Lecture 11
Readings
http://umdberg.pbworks.com/w/page/63757839/The%20electric%20potential%20%282013%29
Electric Potential
- For a single charge,

Notice, there are no vectors in this equation.
- There is no "direction" to electric potential
If the system has multiple charges, find total

- 4 electric quantities in a 2x2 arrangement ( point charges ):
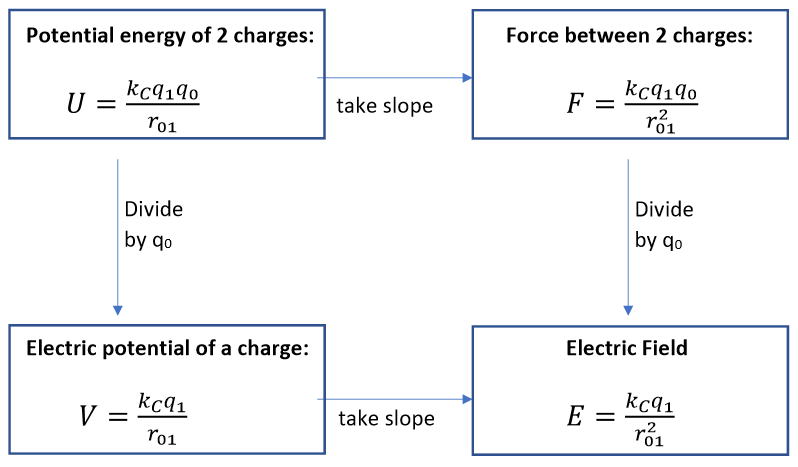
- We've seen this relationship between potential energy (top left) and force (top right) before
- The (negative) slope of potential energy graph gives us the force magnitude and direction
- Not that Electric potential (bottom left) is not the same as potential energy (top left)
- Plot of
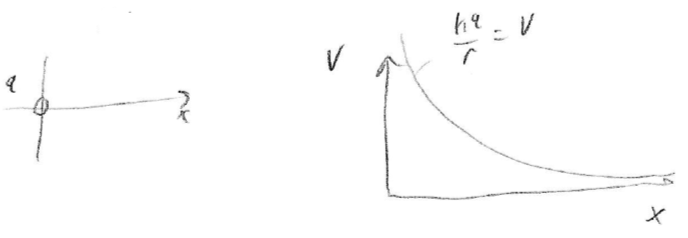
- Slope is negative, so force on a positive charge ( a different positive charge than the one at the origin ) is to the right ( ball "rolls" that way )
- Bigger force for smaller x , because steeper slope
- All of the preceding was for a point charge
- For other arrangements of charge,
- Very common case is
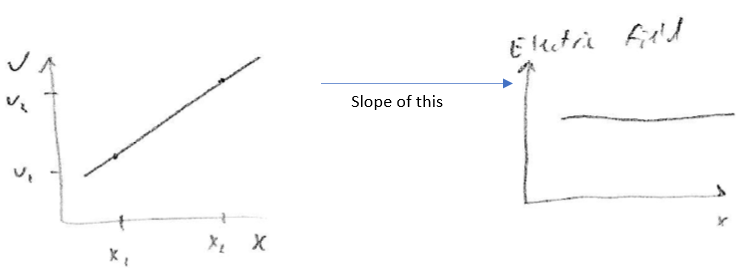
If you know
- This will be used for "capacitors" and biological membranes