BMB 7500 - Exam 3
What is the pH of the following buffer mixture :
The process of folding a protein
has a of and a of
What is the
At what temperature would the unfolding of this protein become favorable ?
For the peptide :
N-terminus = Gly = 9.6
C-terminus = Lys = 2.2
Side-Chains :
- 6.0 = amine
- 10.0 = amine
2.2 , 6.0 , 9.6 , 10.0
@ pH = 9.7 :
- 9.7 < 2.2 ? = False = Deprotonated Carboxylic Acid = -1
- 9.7 < 6.0 ? = False = Deprotonated Amine = 0
- 9.7 < 9.6 ? = False = Deprotonated Amine = 0
- 9.7 < 10.0 ? = True = Protonated Amine = +1
We know its neutral at pH 9.7
What is the overall charge on this peptide :
@ pH = 4 :
- 4 < 2.2 = False = Deprotonated Carboxylic Acid = -1
- 4 < 6.0 = True = Protonated Amine = +1
- 4 < 9.6 = True = Protonated Amine = +1
- 4 < 10.0 = True = Protonated Amine = +1
- Net-Charge =
@ pH = 8 :
- 8 < 2.2 = False = Deprotonated Carboxylic Acid = -1
- 8 < 6.0 = False = Deprotonated Amine = 0
- 8 < 9.6 = True = Protonated Amine = +1
- 8 < 10.0 = True = Protonated Amine = +1
- Net-Charge =
@ pH = 10 :
- 10 < 2.2 = False = Deprotonated Carboxylic Acid = -1
- 10 < 6.0 = False = Deprotonated Amine = 0
- 10 < 9.6 = False = Deprotonated Amine = 0
- 10 = 10.0 = Half-Deprotonated Amine and Half-Protonated Amine =
- Net-Charge =
In three to four sentences explain the importance of the hydrophobic effect on protein folding and structure
The hydrophobic effect kick starts protein folding
There are enumerable conformations a protein could fold into
Immediately , the proteins non-polar side chains seek to minimize their interactions with water.
- So they fold inward in response to their polar cytosolic environment
In three to four sentences explain how oxygen affects ( at the molecular level ) the process of hemoglobin transitioning from the
Hemoglobin and oxygen binding has "cooperativity"
After the first oxygen binds to the T-state , it opens up the pore of hemoglobin , causing it to transition into the R-state
- Because the first oxygen has already opened up the pore slightly , the second oxygen has an easier time accessing its binding site.
- The second oxygen binds and further opens up the pore for the 3rd oxygen.
- This continues , and the 4th oxygen has the easiest time binding because there is no steric hinderance
Each time oxygen binds , it further promotes stabilization of the R-state , and makes it increasingly likely that more oxygen will bind
What is the sequence of the polypeptide ?
Sequencing of an unknown polypeptide has yielded the following information :
- Vl , Ile , Trp , and Phe are in a 2:1:1:1 kolar ratio
- Treatment with 1-flouro-2,4-dinitrobenzene ( FDNB ) yielded complete hydrolysis and 2,4-dinitrophenyl tryptophan , and no free tryptophan
- Digestion with chymotrypsin yielded free tryptophan , a dipeptide containing only Val , and a dipeptide of Ile and Phe
- Try || IIe-Phe || Val-Val
- Sequence =
A child in the midst of a hissy fit takes several rapid deep breaths ( hyperventilates ) right before holding his breath to the point of passing out to prove his point. Did the hyperventilating increase
- They child expelled a lot of
- This caused a shift in the oxygen saturation / heme binding curve
- Basic environments stabilizes the
- NO , it causes less oxygen to be released to tissues
- They child expelled a lot of
Assume you need to separate the
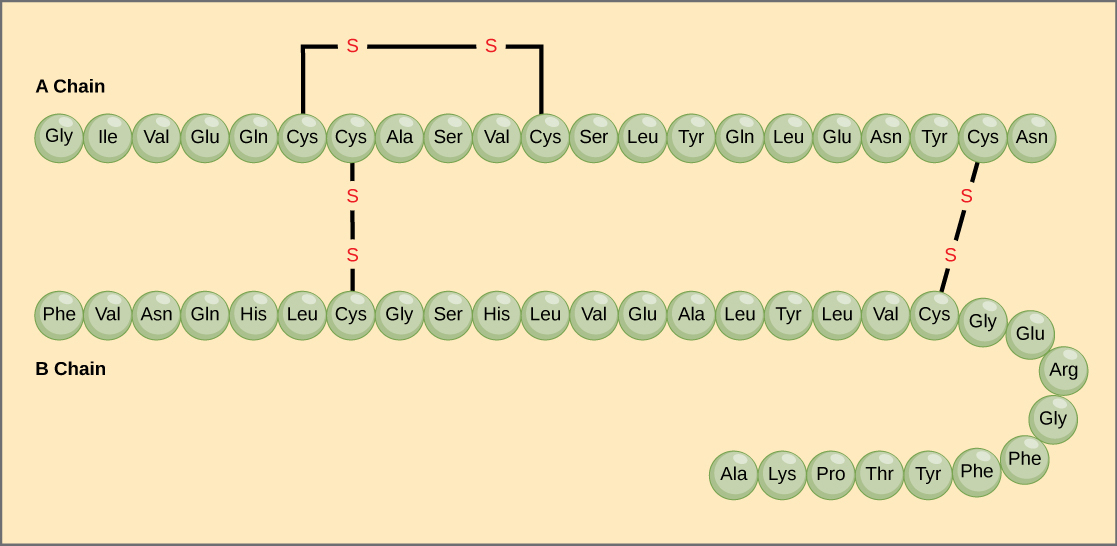
- You could use affiinity chromatography if you could make a receptor that bound specifically for either the alpha or beta chain only
- You can't use polarity , they both seem to have an equal distribution of polar and non-polar amino acids
- Bot most likely they will have different net charges , so you could separate them based on Ion-Exclusion Chromatography
A protein bind a ligand with association rate of