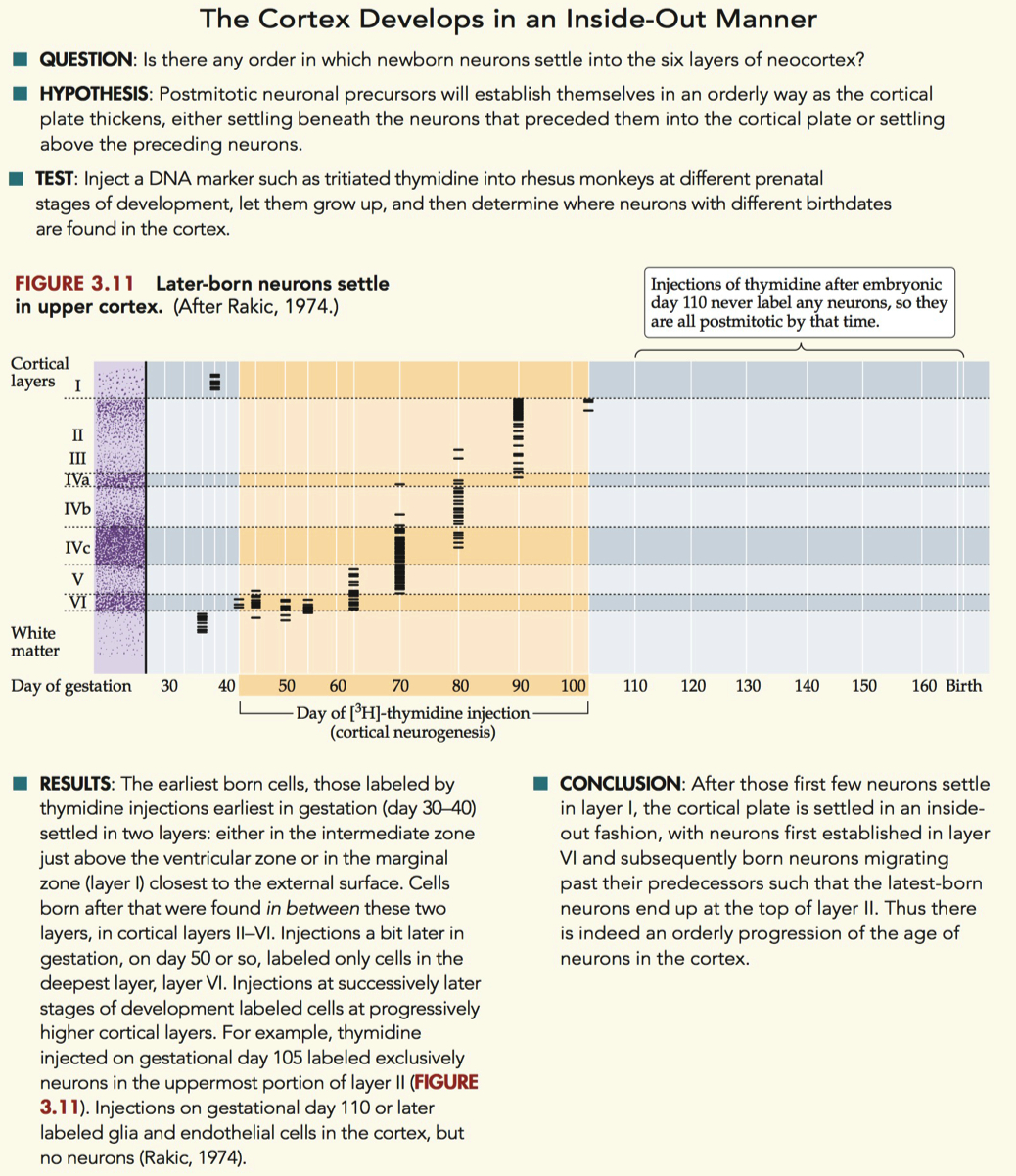
Figure 3.11
first create neurons on “top” and “bottom”
everything else fills “inside out” pattern
Neurons in Rhesus Monkey Visual Cortex = Paper
did a tridiated thymidine experiment
they did this with multiple animals
and injected them on different days of embryonic development
whatever cells were born at E45 , will be labeled permanently in the monkey
each horizontal line = indicates abundance of radioactive cells
deep layers are born first
over time the upper layers are born later
cells that are arrange vertically are usually processing the same information together as a unit
organization and connection
cells are born first
every new cell that passes by has to interact with the first born cell , and they know they will / can interact later
new neurons have to migrate past old neurons to get to their resting place
dye is only taken up by dividing cells
post mitotic cells don’t take up the label