Lipid Synthesis
Fatty Acid Synthesis vs β-Oxidation
| Synthesis | Degradation | |
|---|---|---|
| Greatest Flux Through Pathway | After Carbohydrate-Rich Meal | In Starvation |
| Hormonal State Favoring Pathway | High Insulin / Glucagon Ration | Low Insulin / Glucagon Ration |
| Major Tissue Site | Primarily Liver | Primarily Mitochondria |
| Subcellular Location | Primary Cytosol | Primarily Mitochondria |
| Carriers of Acyl /Acetyl Groups Between Mitochondria and Cytosol | Citrate ( mitochondria to cytosol ) | Carnitine ( Cytosol to Mitochondria ) |
| Phosphopantetheine-Containing Active Carriers | Acyl Carrier Protein Domain , Coenzyme A | Conenzyme A |
| Oxidation / Reduction Coenzymes | NADPH ( reduction ) | NAD+ , FAD ( oxidation ) |
| Two-Carbon Donor / Product | Malonyl CoA: Donor of 1 acetyl group | Acetyl-CoA: Product of β-Oxidation |
| Activator | Citrate | |
| Inhibitor | Long-Chain Fatty acyl-CoA ( inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase ) | Malonyl CoA ( inhibits carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 ) |
| Product of Pathway | Palmitate | Acetyl-CoA |
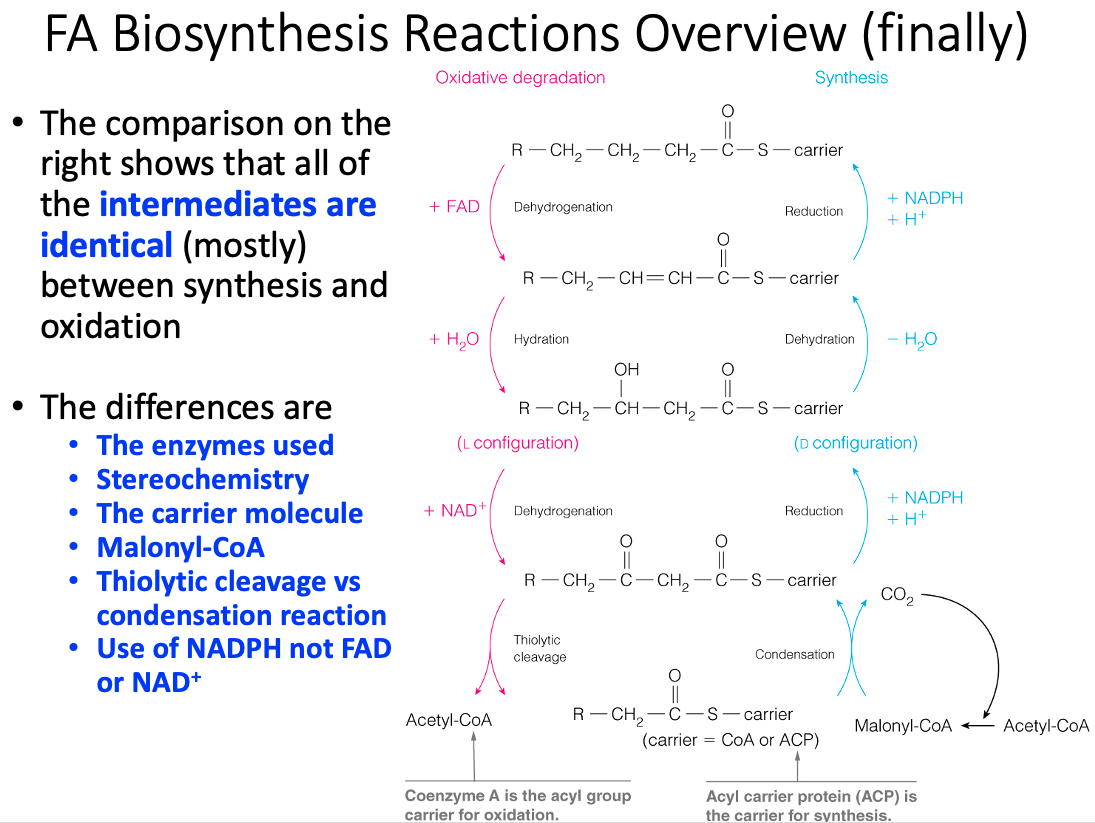
| Repetitive Four-Step Process | Condensation ,Reduction , Dehydration , Reduction | Dehydrogenation , Hydration , Dehydrogenation , Thiolysis |


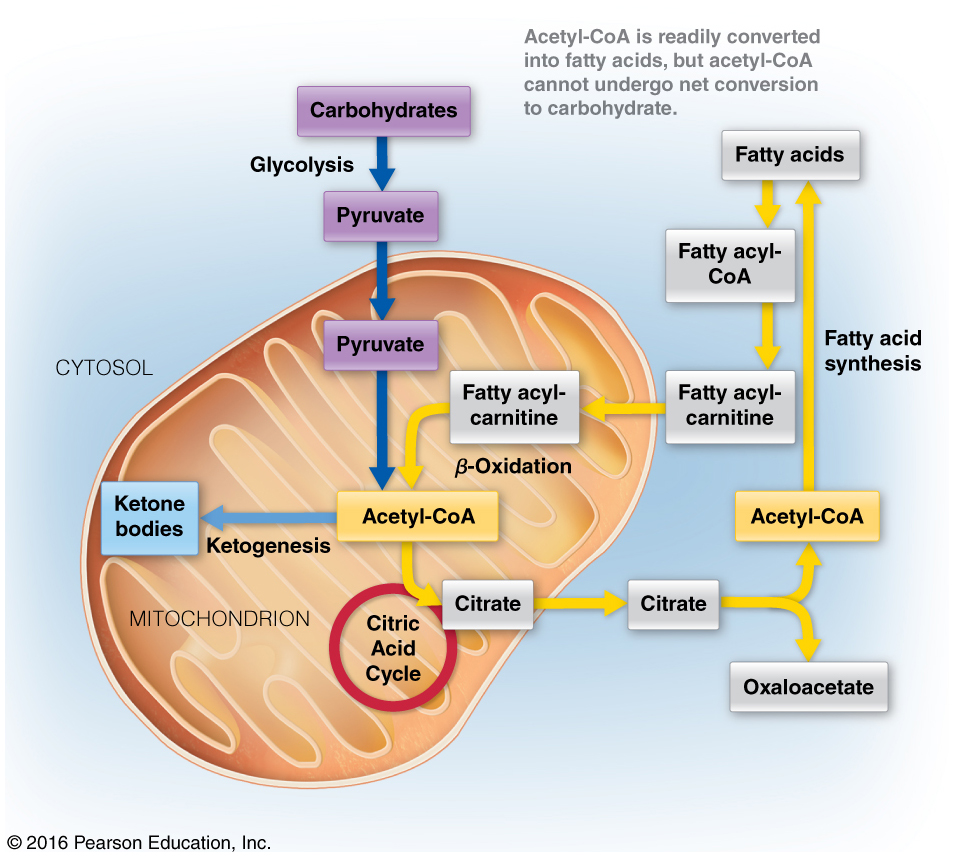
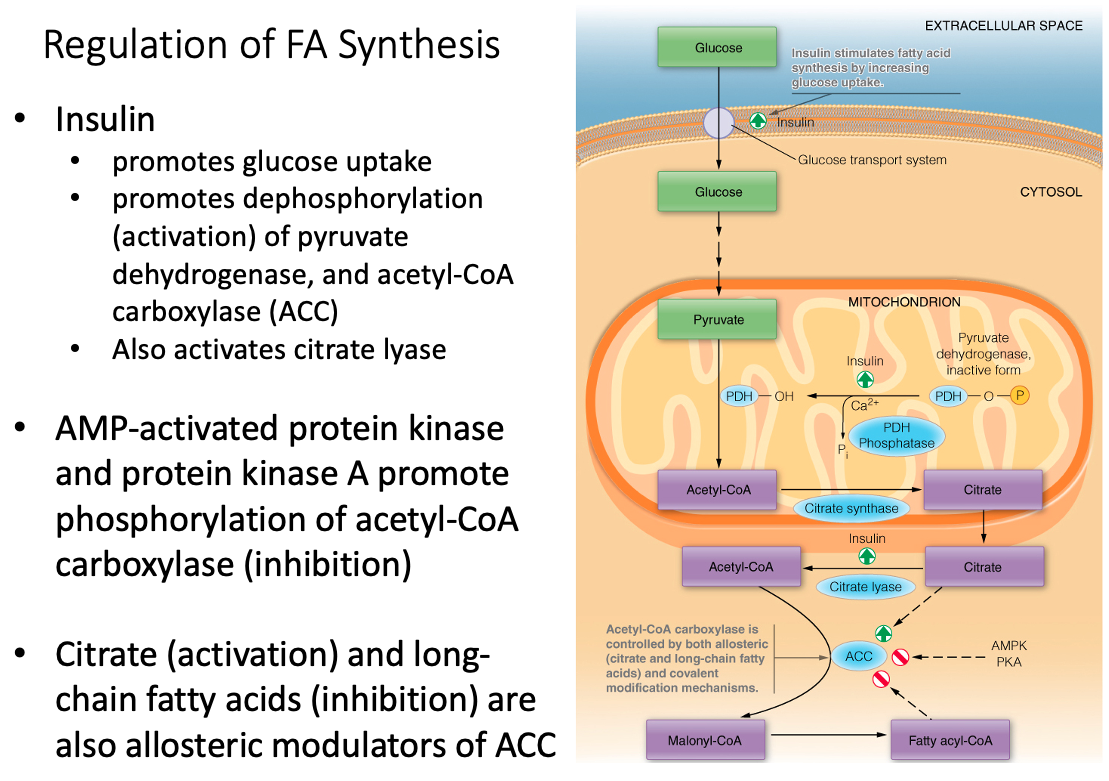
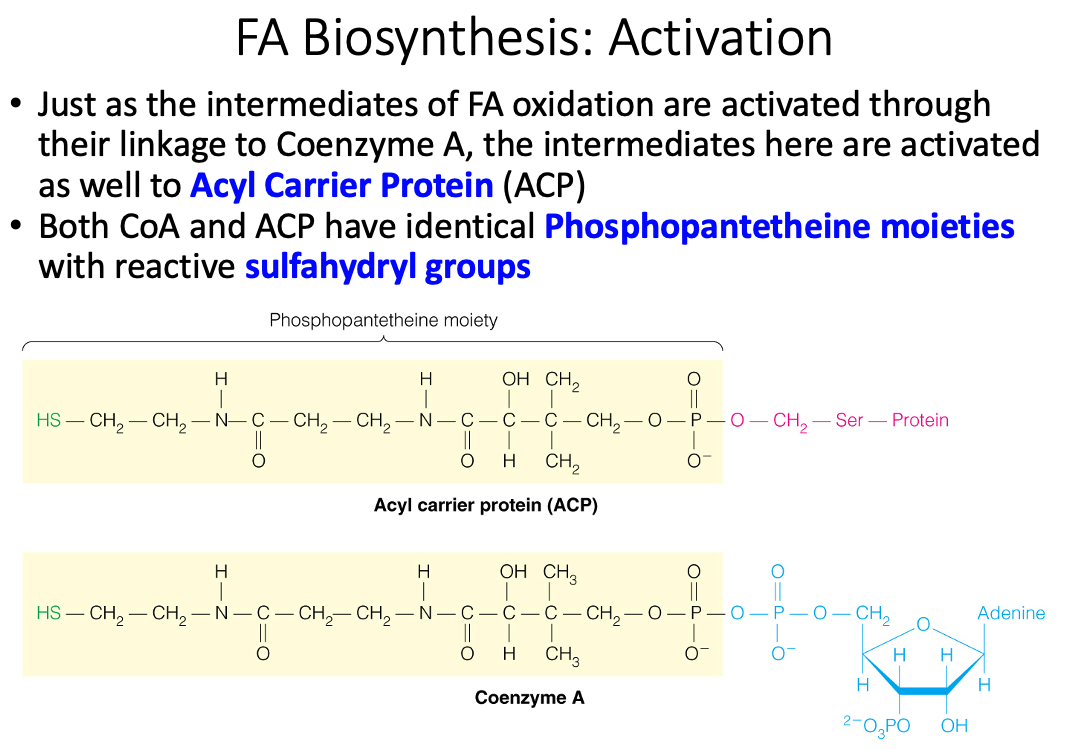
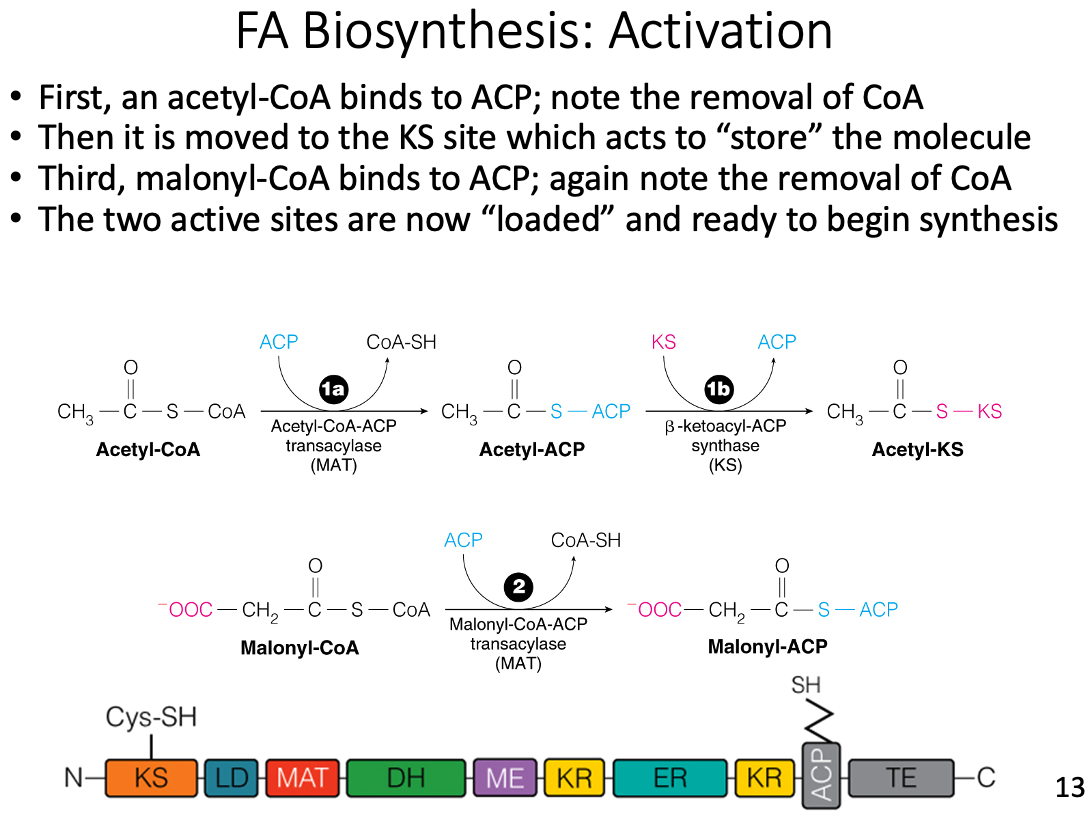


Discuss the metabolic rationale for phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)
| -oxidation | Fatty Acid Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Catabolic | Anabolic |
| Location = mitochondria | Location = cytoplasm |
| Separate soluble enzymes are used | 1 multifunction enzyme is used |
| Acyl Carrier = CoA | Acyl Carrier = Protein bound phosphantethiene |
| NAD , FAD | NADP |
| Precursors = Fatty acyl CoA Products = Acetyl CoA | Precursors = Acetyl CoA and Malonyl CoA Products = Fatty Acid Chains |
| Regulation = Substrate Availability | Regulation = Allosteric |
Would it be possible to synthesize a fatty acid in mammalian cells starting from a C-16 or C-18 carbon fatty acid? Explain
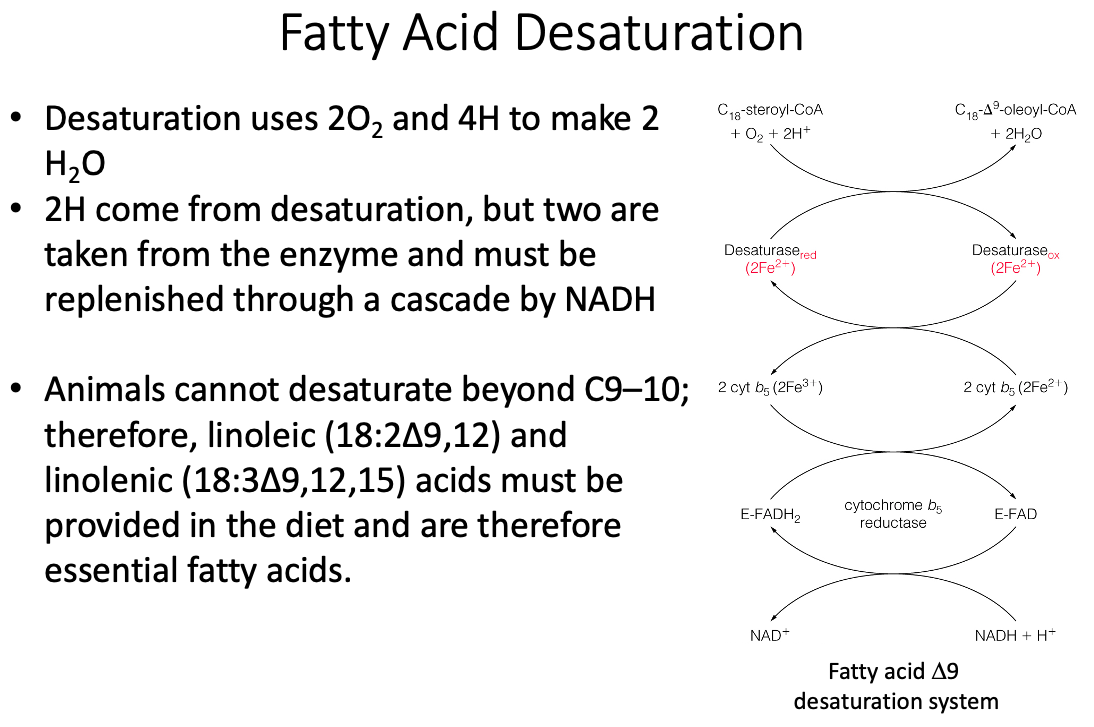
- No , fatty acid takes place in plants
- Mammals are not able to introduce double bonds in fatty acid beyond carbon 9
- Mammals only have , , 5, and
What is the system name for a C-18 fatty acid? Is such a fat essential? How do you know?
- delta-x =
- omega-x =
- Linoleic Acid
- Essential Fatty Acid
- We can't make double bonds past carbon 9, so therefore it is essential.
What is the system name for a C-18 fatty acid? Is such a fat essential? How do you know?
- delta-x =
- omega-x =
- Essential Fatty Acid
- We can't make double bonds past carbon 9, so therefore it is essential.
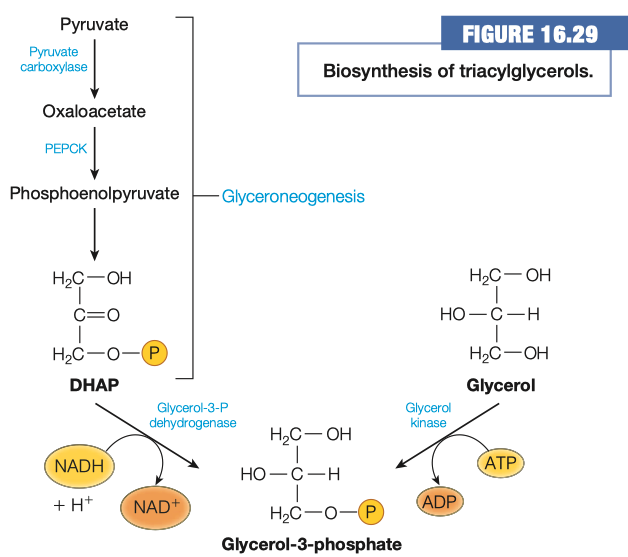
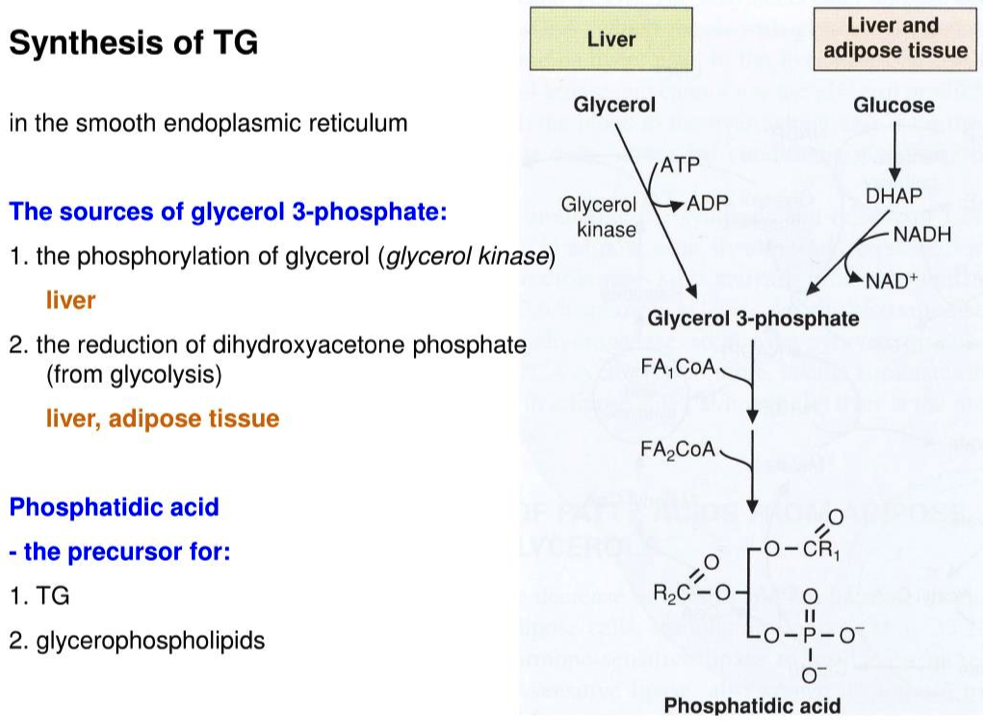
Explain why adipocytes ( fat cells ) need glucose to synthesize triglycerides.
Adipocytes don't have glycerol kinase to turn glycerol into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- So they have to use the glycolytic intermediate DHAP to synthesize G3P
The 3-carbon glycerol backbone of triglycerides is derived from the 3 carbon glucose breakdown products
How does this Acetoacetate act to fuel contraction in cardiac myocytes?
- Acetoacetate and insulin stimulate the incorporation of glucose into glycogen and change the relative contribution of exogenous glucose and endogenous carbohydrate to myocardial energy metabolism, but they most likely do so by different mechanisms
- Insulin and acetoacetate have additive effects on increasing the incorporation of exogenous glucose into glycogen
- Insulin stimulation and acetoacetate oxidation affect the relative contributions of exogenous glucose and endogenous carbohydrate including glycogen to energy metabolism
Even in the presence of acetoacetate, pyruvate is required to maintain flux through the citric acid cycle. Explain
- Acetyl CoA is converted to acetoacetate ( a ketone body )
- Acetoacetate is transported by the blood to the extrahepahic tissues, where it is oxidized via the citric acid cycle to provide energy to skeletal muscles and renal cortex
- Pyruvate is required to maintain the acetyl-CoA concentration in the citric acid cycle
About ninety percent of the cholesterol used in cell membranes is synthesized in the liver. The rest is obtained from dietary sources. A single enzyme controls the entry of carbons into cholesterol biosynthesis. What enzyme is it? What molecules are given to individuals to lower endogenous cholesterol production?
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA)
- Regulatory enzyme for cholesterol metabolism
Cholesterol production is controlled by regulation of plasma cholesterol levels through low density and high density receptor mediated uptake.
The regulation can also be done by enzyme cholesterol acyl transferase.
The regulation of HMG-CoA and its activity levels
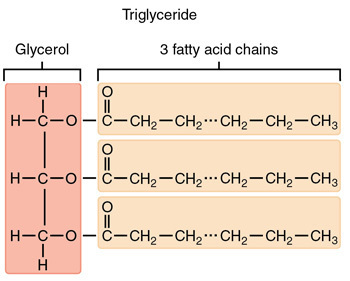
Triglyceride
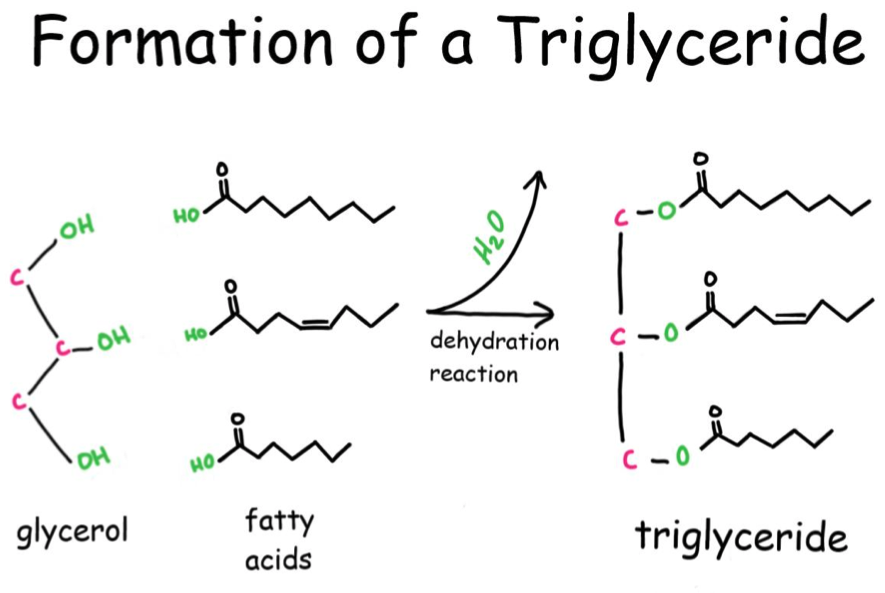
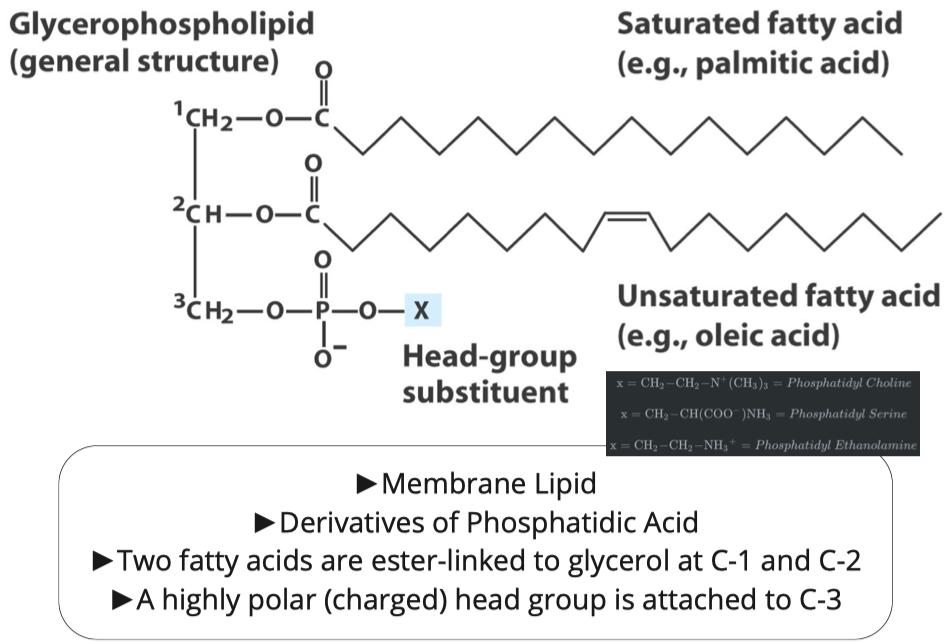
Glycerophospholipids
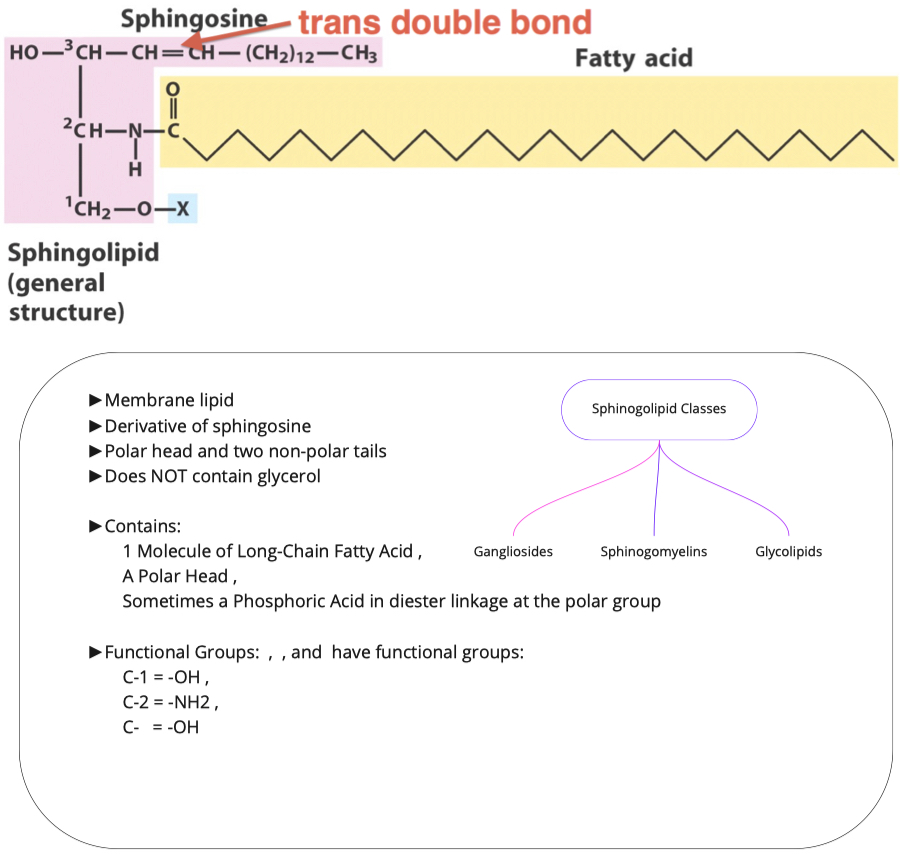
Sphinolipids
Triacylglycerols
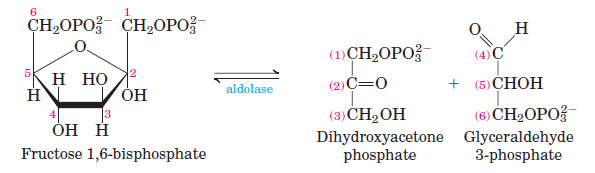
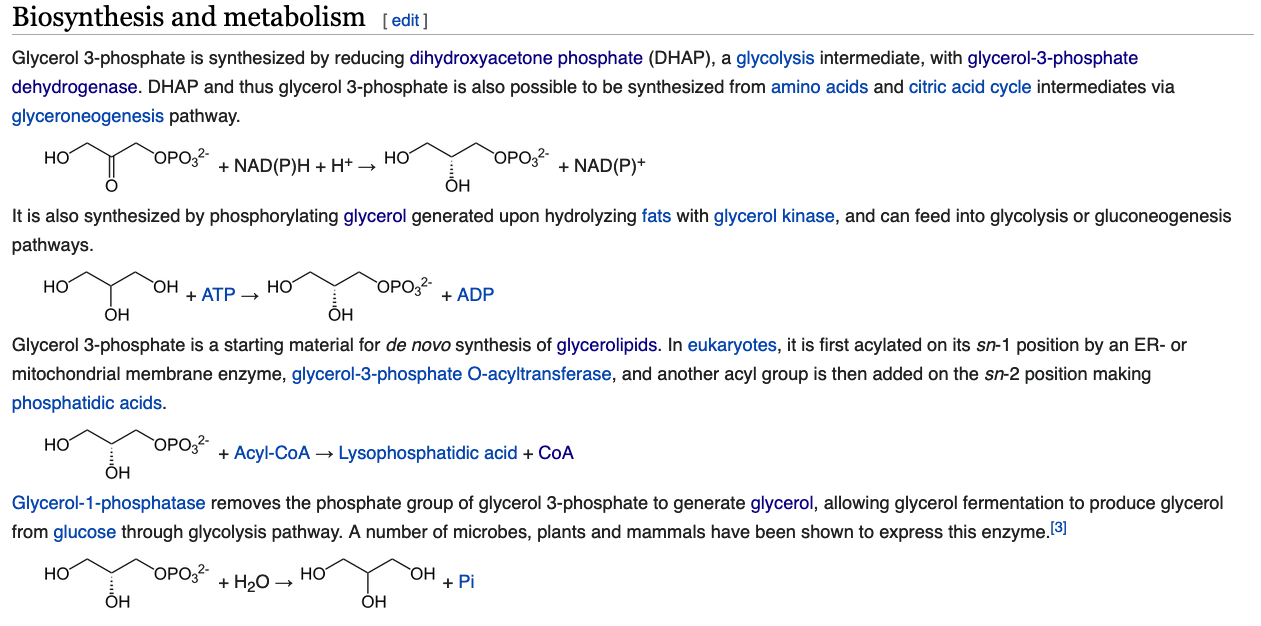
How is glycerol-3-phosphate made using intermediates in central metabolism? What metabolic pathway is this similar to? How is it different?
- Glycerol to Glycerol-3-phosphate is similar to glycolysis
- Pyruvate to DHAP is similar to gluconeogenesis
- Overall , energy consuming step and rate limiting step
Which method is used in adipocytes and why?
- Adipocytes don't have glycerol kinase
- Adipocytes get DHAP from glycolysis
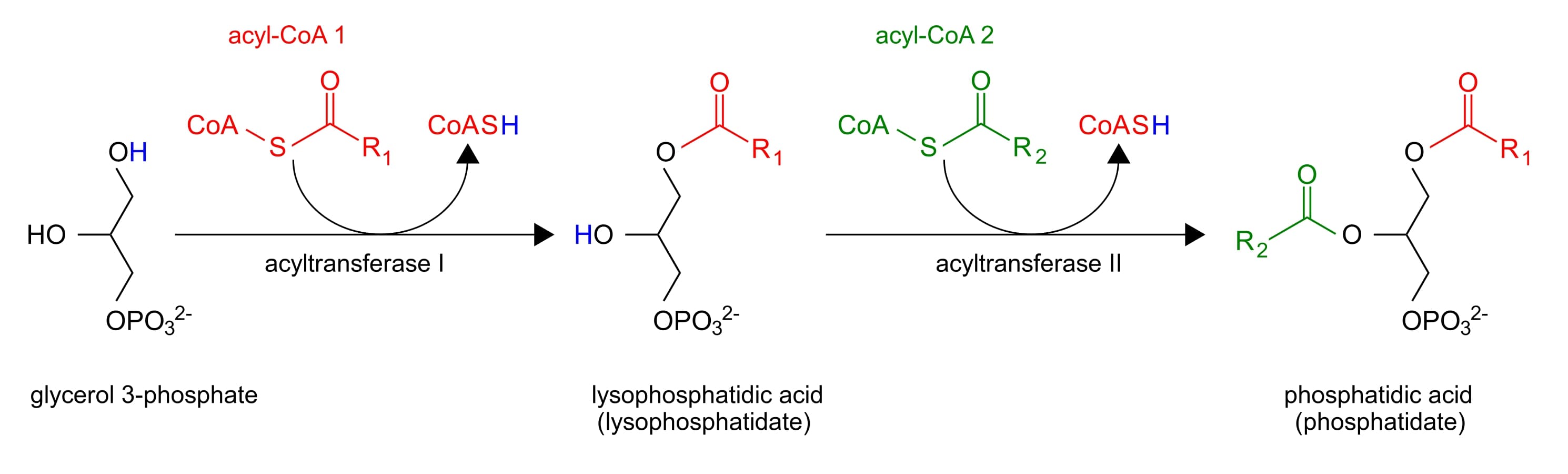
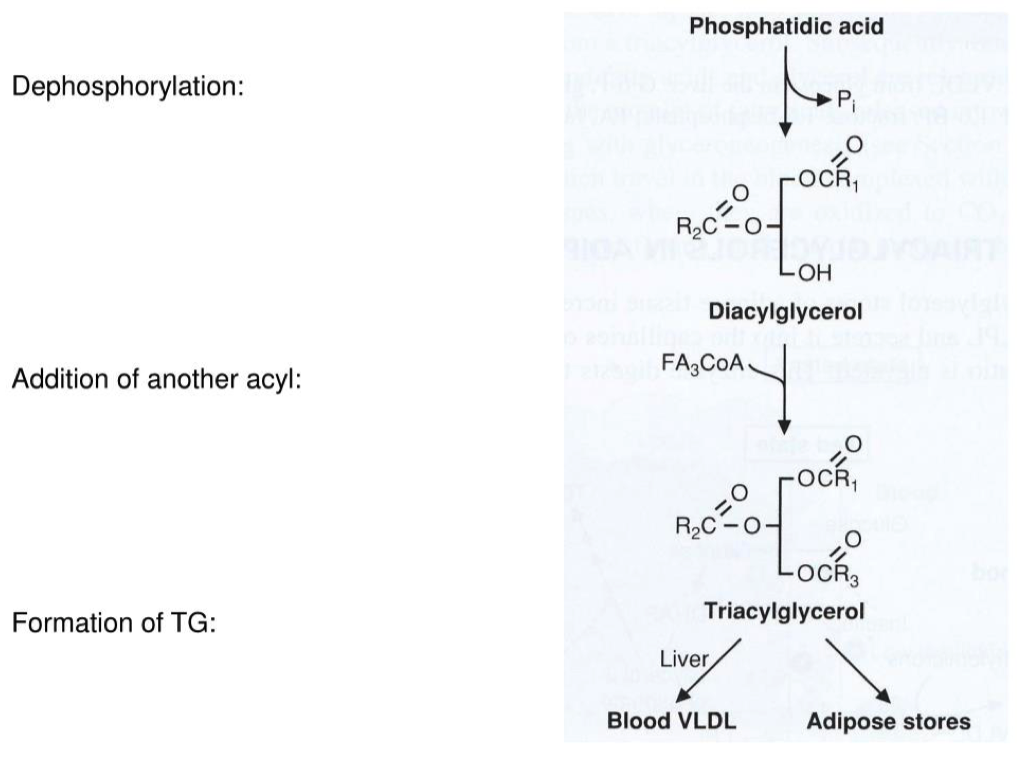
Now that we have Glycerol-3-phosphate, two fatty acids are added via esterification reactions. What class of lipids are generated in this step?
Adding two fatty acids to glycerol-3-phosphate to make a phosphatidic acid
To make a triacylglycerol:
- you have to first make a phospholipid
- You then have to remove the phosphate head and make diacylglycerol
- And then add the 3rd fatty acid to make a triacylglycerol
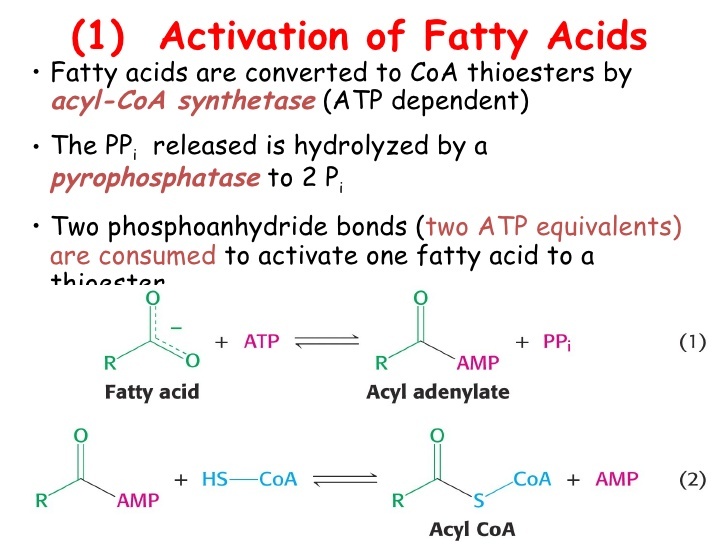
Are fatty acids Activated?
- Fatty acids first be converted to an active intermediate before they can be catabolized
- This is the only step in the complete degradation of fatty acid that requires energy from ATP
- The activation of a fatty acid is accomplished to two steps
Phosphatidic acids have two fatty acid chains, but triacylglycerols have three. What remaining steps must take place in order for triacylglycerol synthesis to be completed?
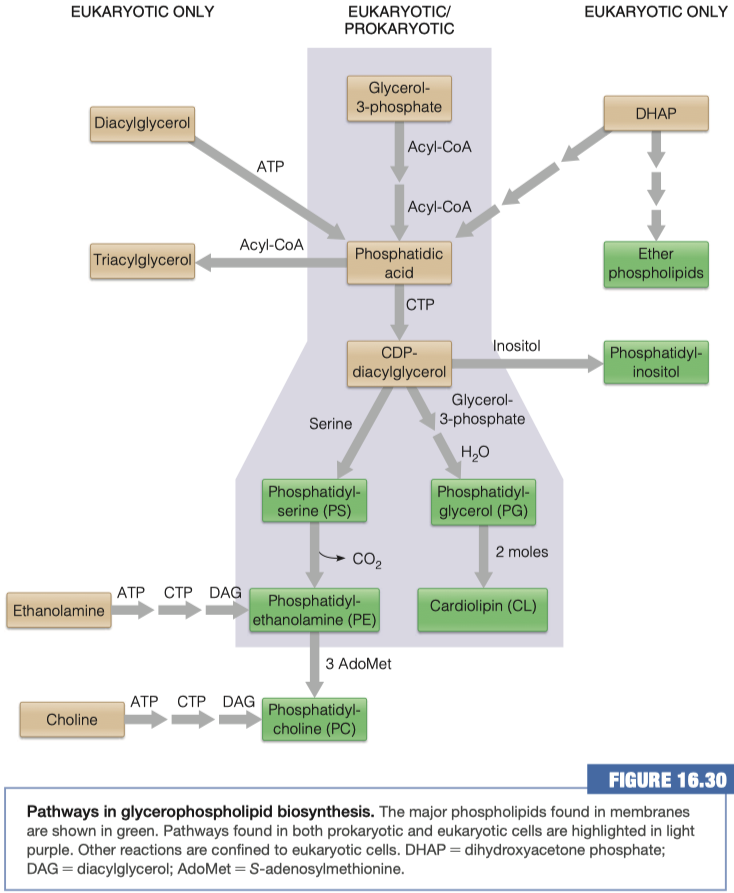
Glycerophospholipids
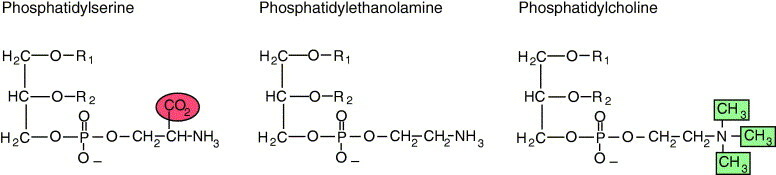
Similar to triacylglycerols, the glycerophospholipids use phosphatidic acid as a precursor, indeed phosphatidic acids are glycerophospholipids themselves. What are the six main phospholipid classes found in our membranes?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Membrane_lipid#Major_classes
- Phospholipids
- Glycolipids
- Fatty Acids
- Phosphoglycerides
- Sphinogolipids
- Sterols
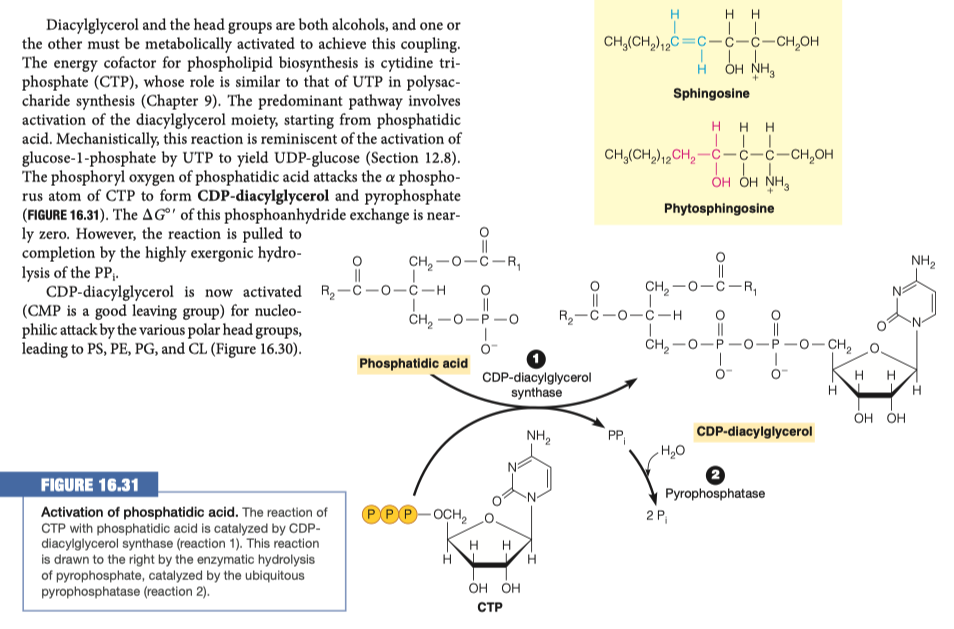
In order to modify the phosphate group on the phospholipid it must first be activated. How is the phosphatidic acid activated?
Phosphatidic acid is activated by adding CTP
- a is removed
CDP-diacylglycerol is similar to:
In the pentose phosphate pathway, adding UTP to glucose to make UDP-glucose
Glycogen synthesis
In the first steps going backward in glycogen synthesis, you have to activate your sugars
Similar idea of having something available as your leaving group to provide the energy for something to takes places
In this instance we are making CDP-diacylglycerol
- CDP-diacylglycerol is the precursor to many different glycero-phospholipids
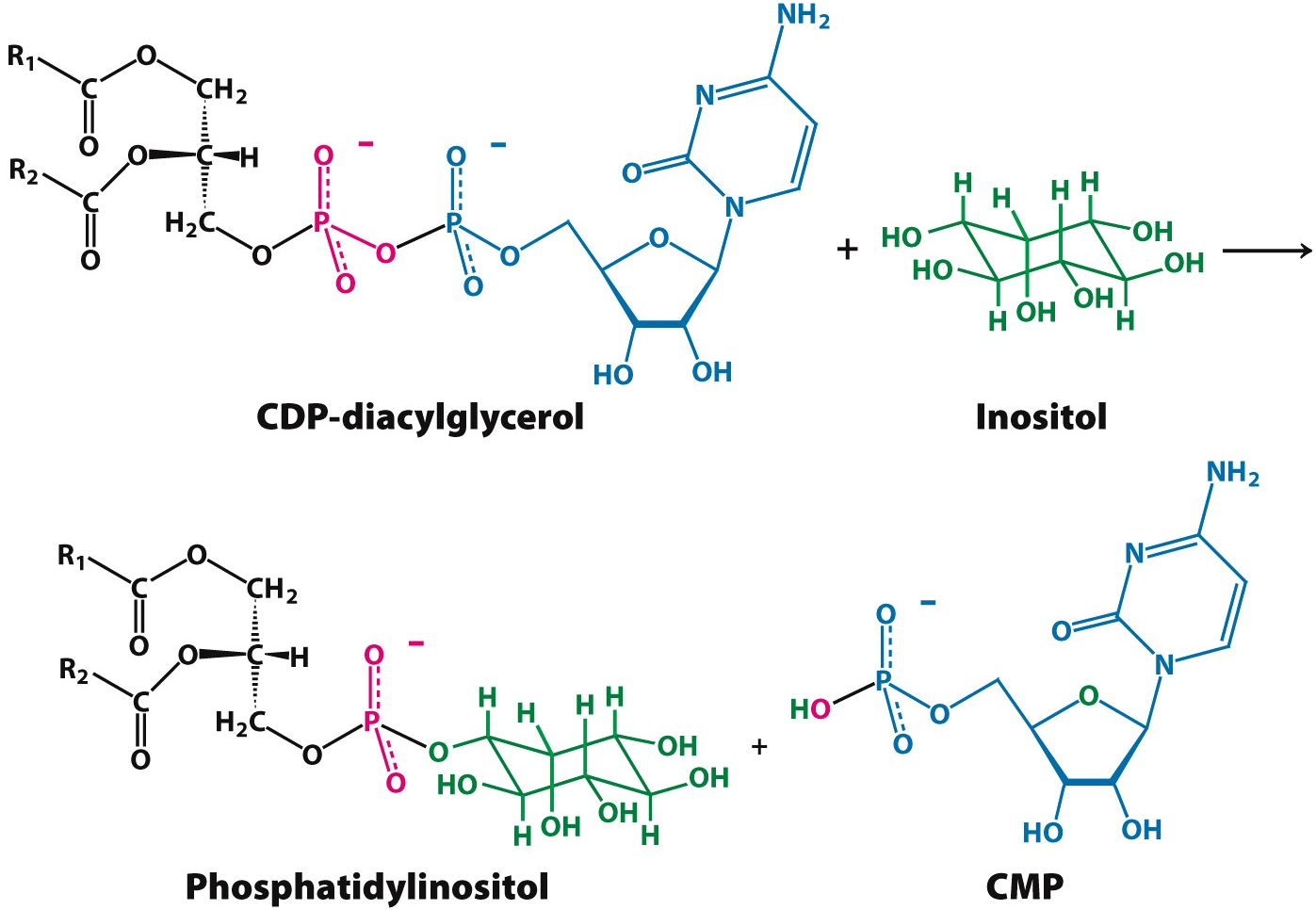
In order to make what molecule must be added to CDP-diacylglycerol and where?
Inositol group replaces CDP-diacylglycerol
Sphinogolipids
What are the two molecules needed to make sphingosine? How is this different from triacylglycerol and phospholipid synthesis?
- palmitoyl CoA and Serine
- In Triacylglycerol synthesis we added two groups, here we are adding a serine
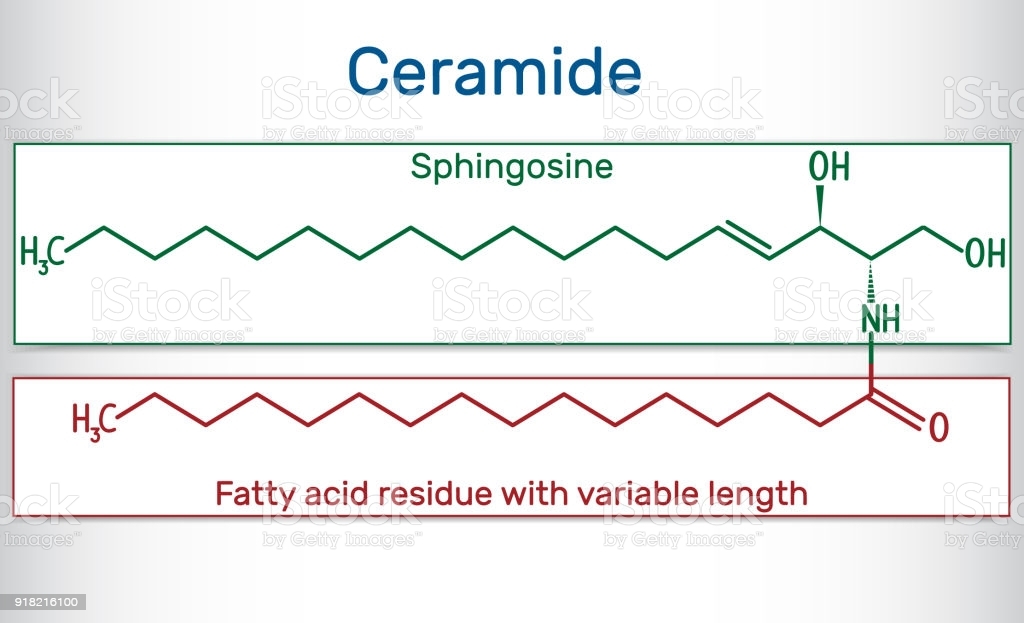
What must be added to sphingosine (and where) in order to make a ceramide? Is this an esterification reaction?
Ceramides:
do not have phosphates
have amide bridge
only two fatty acid chains
1 is unsaturated chain
- First fatty acid has very specific form and structure because it comes from palmitoyl
- we do processing to make it unsaturated
1 is unsaturated or saturated chain
Glycerophospholipids:
- do have phosphates
- 3 fatty acid chains
making an amide link
What is added to a ceramide to make sphingomyelin? What other group of lipids is this similar to?
Adding a phosphate group
- Specifically, adding Phosphatidylcholine
- Phosphate is left, and diacylglycerol leaves as side product to be reused somewhere
Similar to Phosphatidylcholine
Cerebroside is in the class of lipids called glycosphingolipids. What molecules must be added to ceramide to make this class of lipids?
- Ceramide + sugar = cerebroside = "glycoso-sphino-lipid"
New carbon units are loaded onto which subunit of fatty acid synthase?
- Acyl carrier protein (ACP)
- New carbon units, from malonyl-CoA, are covalently loaded onto acyl carrier protein (ACP) at the beginning of each new cycle.
What is reduced in each round of fatty acid synthesis?
The beta carbonyl carbon of the acyl chain
- In each round of fatty acid synthesis, occurring on fatty acid synthase, NADPH is oxidized to NADP+.
- The electrons stripped from NADPH are used to reduce the growing beta-carbonyl carbon fatty acyl chain.
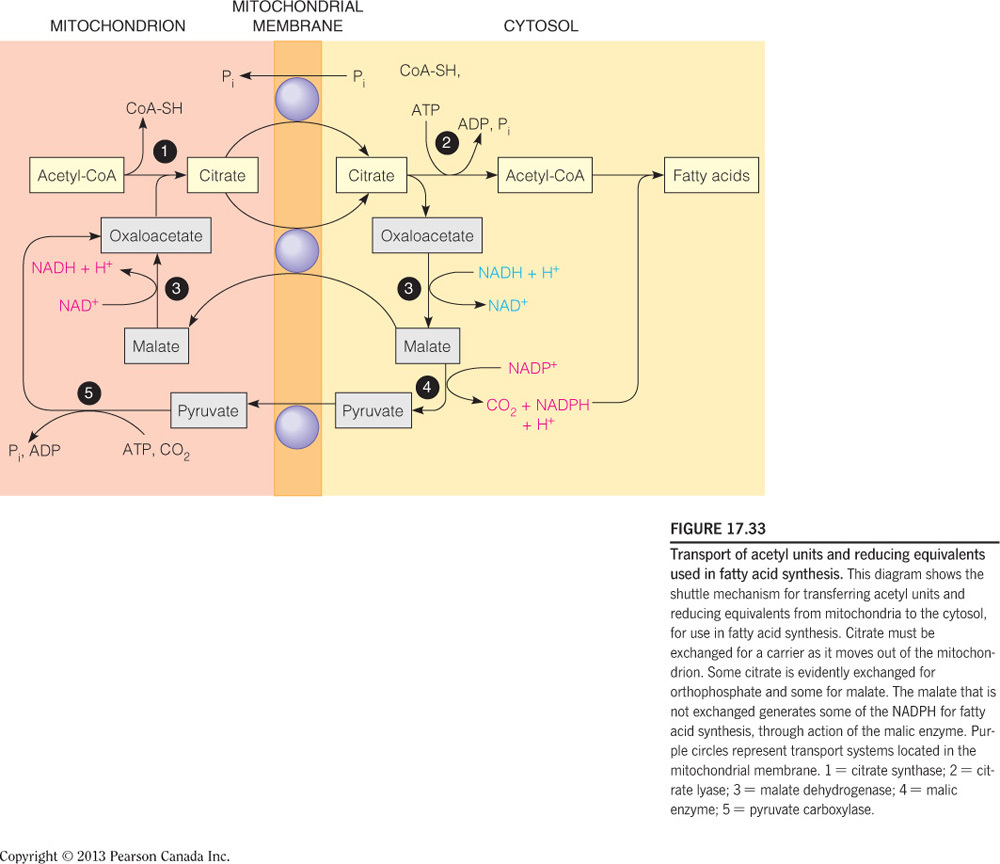
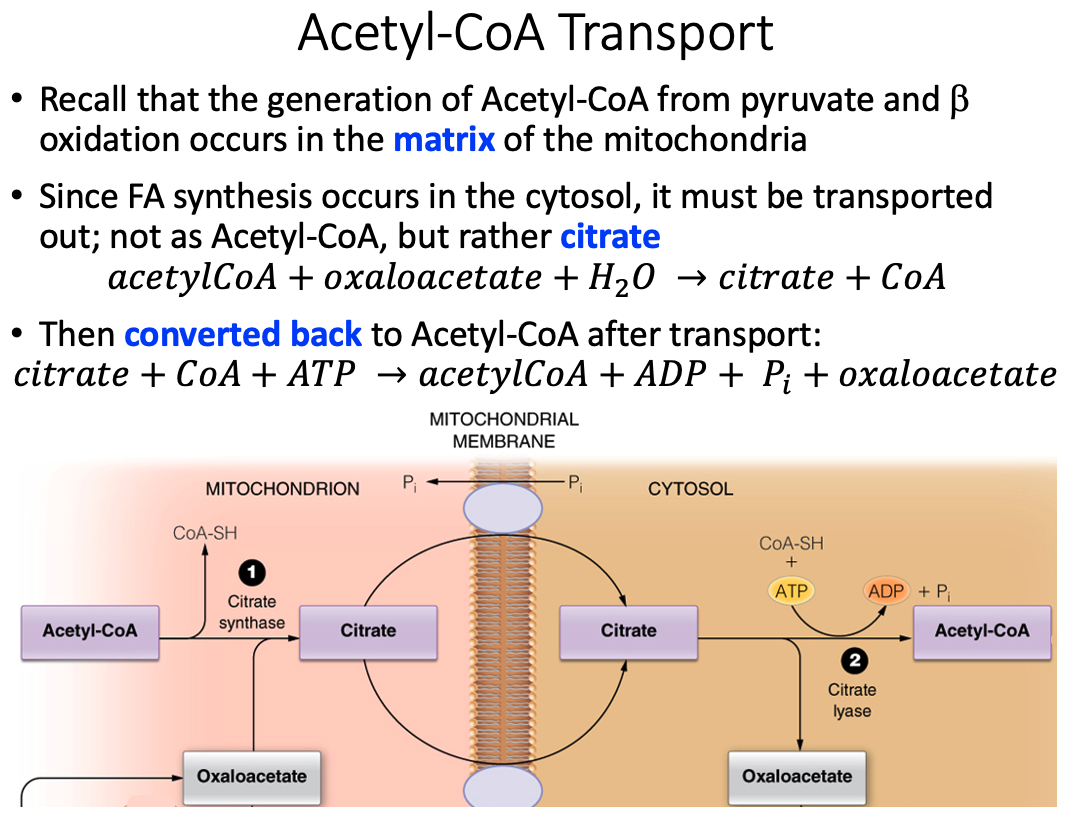
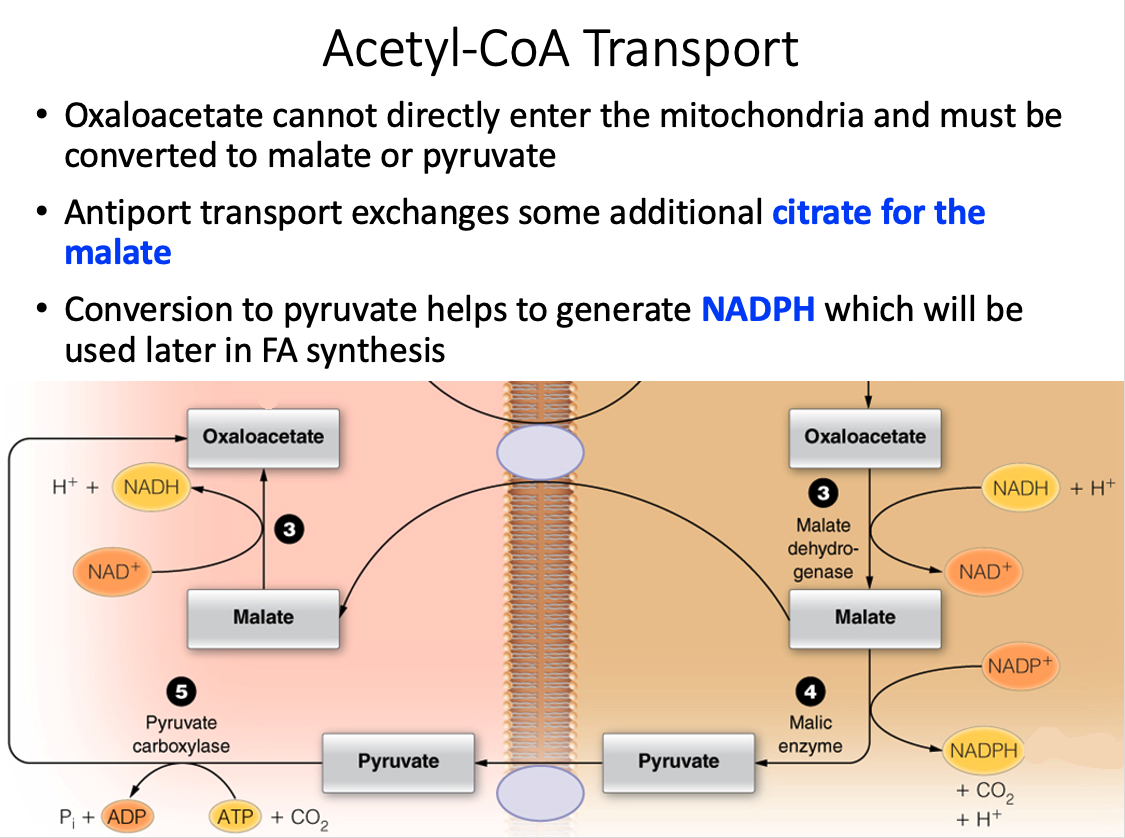
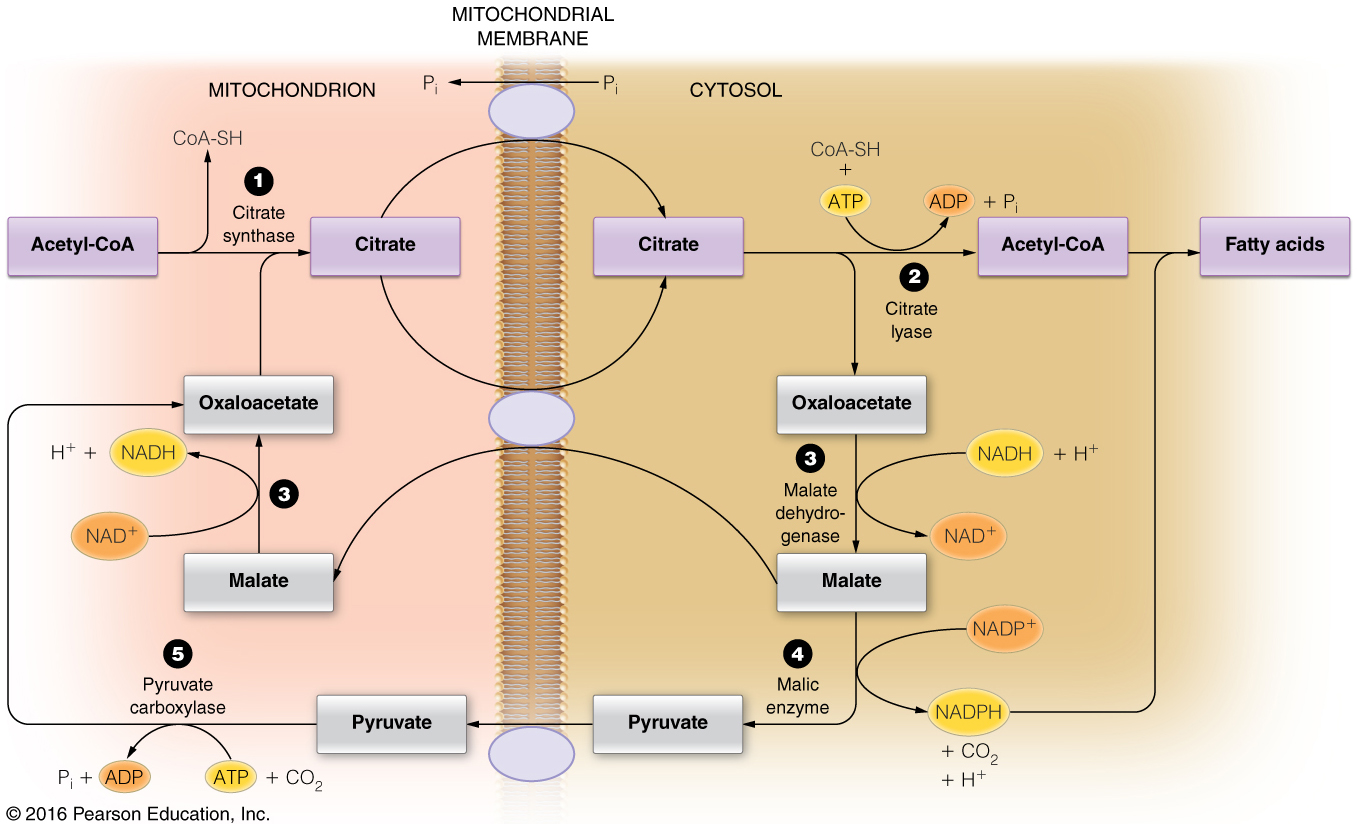
How is the two-carbon building block for fatty acid synthesis moved from the mitochondrial matrix into the cytosol?
Citrate shuttle
- Acetyl-CoA, the two-carbon building block of fatty acid (and sterol) synthesis is generated in the mitochondrial matrix and needs to be moved into the cytosol where the lipid biosynthesis enzymes reside.
- Acetyl-CoA, however, cannot cross the mitochondrial membranes and therefore the citrate shuttle system is required.
- In the matrix, citrate synthase combines OAA and acetyl-CoA to form citrate.
- When the citrate is high in the matrix, this molecule will be transported into the cytosol.
- In the cytosol, citrate lyase breaks this six-carbon molecule into acetyl-CoA and OAA.
- To complete the shuttle, OAA is reduced to malate and then malate is oxidized to pyruvate, which then crosses back into the mitochondrial matrix.
- The oxidation of malate to pyruvate generates NADPH, which is the coenzyme needed by fatty acid synthase.
- Thus, the shuttle serves two purposes: (1) to move acetyl units into the cytosol and (2) to generate NADPH for fatty acid synthase.
- This process is summarized in the figure below.
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the rate-limiting step in sterol synthesis?
HMG-CoA reductase
What is oxidized in each round of fatty acid synthesis?
NADPH
- In each round of fatty acid synthesis, occurring on fatty acid synthase, NADPH is oxidized to NADP+.
- The electrons stripped from NADPH are used to reduce the growing beta-carbonyl carbon fatty acyl chain.
Which molecule enters as the new carbon units in fatty acid synthase?
Malonyl-CoA
- Malonyl-CoA is covalently loaded onto ACP at the beginning of each new cycle.
- During condensation, the decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA generates a good nucleophile (enolate) that attacks the thioester carbonyl of the growing acyl chain.
How many cycles of fatty acid synthesis are required to synthesize a palmitate?
7
- Seven cycles of fatty acid synthesis are required to synthesize a palmitate.
- Palmitate is the 16:0 fatty acid product of fatty acid synthase.
- Each cycle of catalysis increases the carbon chain by two carbons, except the first round where two two-carbon units are condensed.
- The subtraction of one accounts for the first cycle in fatty acid synthesis that condenses two two-carbon units.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in cellular fatty acid biosynthesis?
Citrate shuttle → Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase → Fatty Acid Synthase
Fatty acid biosynthesis requires a two-carbon building block, acetyl-CoA.
This molecule is made in the mitochondrial matrix and cannot cross into the cytosol, where fatty acid biosynthesis occurs
- therefore, the citrate shuttle is needed to ferry two carbons across the mitochondrial membranes.
Once citrate is in the cytosol, citrate lyase breaks citrate into acetyl-CoA and OAA.
Acetyl-CoA is carboxylated by acetyl-CoA carboxylase to produce malonyl-CoA.
Malonyl-CoA is the carbon building block (in addition to one acetyl-CoA) used by fatty acid synthase.
Therefore, the correct order is: citrate shuttle → acetyl-CoA carboxylase → fatty acid synthase.
Things To Know
Why Fatty acid synthesis?
- Because carbohydrate storage is limited by size and quantity.
- Excess carbohydrates in the diet are converted to pyruvate and eventually acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA transport
- Molecular Carrier is Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP)
- Citrate ( mitochondria to cytosol )
Molecules involved
- NADP
- Precursors = Acetyl CoA and Malonyl CoA
- Products = Fatty Acid Chains
How NADPH is generated
- generated by reducing the beta carbonyl carbon on the fatty acid chain
Differences between Fatty acid oxidation and synthesis
- See Multiple Charts
How is Malonyl-CoA formed and why is it necessary?
- Acetyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase = Malonyl-CoA
- Necessary for both Fatty Acid Synthesis and Fatty Acid Oxidation
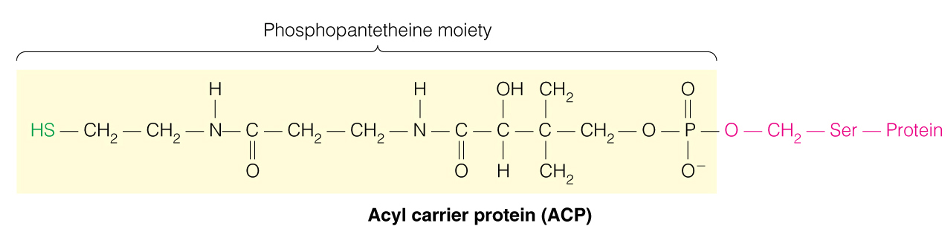
What is a Phosphopantetheine moiety and how are fatty acids attached?
- Acyl Carrier = Protein bound phosphantethiene
How many cycles to make palmitate
7
Quantities of reactants and products used/generated
FA Elongation
- process inside the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that adds 2 carbons from malonyl CoA to growing Fatty Acyl CoA
Desaturation
- Adding double bonds in specific locations to make non-essential fatty acids
Essential fatty acids
- Cannot be synthesized in human body
- Can't make double bonds past carbon 9
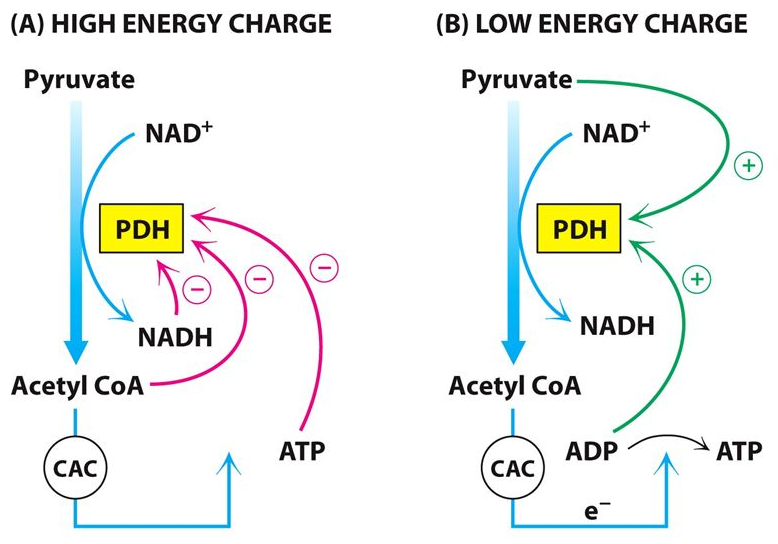
Regulation of ACC and pyruvate dehydrogenase
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) is Regulated By:
- allosteric ( citrate and long-chain fatty acids )
- covalent modification mechanisms
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase is Regulated By:
- Insulin promotes dephosphorylation (activation)