Exam 4 - 2021
1.A. What is the "order" of the reaction :
1.B. What are enzyme allosteric effectors and how do they affect enzyme activity?
Small chemicals that bind to multisubunit enzymes
inducing cooperative conformational changes
- that then increase or decrease the rate of enzymatic catalysis
1.C. What is the likely optimum pH for an enzyme that has His acting as a general acid / base catalyst in the active site?
- centered around the
1.D. What are enzyme cofactors, and what functions do they provide that are essential for enzyme activity?
- non-protein substance , typically vitamins and metal ions
- they help activate the enzyme by changing shape , balancing negative charge , acting as a ligand binding sink.
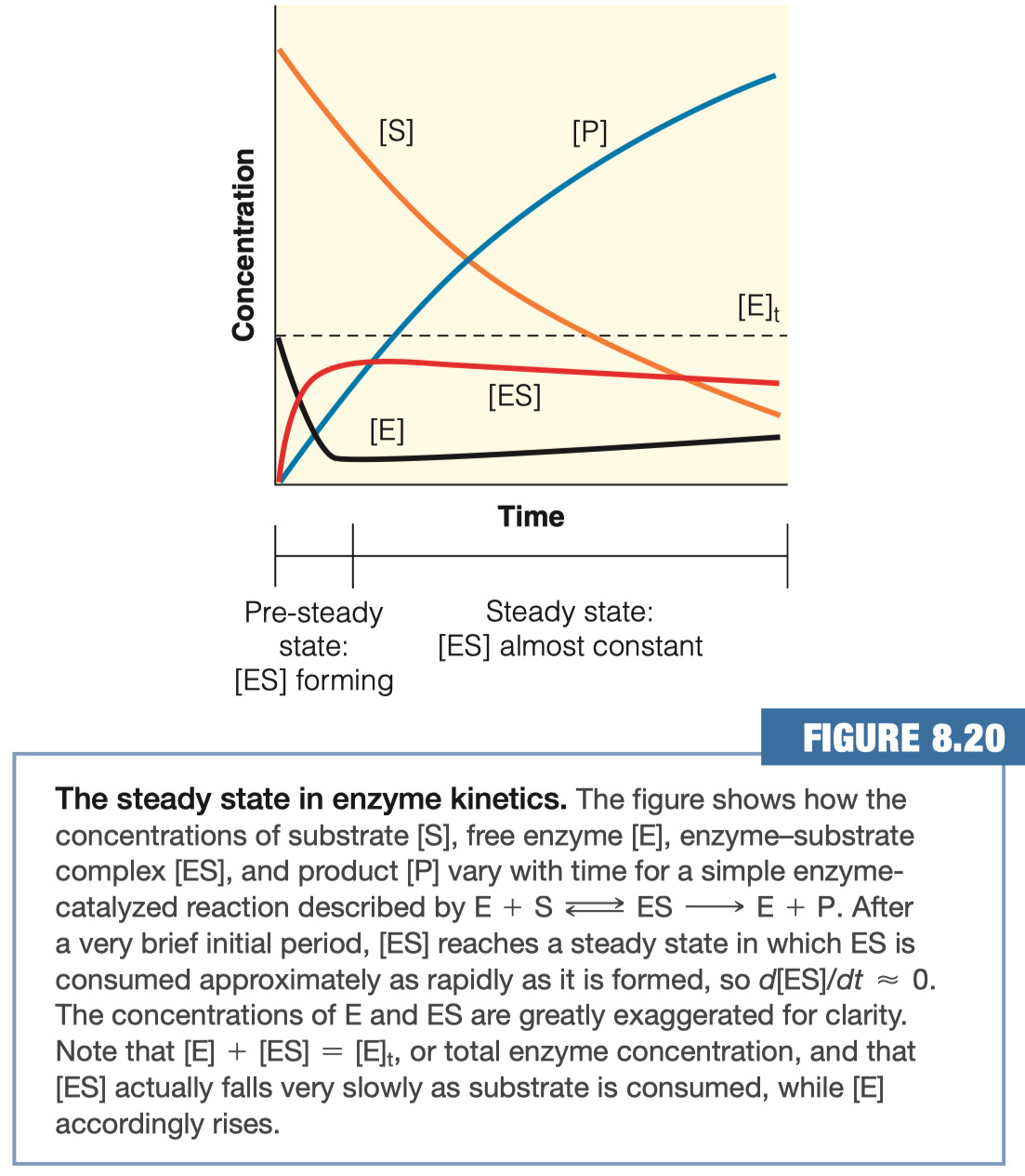
1.E. Sketch a graph that clearly shows the steady state approximation, which is the basis for Michaelis-Menten calculations (make sure to label all the lines/ axes).
A competitive inhibitor yielded the following equations from a Lineweaver-Burk plot:
- No Inhibitor :
- 3 mM Inhibitor :
- 5 mM Inhibitor :
- No Inhibitor :
What is the apparent
Y-Intercept =
X-Intercept =
No Inhibitor one lets us find
Set the equation to zero and solve for x-intercept =
Find
Now we can solve for
Now we can solve for
The specificity pocket of trypsin is show in the figure below. If the trypsin enzyme were mutated to have a Lys at position 189 (instead of serine) how would you predict the Km values for the following substrate peptides would change?
- Substrate Peptide A – has Arg at position N-1 ( position next to scissile bond , N )
- Substrate Peptide B – has a Glu at position N-1 ( position next to scissile bond , N )
- Please note you do not need to determine the actual
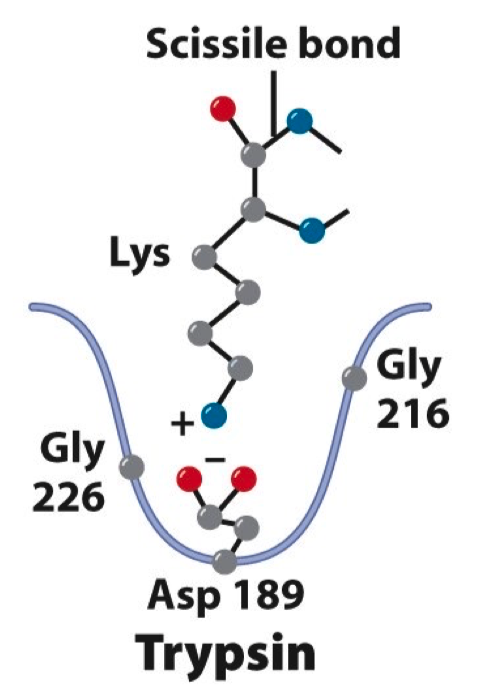
normally it has a negative charge
if we replace it with a positive charge , the
Determine the velocity of the reaction :
The kinetic parameters for two substrates that are acted on by an enzyme are given below. Which is a better substrate for this enzyme ( as measured by efficiency of the enzyme ) ? Justify your answer.
Substrate A B Substrate
Substrate
If we only care about efficiency , then Substrate
When experiments were conducted to study a newly discovered enzyme, the following observations were made: the enzyme has a very broad pH range in which it is at its optimum catalytic activity, ranging from pH = 6.5 to 8.5. However a competitive inhibitor is effective only at pH 6.5 , not 8.5. Explain this observation.
enzyme is active in 6.5 to 8.5
competitive inhibitor can only bind at 6.5
at pH of 8.5 , the competitive inhibitor is deprotonating , and then no longer able to interact with the enzyme
- unlikely enzyme would be deprotonating