Glutametergic Synapse and Plasticity
https://neurowiki.case.edu/JSNeuroSim/simulations/synapse_currentclamp_glutamatergic_jqplot.html
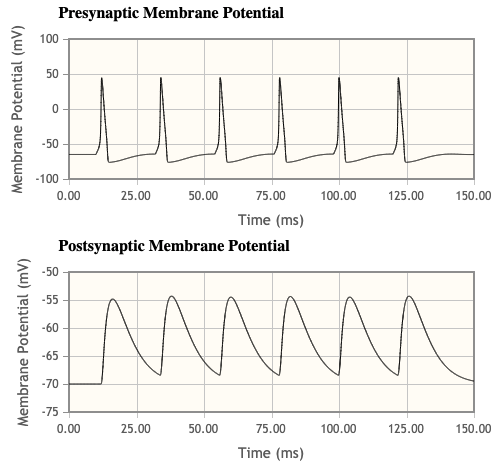
- Under the default conditions set in the simulation what is the relationship between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron firing activity?
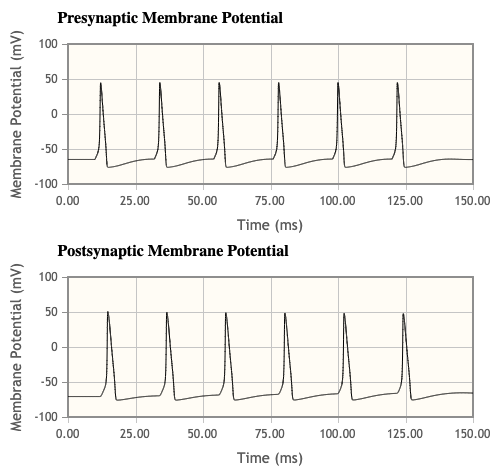
- Presynaptic peaks occur just before post synaptic
- Also, make observations about what is going on with the postsynaptic [Ca2+]i
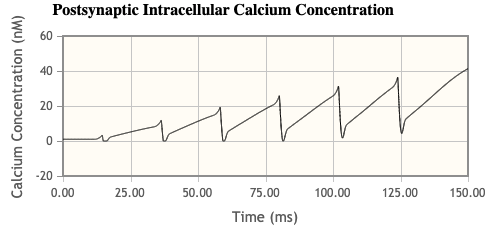
- Calcium levels build up as more action potentials happen
- Since this is a glutamatergic synapse represented in this simulation, both glutamatergic receptors, AMPA and NMDA are represented. Try eliminating NMDA receptors by setting the NMDA maximum conductance (under Synapse Properties) to 0µS. What happened to the relationship between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron firing activity?
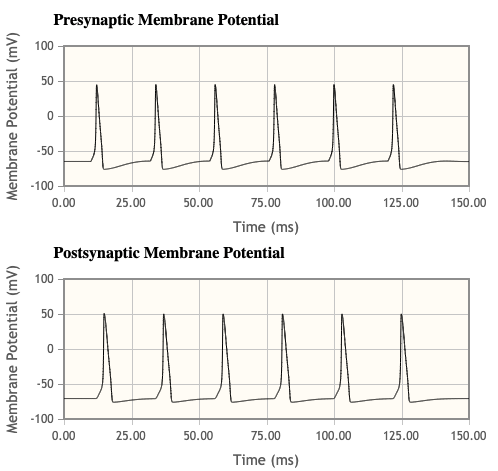
- Post synaptic potentials are more delayed
- Were there any changes associated with the postsynaptic [Ca2+]i?
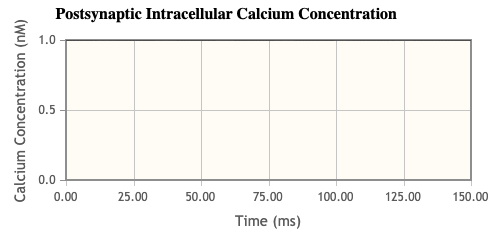
- Zero Calcium Concentration on Post Synaptic side
- What does this tell us about a role for NMDA receptors?
- If there is no NMDA current, there is no calcium influx
- Now if you block NMDA receptors (set the NMDA maximum conductance to 0µS (if it isn’t still set there) as well as block fast transient sodium conductance and delayed rectifier potassium conductance by setting both to 0µS (both under the Postsynaptic Cell Properties), what do you notice happens to the postsynaptic conductance?
- asdf
- What conductance is mediating these postsynaptic changes?
- Sodium and potassium
- Now return the simulation to default values (click on Default simulation near the bottom of the screen). Block AMPA receptors by setting the AMPA max conductance and the AMPA minimum conductance both to 0µS. Then set the total duration of the simulation to 300ms (under Simulation Settings) and change the number of pulses in the presynaptic neuron to 12 (under Presynaptic Current Clamp). What is the relationship between the presynaptic and postsynaptic firing activity?
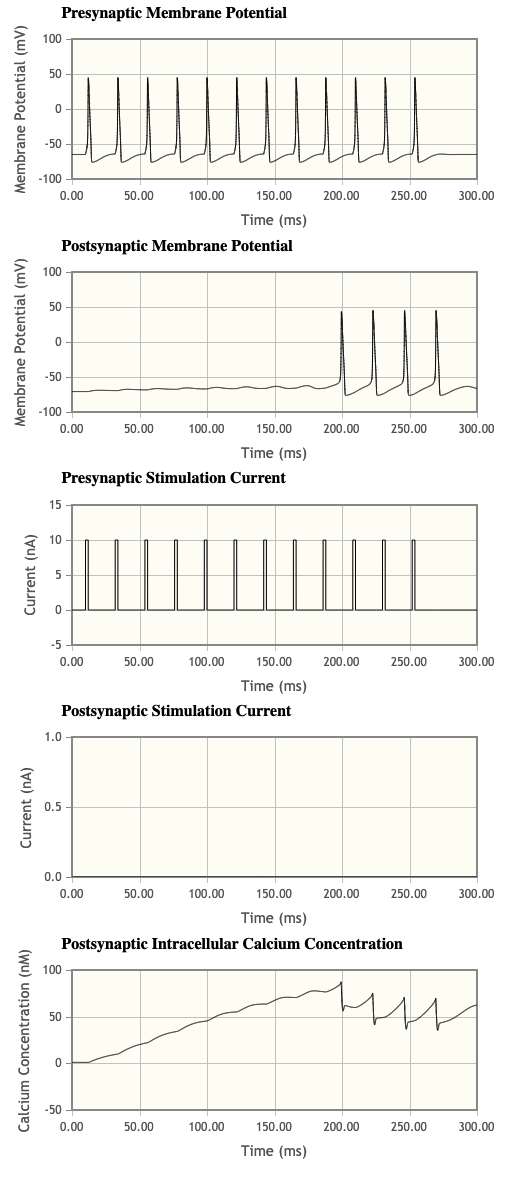
- asdf
- What is happening with the postsynaptic [Ca2+]i in this simulation paradigm?
- asdf
- What role would you expect AMPA versus NMDA receptors to play in retaining a memory of the inputs that have just previously occurred?
- asdf
- Click on Default simulation and then LTP simulation. Note that we start off now by simultaneously stimulating both the pre- and postsynaptic neurons. How many APs are elicited postsynaptically during the first and second presynaptic stimulations?
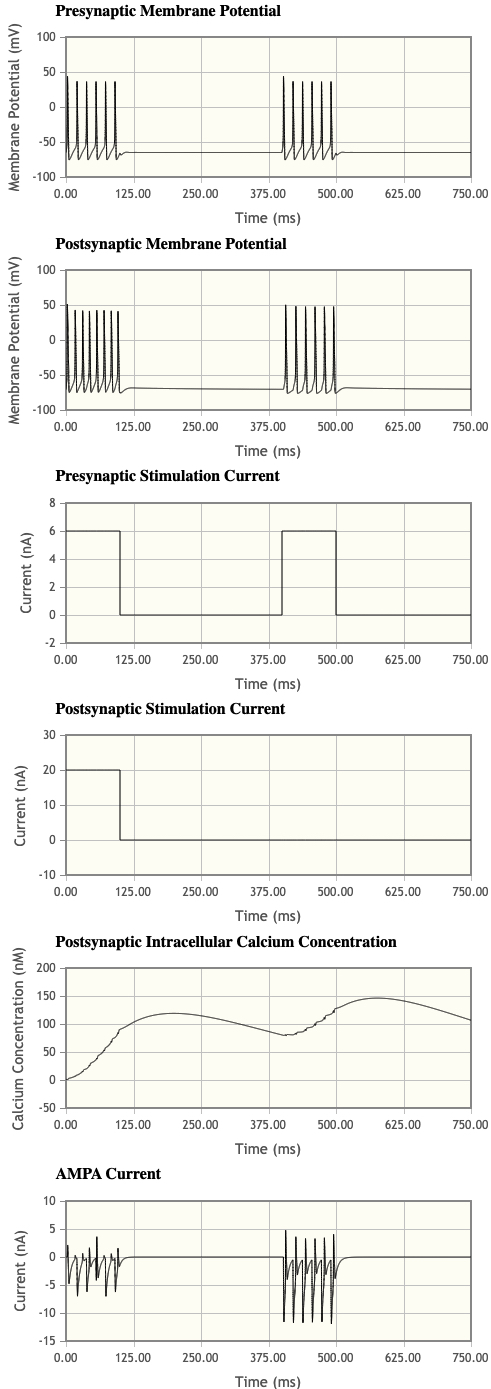
- 8 and 6
- What are the changes in the [Ca2+]i postsynaptically?
- Increases, then dips back down, and then increases again
- What are the differences in the AMPA currents during the first and second set of postsynaptic APs?
- the second set of post synaptic AP caused a greater amplitude in AMPA current
- Now set the Stimulus current first pulse to 0nA, eliminating the first postsynaptic stimulation. How many APs are now elicited postsynaptically during the first and second presynaptic stimulations?
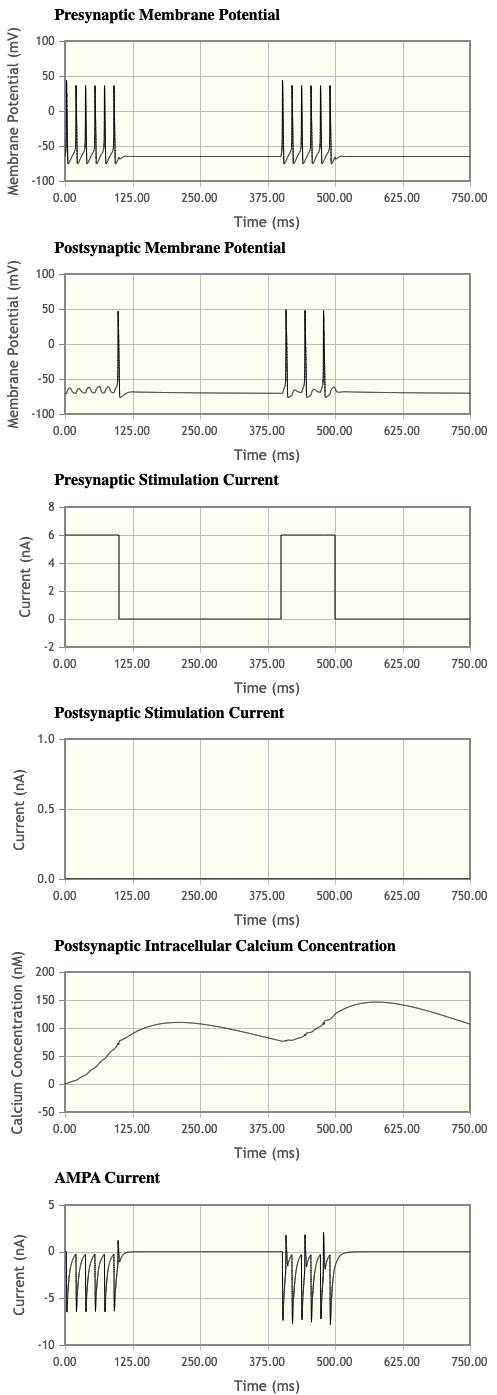
- 1 and 3
- What are the changes in the [Ca2+]i postsynaptically?
- no change really
- What are the differences in the AMPA currents during the first and second set of postsynaptic APs?
- asdf
- Why would the differences in postsynaptic APs elicited and AMPA current amplitudes be different merely by eliminating a single postsynaptic excitation that occurs simultaneously with the presynaptic excitation?
- By eliminating post synaptic excitation, the frequencies were different
- There for long term potentiation didn't occur