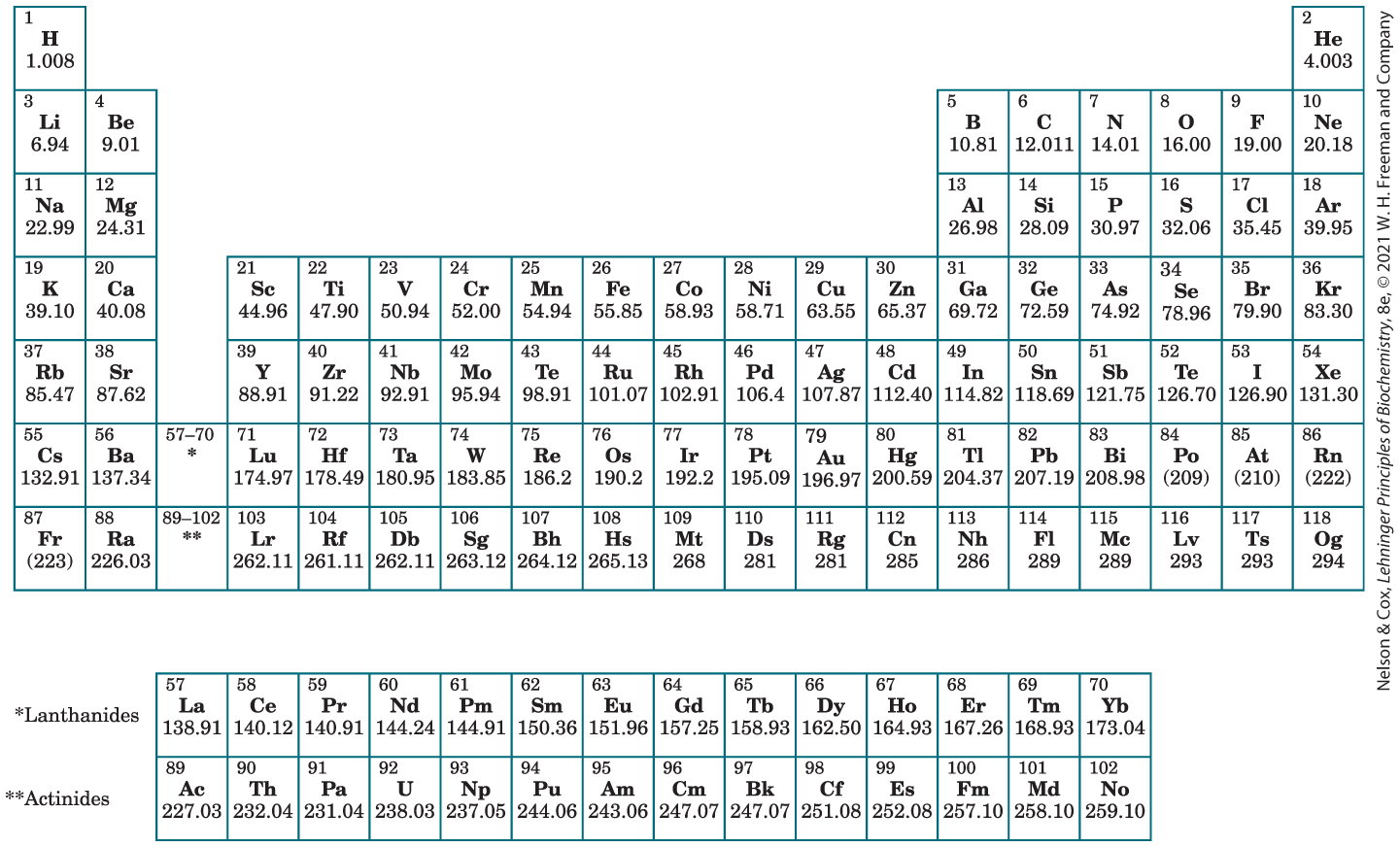
The periodic table has 19 columns and seven main rows. Two additional rows below show the lanthanides and actinides. Each cell includes the atomic number, abbreviation for the element, and atomic mass. The data in the table is as follows by row. Row 1: column 1 H, atomic number 1, atomic mass 1.008; columns 2 through 18 blank; column 19 H e, atomic number 2, atomic mass 4.003. Row 2: column 1 L i, atomic number 3, atomic mass 6.94; column 2 B e, atomic number 4, atomic mass 9.01; columns 3 through 13 blank; column 14 B, atomic number 5, atomic mass 10.81; column 15 C, atomic number 6, atomic mass 12.011; column 16 N, atomic number 7, atomic mass 14.01; column 17 O, atomic number 8, atomic mass 16.00; column 18 F, atomic number 9, atomic mass 19; column 19 N e, atomic number 10, atomic mass 20.18. Row 3: column 1 N a, atomic number 11, atomic mass 22.99; column 2 M g, atomic number 12, atomic mass 24.31; columns 3 through 13 blank; column 14 A l, atomic number 13, atomic mass 26.98; column 15 S i, atomic number 14, atomic mass 28.09; column 16 P, atomic number 15, atomic mass 30.97; column 17 S, atomic number 16, atomic mass 32.06; column 18 C l, atomic number 17, atomic mass 35.45; column 19 A r, atomic number 18, atomic mass 39.95. Row 4: column 1 K, atomic number 19, atomic mass 39.10; column 2 C a, atomic number 20, atomic mass 40.08; column 3 blank; column 4 S c, atomic number 21, atomic mass 44.96; column 5 T i, atomic number 22, atomic mass 47.90; column 6 V, atomic number 23, atomic mass 50.94; column 7 C r, atomic number 24, atomic mass 52; column 8 M n, atomic number 25, atomic mass 54.94; column 9 F e, atomic number 26, atomic mass 55.85; column 10 C o, atomic number 27, atomic mass 58.93; column 11 N i, atomic number 28, atomic mass 58.71; column 12 C u, atomic number 29, atomic mass 63.55; column 13 Z n, atomic number 30, atomic mass 31; column 14 G a, atomic number 31, atomic mass 69.72; column 15 G e, atomic number 32, atomic mass 72.59; column 16 A s, atomic number 33, atomic mass 74.92; column 17 S e, atomic number 34, atomic mass 78.96; column 18 B r, atomic number 35, atomic mass 79.90; column 19 K r, atomic number 36, atomic mass 83.30. Row 5: column 1 R b, atomic number 37, atomic mass 85.47; column 2 S r, atomic number 38, atomic mass 87.62; column 3 blank; column 4 Y, atomic number 39, atomic mass 88.91; column 5 Z r, atomic number 40, atomic mass 91.22; column 6 N b, atomic number 41, atomic mass 92.91; column 7 M o, atomic number 42, atomic mass 95.94; column 8 T e, atomic number 43, atomic mass 98.91; column 9 R u, atomic number 44, atomic mass 101.07; column 10 R h, atomic number 45, atomic mass 102.91; column 11 P d, atomic number 46, atomic mass 106.4; column 12 A g, atomic number 47, atomic mass 107.87; column 13 C d, atomic number 48, atomic mass 112.40; column 14 I n, atomic number 49, atomic mass 114.82; column 15 S n, atomic number 50, atomic mass 118.69; column 16 S b, atomic number 51, atomic mass 121.70; column 17 T e, atomic number 52, atomic mass 126.70; column 18 I, atomic number 53, atomic mass 126.90; column 19 X e, atomic number 54, atomic mass 131.30. Row 6: column 1 C s, atomic number 55, atomic mass 132.91; column 2 B a, atomic number 56, atomic mass 137.34; column 3 57 to 70 *; column 4 L u, atomic number 71, atomic mass 174.97; column 5 H f, atomic number 72, atomic mass 174.97; column 6 T a, atomic number 73, atomic mass 180.95; column 7 W, atomic number 74, atomic mass 183.85; column 8 R e, atomic number 75, atomic mass 186.20; column 9 O s, atomic number 76, atomic mass 190.2; column 10 I r, atomic number 77, atomic mass 192.2; column 11 P t, atomic number 78, atomic mass 195.09; column 12 A u, atomic number 79, atomic mass 196.97; column 13 H g, atomic number 80, atomic mass 196.97; column 14 T l, atomic number 81, atomic mass 204.37; column 15 P b, atomic number 82, atomic mass 207.19; column 16 B i, atomic number 83, atomic mass 208.98; column 17 P o, atomic number 84, atomic mass (209); column 18 A t, atomic number 85, atomic mass (210); column 19 R n, atomic number 86, atomic mass (222). Row 7: column 1 F r, atomic number 87, atomic mass (223); column 2 R a, atomic number 88, atomic mass 226.03; column 3 89 to 102 **; column 5 L r, atomic number 103, atomic mass 262.11; column 5 R f, atomic number 104, atomic mass 261.11; column 6 D b, atomic number 105, atomic mass 262.11; column 7 S g, atomic number 106, atomic mass 263.12; column 8 B h, atomic number 107, atomic mass 264.12; column 9 H s, atomic number 108, atomic mass 265.13; column 10 M t, atomic number 109, atomic mass 268; column 11 D s, atomic number 110, atomic mass 281; column 12 R g, atomic number 111, atomic mass 281; column 13 C n, atomic number 112, atomic mass 285; column 14 N h, atomic number 113, atomic mass 286; column 15 F l, atomic number 114, atomic mass 289; column 16 M c, atomic number 115, atomic mass 289; column 17 L v, atomic number 116, atomic mass 293; column 18 T s, atomic number 117, atomic mass 293; column 19 O g, atomic number 118, atomic mass 294. * Lanthanides: L a, atomic number 57, atomic mass 138.91; C e, atomic number 58, atomic mass 140.12; P r, atomic number 59, atomic mass 140.91; N d, atomic number 60, atomic mass 144.24; P m, atomic number 61, atomic mass 144.24; S m, atomic number 62, atomic mass 150.36; E u, atomic number 63, atomic mass 151.96; G d, atomic number 64, atomic mass 157.25; T b, atomic number 65, atomic mass 158.93; D y, atomic number 66, atomic mass 162.50; H o, atomic number 67, atomic mass 164.93; E r, atomic number 68, atomic mass 167.26; T m, atomic number 69, atomic mass 168.93; Y b, atomic number 70, atomic mass 173.04. ** Actinides: A c, atomic number 89, atomic mass 227.03; T h, atomic number 90, atomic mass 232.04; P a, atomic number 91, atomic mass 231.04; U, atomic number 92, atomic mass 238.03; N p, atomic number 93, atomic mass 237.05; P u, atomic number 94, atomic mass 244.06; A m, atomic number 95, atomic mass 243.06; C m, atomic number 96, atomic mass 247.07; B k, atomic number 97, atomic mass 247.07; C f, atomic number 98, atomic mass 251.08; E s, atomic number 99, atomic mass 252.10; F m, atomic number 100, atomic mass 257.10; M d, atomic number 101, atomic mass 258.10; N o, atomic number 102, atomic mass 259.10.