The Role of GABAA and GABAB Receptors in Presynaptic Inhibition of Ia EPSPs in Cat Spinal Motoneurons
Summary
The role of GABAA and GABAB receptors in presynaptic inhibition was studied by examining the effect of local application of antagonists by ionophoresis during intracellular recording of presynaptic inhibition of compound and unitary group Ia afferent excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in gastrocnemius motoneurons.
lonophoresis of the GABAA antagonist bicuculline methochloride (BMC) was found to block presynaptic inhibition of both compound and unitary EPSPs by up to 85 %.
- BMC also substantially reduced, and occasionally abolished, the late part of the inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) evoked in motoneurones by the conditioning stimulation.
- The early part of this IPSP was found to be sensitive to ionophoresis of strychnine hydrochloride.
- lonophoresis of 2-OH-saclofen caused a reduction in presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs by 5-25 %, but had no effect on the IPSP evoked in motoneurones by the conditioning stimulation.
lonophoresis of the GABAB antagonist (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs; however it had little effect on presynaptic inhibition.
It was concluded that at the Ia afferent-motoneurone synapse presynaptic inhibition is mediated primarily through the activation of GABAA receptors.
- The activation of GABAB receptors appears to play only a minor role in presynaptic inhibition at this synapse.
- This contrasts with the relative ease with which (baclofen can reduce transmitter release from I a afferent terminals and suggests that the receptors activated by (-)-baclofen are predominantly extrasynaptic.
Introduction
It is now generally accepted that in the mammalian spinal cord presynaptic inhibition of transmitter release from primary afferent fibres is mediated by the release of y-aminobutyric acid (GABA) at axo-axonic synapses
However, the mechanism by which GABA reduces transmitter release is unknown.
- As GABA has been shown to activate two types of receptors, GABAA and GABAB , and both types of GABA receptors appear to be present on primary afferent terminals, it is possible that either, or both, of these GABA receptors may be involved in mediating presynaptic inhibition.
Activation of GABAA receptors is usually associated with an increase in chloride conductance, whereas activation of GABAB receptors has been shown to decrease a voltage-dependent calcium conductance in the cell bodies of dorsal root ganglion cells and also to increase a potassium conductance in the cell bodies of many central neurones
A recent report also suggests that GABA and baclofen, a GABAB agonist, can shift the voltage dependence of inactivation of a transient potassium current, recorded in the cell bodies of cultured hippocampal neurones, to more depolarized potentials
Any one of these GABA-mediated actions, if present during invasion of an action potential into primary afferent terminals, could reduce calcium influx and decrease the probability of transmitter release.
Previous studies on the pharmacology of presynaptic inhibition in the mammalian spinal cord have used relatively indirect methods to assess 'presynaptic' inhibition.
Changes in the level of presynaptic inhibition have usually been inferred from changes in the inhibition of ventral root reflexes or the dorsal root potential evoked by the conditioning stimulation
The 'prolonged inhibition' of ventral root reflexes will undoubtedly be complicated by the postsynaptic hyperpolarization which occurs in conjunction with presynaptic inhibition whereas the dorsal root potential merely indicates depolarization of primary afferent fibres and is not itself a measure of presynaptic inhibition.
In addition, previous pharmacological studies have usually examined the effects of drugs administered either by systemic injection or topical application which may modify synaptic transmission through the polysynaptic pathways that mediate presynaptic inhibition
The present study has attempted to overcome some of these problems by combining the local application of specific GABA antagonists by ionophoresis with intracellular recording of presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs).
The aim of the study was to evaluate the role of GABAA and GABAB receptors in presynaptic inhibition of I a EPSPs in the mammalian spinal cord.
Methods
- All experiments were performed on adult cats anaesthesized with sodium pentobarbitone.
- Cats were initially anaesthetized by an intra-peritoneal injection (40 mg kg-') and the trachea, left common carotid artery and left cephalic vein were then cannulated and anaesthesia continued by intravenous injection (approximately 6 mg h-', or as required).
- Blood pressure, heart rate and end-tidal CO2 levels were monitored continuously throughout the experiment.
- Body temperature was maintained at 37+1 °C by a feedback-controlled electric blanket.
- A bilateral pneumothorax was performed and the animals were artificially respired.
- Endtidal CO2 levels were maintained at 4 %.
- The neuromuscular blocking agent pancuronium bromide (Organon, The Netherlands) was given to maintain stability of recordings (0-2 mg kg-'); supplementary doses were given only after recovery from the previous dose, and only after the level of anaesthesia had been checked by corneal and toe-pinch reflexes.
- The level of anaesthesia was also monitored by the level of muscular tone in the jaw and the degree of pupillary constriction.
- The nerves to posterior biceps and semitendinosus (PBSt) muscles in the left hindlimb were separated from surrounding tissue, cut distally and mounted on a stimulating electrode.
- Usually the most proximal branch to posterior biceps, which runs together with a branch of anterior biceps, was not used.
- The nerve to medial gastrocnemius (MG) was also freed from surrounding tissue, mounted on a stimulating electrode and usually cut distally.
- In the experiments where single Ia afferent fibres were stimulated the MG muscle nerve was left intact and the MG muscle separated as much as possible from surrounding tissue.
- A thread was tied around the MG muscle tendon and the tendon cut distally.
- A laminectomy was performed to expose the spinal segments from L4 to 81.
- The dura was cut longitudinally and a dural sling constructed by gentle retraction of the cut edges of the dura using 5-0 silk sutures.
- A silver-silver chloride electrode was secured to the exposed muscle next to the spinal cord to act as the indifferent electrode and this was connected to the equipment ground.
- The spinal cord and surrounding tissue were covered with warm liquid paraffin and heated by radiant heat.
- A separate leg pool was formed and the hindlimb muscle nerves covered with warm liquid paraffin.
- All electrical stimuli to muscle nerves were applied via bipolar stimulating electrodes using isolated stimulators.
- Stimulus pulses of 0-2 ms duration were used.
- A ball electrode was used to record the arrival of the afferent volley from the cord dorsum.
- This ball electrode was also used to gently retract the L7 dorsal root medially, allowing microelectrode access to the motoneurone pools in the ventral horn of the L7-Sl spinal segments.
Recording Procedures
- Intracellular recordings were made from antidromically identified MG motoneurones (resting membrane potentials greater than -55 mV, spike height greater than 60 mV) using an Axoclamp 2A amplifier (Axon Instruments, USA).
- Two extracellular ionophoretic barrels were glued to the intracellular recording barrel and offset approximately 100 gm back from its tip (Curtis, 1968).
- The intracellular recording electrode was filled with 2 M-KCH3SO4 and the ionophoretic barrels filled with either (-)-baclofen hydrochloride (5 mM in 150 mM-NaCl, pH 3 0), bicuculline methochloride (BMC) (10 mm in 150 mM-NaCl, pH 3 0), 2-OH-saclofen (20 mm in 80 mM-NaCl, pH 3 0) or strychnine hydrochloride (5 mm in 150 mM-NaCl, pH 3 0).
- The pH of these solutions was adjusted with weak hydrochloric acid.
- All compounds were ejected as cations.
- Jonophoretic electrodes typically had resistances of 50 MQ and retaining currents of -20 nA were routinely used.
- The coupling resistance between the ionophoretic barrels and the intracelluar recording barrel was less than 10 kQ.
- Hence, the passage of a cationic current of 100 nA resulted in a coupling artifact of less than 1 mV in the depolarizing direction.
- Compound I a EPSPs were evoked in MG motoneurones by stimulation of the MG muscle nerve at 1-5 x group I threshold (T, determined from the cord dorsum recording).
- Unitary EPSPs were recorded following the activation of single MG I a afferent fibres and were obtained in the following way.
- Dorsal root filaments close to the L7-S1 entry zone were placed on a bipolar recording electrode and the number of I a afferent fibres in each filament assessed by the level of activity recorded during brief, passive stretch of the MG muscle.
- Once a filament was found which contained many MG I a afferents, a small platform was positioned under the filament just distal to the bipolar recording electrode.
- This platform stabilized the filament during intra-axonal recording which was made using a second microelectrode filled with 3 M-KCl.
- The MG muscle nerve was stimulated and penetrated axons identified as MG I a afferent fibres by their conduction velocity, stimulus threshold and response to brief, passive stretch of the MG muscle.
- Once a stable recording from a MG Ia afferent was established action potentials were evoked in this axon by passing brief, depolarizing current pulses (1-2 ms in duration, up to 10 nA in magnitude).
- MG motoneurones were then impaled and intracellular records averaged to determine whether a unitary Ia EPSP was present in response to axonal stimulation.
- Presynaptic inhibition of compound and unitary EPSPs was produced by prior stimulation of the PBSt muscle nerve.
- Conditioning PBSt stimulation, composed of a train of three stimuli at 300 Hz, 2 x T, always preceded EPSPs by at least 50 ms and was repeated at 1 s intervals.
- Alternate records of conditioned and unconditioned EPSPs were stored in separate buffers in a microcomputer and averaged.
- Usually ten to twenty complete sequences of conditioned and unconditioned EPSPs were collected and averaged for compound EPSPs, whereas several hundred complete sequences were averaged for unitary EPSPs.
Data Analysis
- The peak amplitude, 10-90% rise time and duration at half-peak amplitude (half-width) of compound and unitary EPSPs were measured.
- The final time constant of decay of EPSPs was determined by displaying an EPSP semilogarithmically and fitting a linear regression line to the decay phase using a least-squares procedure for the best fit.
- Input resistance measurements were made using a single electrode discontinuous current clamp at switching rates of between 3 and 5 kHz from the steady-state voltage response to 1 or 2 nA hyperpolarizing current pulses of between 10 and 30 ms duration.
- The final time constant of decay of this voltage response was measured using the same procedure as that used for determining the final decay time constant of an EPSP.
- As the conditioned EPSP was often superimposed on the repolarizing phase of an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP), a sloping baseline was used in an attempt to overcome some of the distortion of the conditioned EPSP caused by the repolarizing IPSP.
- The amount of presynaptic inhibition is expressed as the percentage decrease in EPSP peak amplitude produced by the conditioning PBSt stimulation.
- Unless otherwise stated, only those results obtained from cells where complete recovery from a particular drug application was established have been included.
Results
Resynaptic Inhibition
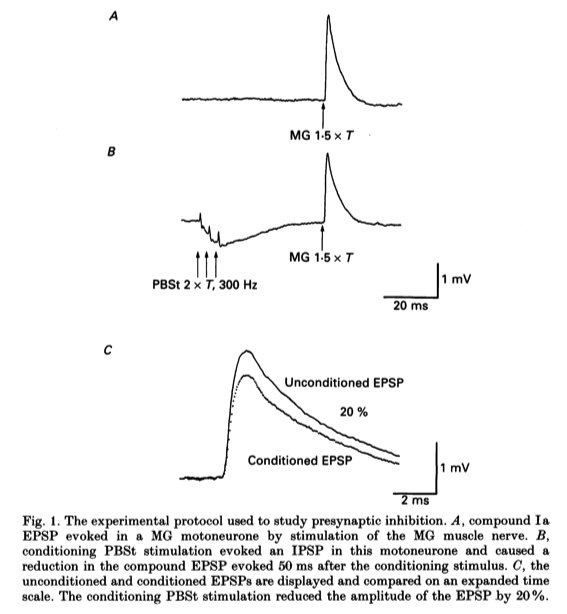
- The procedure for studying presynaptic inhibition of MG la EPSPs is shown in Fig. 1. Stimulation of the MG muscle nerve at 1-5 x T evoked a compound, monosynaptic EPSP in the MG motoneurone shown in Fig. IA.
- Prior conditioning stimulation of the PBSt muscle nerve 50 ms before this EPSP (using three stimuli at 300 Hz, 2 x T) evoked an IPSP in this motoneurone and caused the EPSP to be reduced in amplitude (Fig. IB).
- A comparison of the unconditioned and conditioned EPSPs indicated that the conditioning PBSt stimulation reduced the peak amplitude ofthe EPSP by 20 % (Fig. 1 C).
- This reduction in the amplitude is considered to occur as a consequence of a decrease in transmitter release (Clements, Forsythe & Redman, 1987), as originally proposed by Frank & Fuortes in 1957.
Postsynaptic Inhibition
- The conditioning PBSt muscle nerve stimulation almost always evoked an IPSP in every MG motoneurone examined
- This IPSP varied in size from a few hundred microvolts to several millivolts, had a latency to peak ofbetween 20 and 30 ms (measured from the start of the conditioning stimulus) and usually had a duration of several hundred milliseconds.
- The postsynaptic response evoked in MG motoneurones by the conditioning PBSt stimulation often also included an early EPSP.
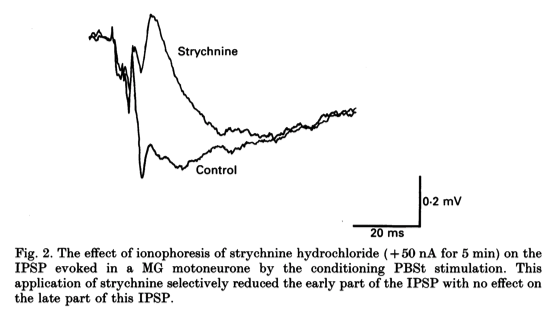
- The early part of the IPSP was selectively reduced by the ionophoretic application of the classical glycine antagonist strychnine hydrochloride.
- An example of this is shown in Fig. 2.
- This application of strychnine had no effect on the late part of the IPSP and converted the early hyperpolarizing response into a depolarizing response, unmasking an early EPSP.
- The late part of the IPSP, as will be shown later, was found to be reduced by the GABAA antagonist BMC.
- As the ventral roots were left intact the early IPSP will, in part, be mediated via Renshaw cells as MG motoneurones receive a small amount of strychnine-sensitive recurrent inhibition following antidromic activation of motor fibres in the posterior biceps muscle nerve.
- The finding that there are strychnine- and bicuculline-sensitive components to the hyperpolarization evoked in MG motoneurones by PBSt stimulation is in agreement with Kellerth (1968).
Effect of the GABAA Antagonist Bicuculline Methochloride on Presynaptic Inhibition of Compound EPSPs
- Ionophoretic application of BMC was used to investigate whether GABAA receptors were involved in mediating presynaptic inhibition.
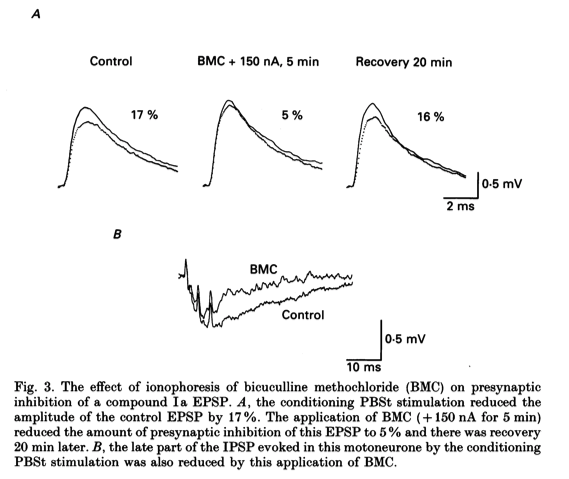
- BMC reduced presynaptic inhibition of compound Ia EPSPs and also the later part of the IPSP evoked in MG motoneurones by the conditioning PBSt stimulation.
- An example of this is shown in Fig. 3. In Fig. 3A the application of + 150 nA of BMC for 5 min substantially reduced the amount of presynaptic inhibition of this compound EPSP from 17 to 5%, a 70% reduction with full recovery in 20 min.
- Figure 3B also clearly shows that the same application of BMC markedly reduced the late part of the IPSP evoked in this motoneurone by the PBSt stimulation.
- Ionophoresis of BMC reduced presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs by between 42 and 76 % (n = 8), using ionophoretic currents of from 40 to 340 nA.
- The percentage decrease in presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs was found to be related to the ionophoretic current used to eject BMC.
- There was also an approximately linear relationship between the percentage decrease in the amount of presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs during the application of BMC and the percentage decrease in the late part of the IPSP (measured between 20 and 30 ms after the start of the conditioning stimulus).
- Presynaptic inhibition of compound Ia EPSPs could not, however, be completely abolished by the ionophoretic application of BMC, even when BMC completely abolished the late part of the IPSP.
- There are two possible explanations for the inability of the ionophoretic BMC to completely abolish presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs.
- The most likely explanation is that with such a localized application of BMC, presumably close to the soma of the motoneurone, it was not possible to block presynaptic inhibition of EPSPs generated at synapses located on distal regions of the motoneurone dendritic tree.
- The second possibility is that while presynaptic inhibition of I a EPSPs appears to be mediated mainly by BMC-sensitive GABAA receptors, a BMC-insensitive receptor or mechanism may also be involved.
- To address the first possibility, the effect of the ionophoretic application of BMC was investigated on presynaptic inhibition of unitary I a EPSPs generated by synapses located near the soma.
- The local concentration of BMC around these synapses should be higher than at more distal synapses and so it would be expected that if presynaptic inhibition was generated purely through the activation of BMCsensitive receptors, then presynaptic inhibition of these near-somatic, unitary EPSPs would be more easily blocked by the ionophoretic application of BMC.
Effect of the GABAA Antagonist Bicuculline Methochloride on Presynaptic Inhibition Unitary EPSPs
- The conditioning PBSt stimulation reduced unitary EPSPs by different amounts independent of their synaptic location (range 4-55 %; n = 22).
- This is consistent with similar findings by Clements et al. 1987), as is the finding that the amount of presynaptic inhibition of unitary EPSPs did not depend on their synaptic location, i.e. presynaptic inhibition reduced somatic EPSPs by similar amounts to EPSPs generated at more distal locations.
- That the time course of the compound EPSP is unchanged during presynaptic inhibition also suggests a rather uniform inhibition of transmitter release at all Ia afferent synapses during presynaptic inhibition.
- The effect of BMC was examined on presynaptic inhibition of six near-somatic, unitary EPSPs.
- Five of these unitary EPSPs had normalized 10-90 % rise times and half-widths consistent with a location 0-2 space constants (A) from the soma the other unitary EPSP had shape indices that suggested a somatic location. Jonophoresis of BMC (100-200 nA) reduced presynaptic inhibition for these unitary EPSPs by between 39 and 85 %.
- The same application of BMC reduced IPSPs recorded in these motoneurones by between 65 and 95 %.
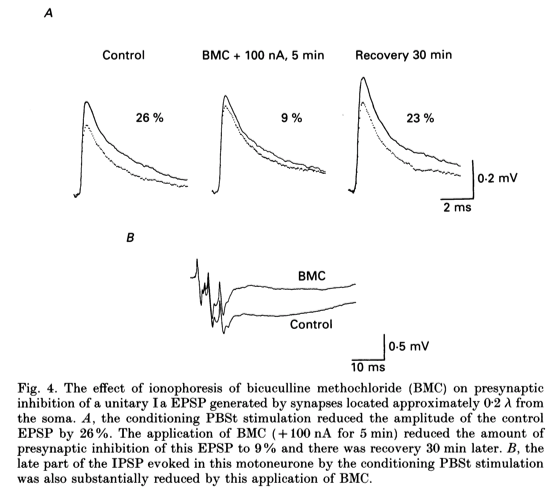
- An example of the effect of the ionophoretic application of BMC on presynaptic inhibition of a near somatic, unitary EPSP is shown in Fig. 4A.
- Here, presynaptic inhibition was reduced from 26 to 9 % during the application of + 100 nA of BMC for 5 min with recovery 30 min later; a reduction of 65 %.
- The late part of the IPSP evoked in this motoneurone by the conditioning PBSt stimulation was also substantially reduced by this application of BMC (Fig. 4B).
- As with the compound EPSPs, the ionophoretic application of BMC did not completely abolish presynaptic inhibition of near-somatic EPSPs.
- This finding suggests that presynaptic inhibition may be mediated in part through a BMCinsensitive receptor or mechanism.
- As there is considerable evidence to suggest that the transmitter released during presynaptic inhibition is GABA, we investigated the possibility that BMC-insensitive GABAB receptors may also be involved in mediating presynaptic inhibition by using the GABAB antagonist 2-OH-saclofen.
- However, before investigating the effect of 2-OH-saclofen on presynaptic inhibition it was necessary to first establish that 2-OH-saclofen could block the activation of GABAB receptors.
- Therefore the ability of 2-OH-saclofen to reduce the effect of the GABAB agonist (-)-baclofen was examined.
Effect of the GABAB Agonist (-) -Baclofen on Compound EPSPs
- When applied ionophoretically (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of Ia EPSPs.
- This was consistent with previous findings using systemic injections and the ionophoretic application of baclofen.
- The decrease in amplitude of compound EPSPs occurred rapidly (within 1 min) and usually recovered within 3-5 min after termination of the ionophoretic current.
- The application of (-)-baclofen caused no detectable change in the membrane potential, input resistance or the final time constant of decay of the voltage response to a current pulse.
- The average input resistance measured in the absence of (-)baclofen was 2-5+04 MQ (+S.E.M., n = 5), compared to 2-5+0-3 MQ during the application of (-)-baclofen, whereas the average decay time constant measured in the absence of (-)-baclofen (5 3 + 2-9 ms) was identical to that measured during the application of (-)-baclofen.
- The same application of (-)-baclofen decreased compound EPSPs recorded in these motoneurones by, on average, 25+6 % (range 17-48%).
- The lack of any effect of (-)-baclofen on the input resistance or decay time constant of motoneurones is in agreement with previous findings and consistent with the idea that (-)-baclofen, presumably via the activation of GABAB receptors on la afferent terminals, decreases the probability of transmitter release.
Antagonism by 2-OH-saclofen of the Decrease in Amplitude of Compound EPSPs Produced by (-)-baclofen
- To establish that 2-OH-saclofen could block the activation of GABAB receptors, we investigated the ability ofthe ionophoretic application of 2-OH-saclofen to reduce the decrease in amplitude of Ia EPSPs produced by (-)-baclofen.
- This proved difficult to demonstrate, as often 2-OH-saclofen had either no effect on the reduction of EPSP amplitude produced by (-)-baclofen or alone reduced the amplitude of Ia EPSPs.
- The reduction in amplitude of compound EPSPs by 2-OH-saclofen occurred without any change in the membrane potential or the final decay time constant of EPSPs, an action which appeared to be very similar to that of (-)-baclofen.
- However, taking into account the concentrations of (-)-baclofen and 2-OH-saclofen in the ionophoretic electrodes and the currents used to eject them, this effect of 2-OH-saclofen was considerably less potent than that of (-)-baclofen.
- That 2-OHsaclofen can reduce the amplitude of Ia EPSPs suggests that it can act as a weak GABAB agonist
- It was possible on some occasions to demonstrate that 2-OH-saclofen could reduce the decrease in amplitude of I a EPSPs by (-)-baclofen.
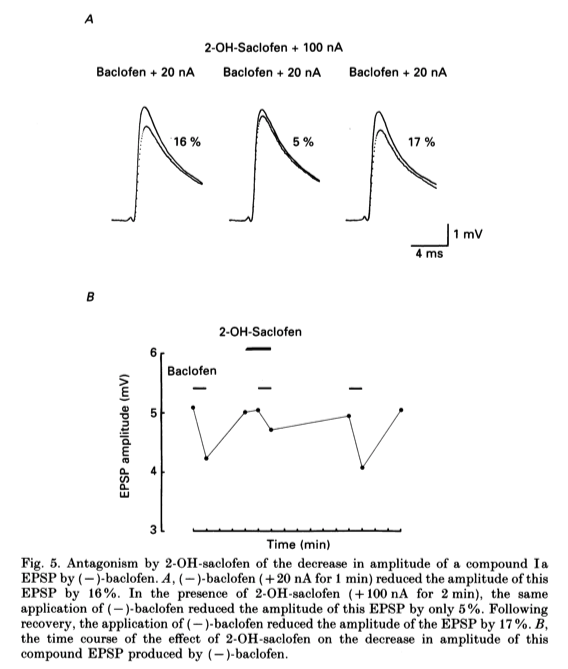
- An example of this is shown in Fig. 5.
- The control record shows that (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of this compound Ia EPSP by 16% with recovery within 3 min.
- During the application of 2-OH-saclofen (which caused little or no change in the size of the control EPSP), the same application of (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of the EPSP by only 5 %.
- The EPSP returned to the control amplitude 6 min later, where (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of the EPSP by 17 %.
- The time course of the effect of 2-OHsaclofen on the decrease in amplitude of this compound EPSP by (-)-baclofen is shown in Fig. 5B. As (-)-baclofen presumably reduces the amplitude of Ia EPSPs by acting at presynaptic GABAB receptors, these results suggest that 2-OH-saclofen can block the activation of presynaptic GABAB receptors on I a afferent terminals.
Effect of the GABAB Antagonist 2-OH-saclofen on Presynaptic Inhibition of Compound EPSPs
- Once it was established that the effect of (-)-baclofen on an EPSP could be reduced by 2-OH-saclofen, the effect of 2-OH-saclofen was examined on presynaptic inhibition of the same la EPSP.
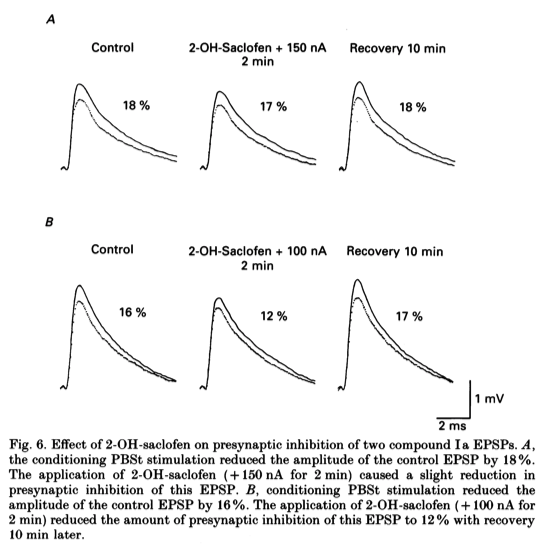
- Two examples of the effect of 2-OH-saclofen on presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs are shown in Fig. 6.
- Presynpatic inhibition of the EPSP shown in Fig. 6A was slightly reduced by 5% in the presence of 2-OH-saclofen (from 18 to 17 %), whereas 2-OH-saclofen reduced presynaptic inhibition of the EPSP shown in Fig. 6B by 25% (from 16 to 12%).
- Presynaptic inhibition of all five compound EPSPs examined was reduced to some extent by 2-OH-saclofen.
- The reduction of presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs by 2-OH-saclofen ranged from 5 % (Fig. 6A) to 25 % (Fig. 6B), using ionophoretic currents of 100-200 nA.
- Two of these compound EPSPs did not show complete recovery back to the control level of presynaptic inhibition after the application of 2-OH-saclofen.
- 2-OH-Saclofen also decreased the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs by 1-13 % (Fig. 6).
- This presumably occurred as a consequence of this compound acting as a weak GABAB agonist.
- As the reduction in presynaptic inhibition by 2-OH-saclofen was always associated with a slight decrease in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP, it was thought possible that this could be responsible for the decrease in presynaptic inhibition.
- To investigate this we examined the ability of (-)-baclofen to reduce presynaptic inhibition.
Effect of the GABAB Agonist (-)-baclofen on Presynaptic Inhibition of Compound EPSPs
- When applied ionophoretically using currents of between 20 and 40 nA for 1-2 min, (-)-baclofen reduced the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs by between 16 and 60 % (n = 11).
- This reduction in the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs was, however, usually not associated with any change in the amount of presynaptic inhibition of the same EPSP or the magnitude of the IPSP evoked in the motoneurone by the conditioning PBSt stimulation.
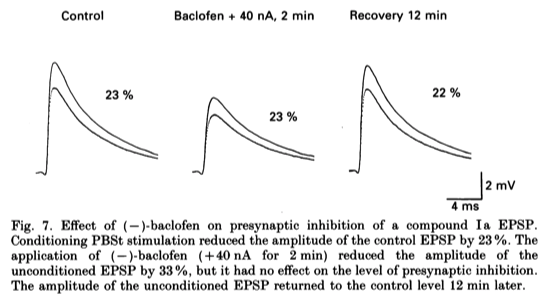
- An example of the effect of (-)baclofen on presynaptic inhibition of a compound EPSP is shown in Fig. 7.
- Here, the application of (-)-baclofen (+ 40 nA for 2 min) reduced the unconditioned EPSP by 33 % with no change in the amount of presynaptic inhibition.
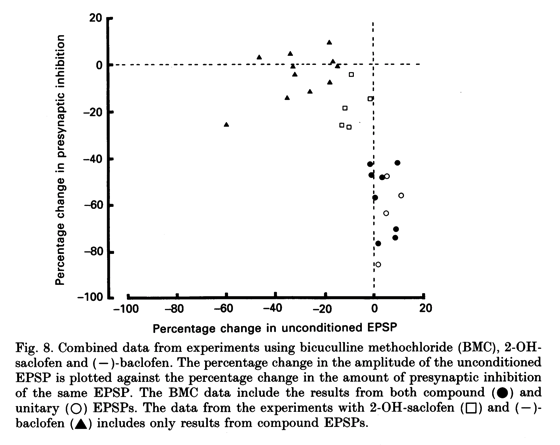
- The percentage change in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP during the application of (-)-baclofen has been plotted against the percentage change in the amount of presynaptic inhibition in Fig. 8 (A).
- While this relationship suggests a slight reduction in presynaptic inhibition following large reductions in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP, there was no significant effect of (-)-baclofen on presynaptic inhibition when the unconditioned EPSP was reduced by less than 20%.
- As the maximum reduction in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP during the application of 2-OH-saclofen was only 13%, this suggests that the decrease in presynaptic inhibition observed in the presence of 2-OH-saclofen was not due to the ability of 2-OH-saclofen to act as a weak agonist at GABAB receptors.
- Figure 8 also includes the pooled data of the effect of BMC and 2-OH-saclofen on the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSPs and presynaptic inhibition.
- The BMC data include the results obtained from both compound (@) and unitary (0) EPSPs and show that BMC often caused a slight increase in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP and a large decrease in the amount of presynaptic inhibition of I a EPSPs by 42-85 %.
- (Two unitary EPSPs were lost during the application of BMC and have not been included in this figure.
- These EPSPs showed reductions in presynaptic inhibition of 39 and 52 %.) 2-OH-saclofen (O), caused a slight decrease in the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs and a small reduction in the amount of presynaptic inhibition of Ia EPSPs by 5-25%.
- In contrast, (-)-baclofen (A), caused a large decrease in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP, but was relatively ineffective in reducing presynaptic inhibition.
Discussion
- Presynaptic inhibition of I a EPSPs was markedly reduced during the ionophoretic application of BMC.
- This is consistent with earlier findings which had shown that picrotoxin and bicuculline (GABAA antagonists) reduced both prolonged inhibition of ventral root reflexes and primary afferent depolarization and suggests that at this synapse presynaptic inhibition is mediated primarily through the activation of GABAA receptors.
- The small reduction in presynaptic inhibition produced by 2-OH-saclofen suggests that GABAB receptors may play a minor role in presynaptic inhibition of Ia EPSPs.
- The effect of 2-OH-saclofen on presynaptic inhibition was complicated by its ability to reduce the unconditioned EPSP.
- This action of 2-OH-saclofen was very similar to that of baclofen and suggested that 2-OH-saclofen can act as a partial agonist at GABAB receptors.
- However, recent in vitro studies have not reported any effect of 2-OH-saclofen on the amplitude of EPSPs in CAI neurones of the hippocampus.
- As the only other study to apply 2OH-saclofen ionophoretically also reported a weak baclofen-like action of 2-OHsaclofen, the reduction of Ia EPSPs by 2-OH-saclofen may occur as a consequence of its ionophoretic application.
- High concentrations of 2-OHsaclofen might be expected to occur close to the tip of the ionophoretic electrode.
- If at high concentrations 2-OH-saclofen can act as a partial GABAB agonist this may explain the reduction in amplitude of I a EPSPs observed in the present study during the application of 2-OH-saclofen.
- Experiments designed to investigate the effect of activation of GABAB receptors on presynaptic inhibition, using the GABAB agonist (-)-baclofen, showed that for reductions in the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs of less than 20 % there was no significant effect of (-)-baclofen on presynaptic inhibition.
- As the maximum reduction in amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs during the application of 2-OHsaclofen was only 13%, this finding suggests that weak activation of GABAB receptors does not account for the small reduction in presynaptic inhibition observed in the presence of 2-OH-saclofen.
- This supports the idea that 2-OH-saclofen decreased presynaptic inhibition by blocking the activation of GABAB receptors.
- It is also possible that 2-OH-saclofen reduced presynaptic inhibition by blocking the activation of GABAA receptors.
- A recent report has cautioned that high concentrations of 2-OH-saclofen will displace the binding of muscimol, a GABAA receptor agonist
- However, previous studies have shown that 2-OH-saclofen, in concentrations necessary to block the activation of GABAB receptors, has little or no effect on the activation of GABAA receptors.
- That 2-OH-saclofen had no effect on the GABAAmediated IPSP evoked in MG motoneurones by the conditioning PBSt stimulation also suggests that 2-OH-saclofen did not block the activation of GABAA receptors.
- It can be concluded that the small reduction in presynaptic inhibition observed in the presence of 2-OH-saclofen is most probably due to the ability of 2-OH-saclofen to block the activation of GABAB receptors.
Pharmacology of Postsynaptic Inhibition
- The early part of the IPSP evoked in motoneurones by the conditioning PBSt stimulation could be reduced by the ionophoretic application of strychnine.
- This suggests that the early part of this IPSP is mediated by inhibitory glycinergic interneurones (possibly Renshaw cells as ventral roots were left intact) which activate postsynaptic glycine receptors on motoneurones and presumably lead to an increase in chloride conductance.
- The application of BMC reduced, and occasionally completely abolished, the late part of this IPSP.
- This suggests that this BMC-sensitive IPSP is mediated by another interneuronal pathway with last-order GABAergic interneurones which activate postsynaptic GABAA receptors and presumably also cause an increase in chloride conductance.
- As this GABAergic IPSP could occasionally be completely abolished by BMC, it is presumably mediated exclusively through the activation of GABAA receptors.
- There was no suggestion of a BMC-insensitive component to this IPSP, as has been observed to follow GABAA-mediated IPSPs in many regions of the brain.
Effects of Bicuculline Methochloride on the Unconditioned EPSP
- As can be seen from Fig. 8, BMC often caused a slight increase in the amplitude of the unconditioned EPSP.
- This possibly reflects' the removal of background GABAA-mediated presynaptic inhibition of these EPSPs.
- However, the small increase in unconditioned EPSPs during the application of BMC was not statistically significant when compared to control amplitudes, suggesting that in the spinal cord of the barbiturate-anaesthetized cat background levels of tonic presynaptic inhibition are low.
Effect of (-)-baclofen on Presynaptic Inhibition
- The ionophoretic application of (-)-baclofen had little effect on presynaptic inhibition of compound EPSPs, except during large reductions in the amplitude of those EPSPs.
- The interpretation of this result is complicated, as the percentage decrease in the amplitude of the EPSP during presynaptic inhibition will depend on the probabilities of transmitter release from the unconditioned group Ia terminals.
- These probabilities will change in the presence of (-)-baclofen.
- As both (-)-baclofen and presynaptic inhibition are believed to affect calcium influx into Ia terminals, and as the relationship between calcium influx and transmitter release is highly non-linear it is extremely difficult to predict what effect (-)-baclofen will have on the amount of presynaptic inhibition.
- A simplistic interpretation of the small decrease in presynaptic inhibition observed during the application of (-)-baclofen is that it causes a small reduction in transmitter release from axo-axonic terminals.
- In agreement with this proposal is the finding that the ionophoretic application of (-)-baclofen can reduce primary afferent depolarization of I a afferent terminals, without any effect on the sensitivity of these terminals to GABAA agonists
- The finding that (-)-baclofen caused only small reductions in presynaptic inhibition following large reductions in the amplitude of unconditioned EPSPs suggests that GABAB receptors on axo-axonic terminals are less effective in reducing transmitter release than similar receptors on I a afferent terminals.
- This is consistent with previous reports that in the mammalian spinal cord synaptic transmission at the terminals of interneurones and descending spinal projections is less sensitive to baclofen than synaptic transmission at the terminals of primary afferent fibres
Antagonism of Presynaptic GABAB Receptors
- Early reports using the baclofen antagonist phaclofen found that phaclofen could selectively reduce GABAB receptormediated responses produced by either baclofen or GABA, in the presence of BMC.
- However, many presynaptic effects of baclofen in the CNS were found to be insensitive to phaclofen
- These findings led to the suggestion that there may be pharmacological differences between pre- and postsynaptic GABAB receptors in the mammalian CNS.
- Recently, however, the more potent antagonist 2-OH-saclofen has been shown to reduce the presynaptic effects of baclofen in the hippocampus.
- In agreement with extracellular studies, the results from the present study show that in the mammalian spinal cord the activation of presynaptic GABAB receptors can also be blocked by 2-OH-saclofen.
Conclusion
- The main findings from this study suggest that at the la afferent-motoneurone synapse presynaptic inhibition is mediated primarily through the activation of GABAA receptors.
- The activation of GABAB receptors appears to play only a minor role in presynaptic inhibition at this synapse.
- This contrasts with the relative ease with which (-)-baclofen, presumably via the action ofGABAB receptors, can reduce transmitter release from I a afferent terminals and suggests that the receptors activated by (-)-baclofen are predominantly extrasynaptic.