Complex Lipid Synthesis
Pre-Activity
Compare and contrast tryacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, and Sphinolipids
a. Look at overall structure
b. Look at individual components
c. Look at chemical properties
Using your analysis from Q1 , identify the main differences between the molecular groups above
a. Triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids
b. Triacylglycerols and sphinogolipids
c. Glycerophospholipids and sphinogolipids
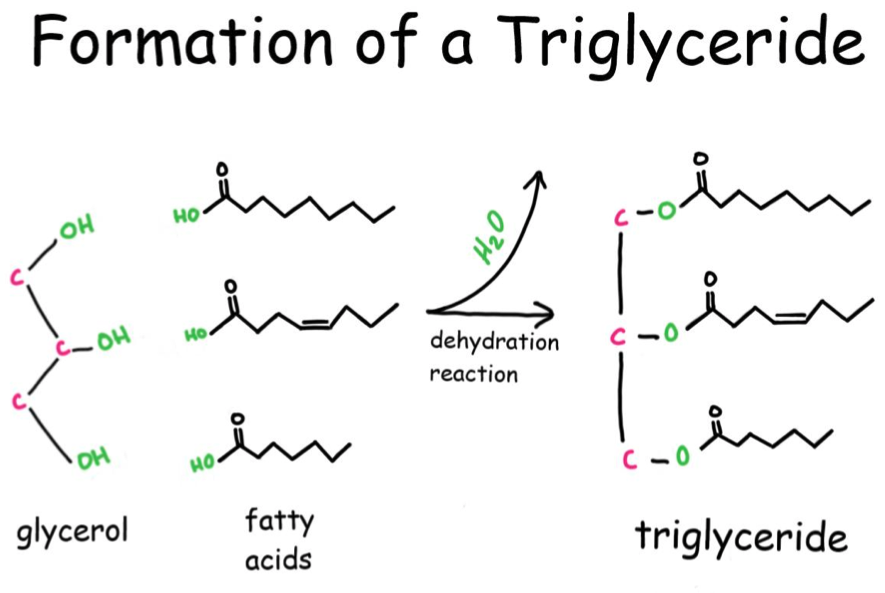
Triglyceride
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride
Glycerophospholipids
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycerophospholipid

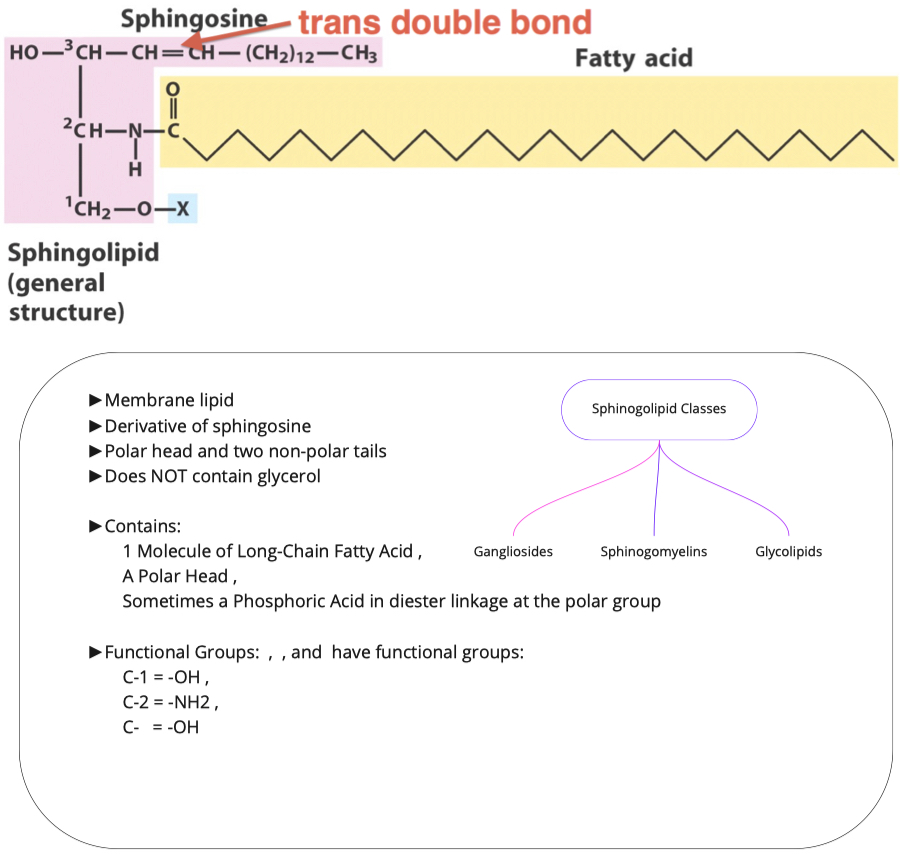
Sphinolipids
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sphingolipid
Activity
Triacylglycerols
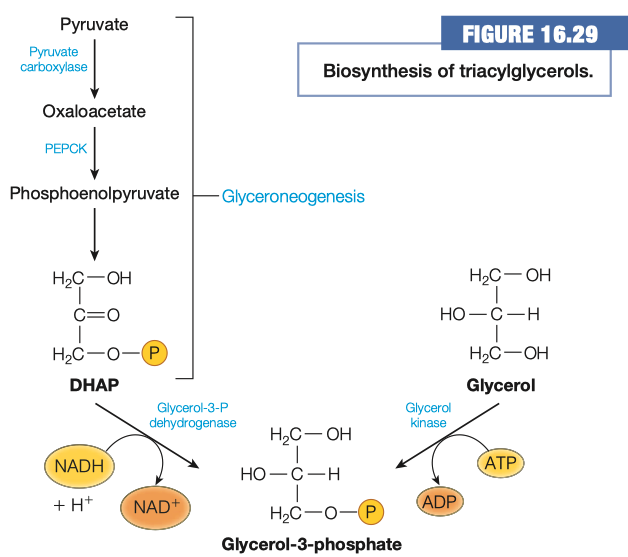
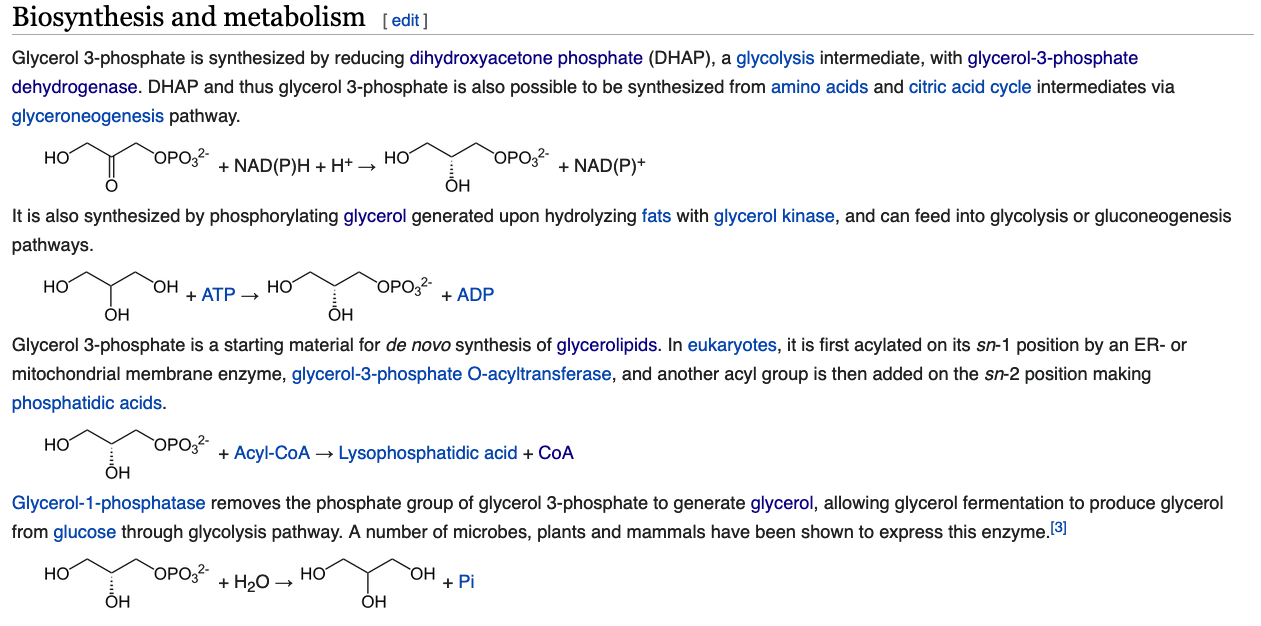
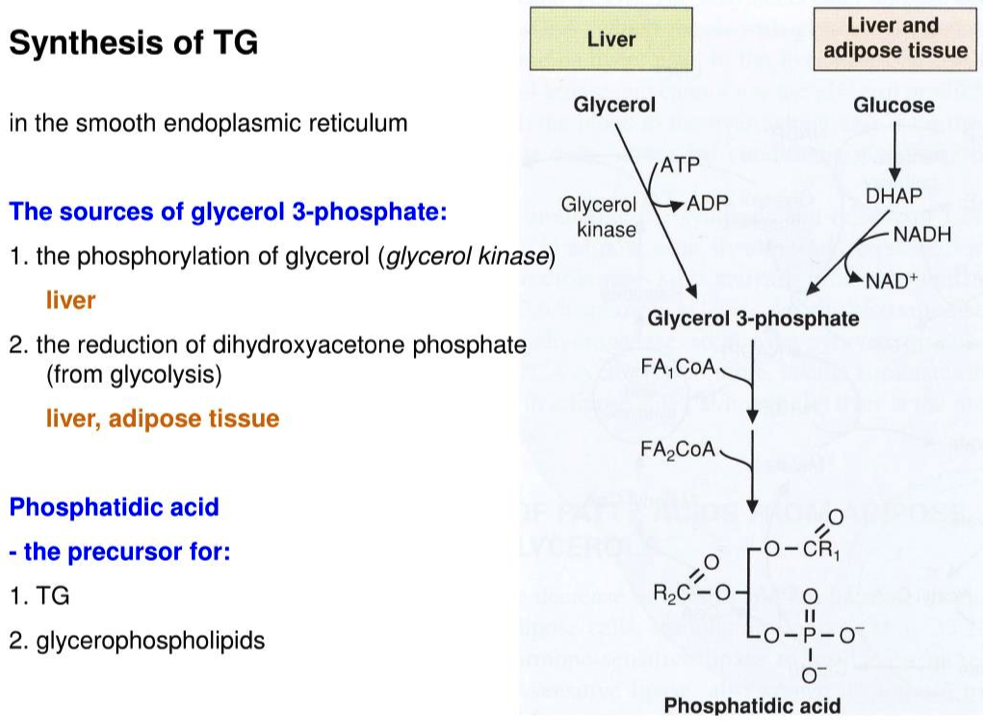
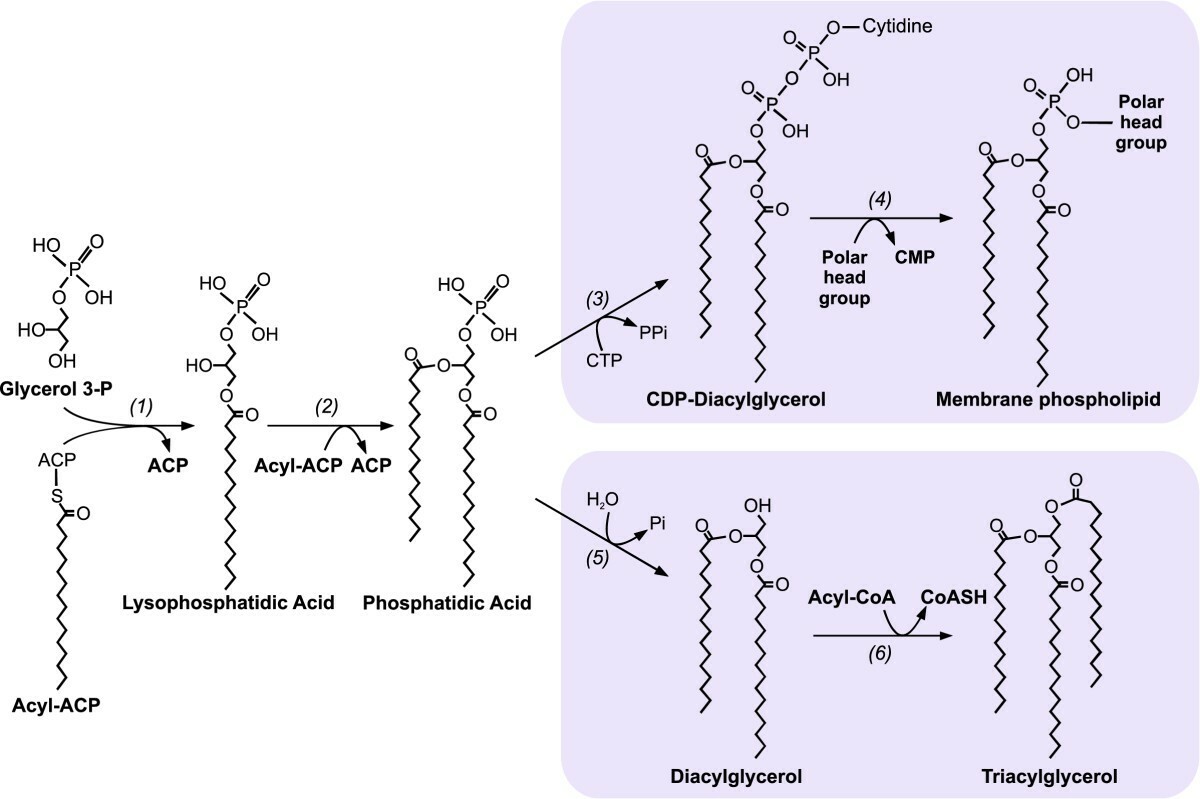
- As you undoubtedly know the backbone to a triacylglycerol is glycerol, however you might not be aware that the precursor needed is actually Glycerol-3-phosphate.
1.A. How is glycerol-3-phosphate made using glycerol?
1.B. How is glycerol-3-phosphate made using intermediates in central metabolism? What metabolic pathway is this similar to? How is it different?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycerol_3-phosphate
1.C. Which method is used in adipocytes and why?
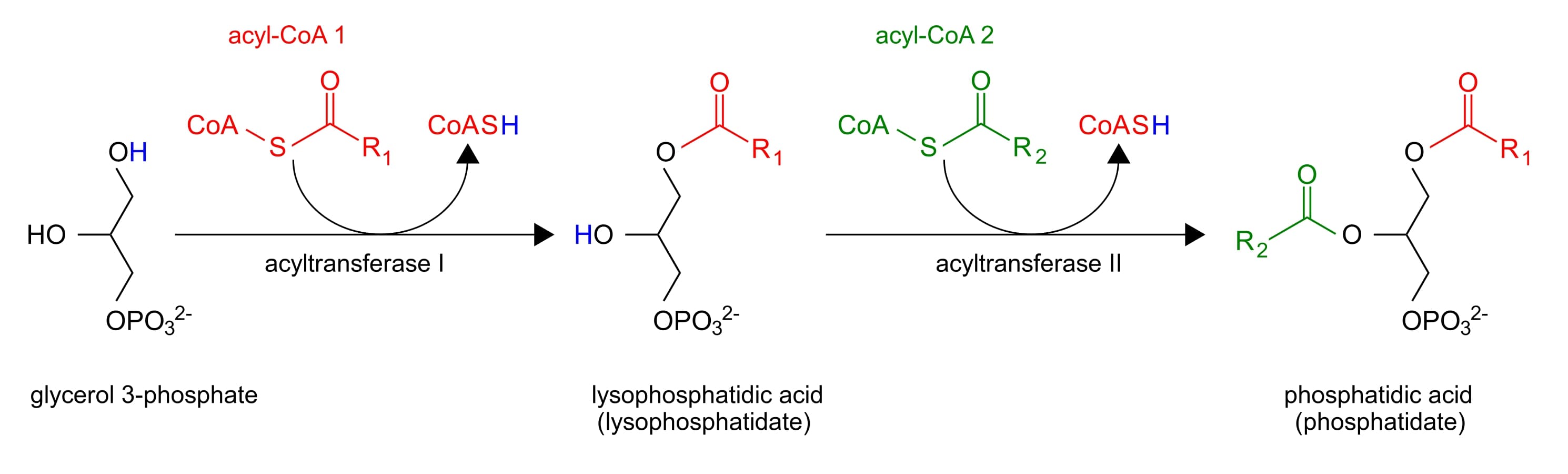
- Now that we have Glycerol-3-phosphate, two fatty acids are added via esterification reactions.
2.A. What class of lipids are generated in this step?
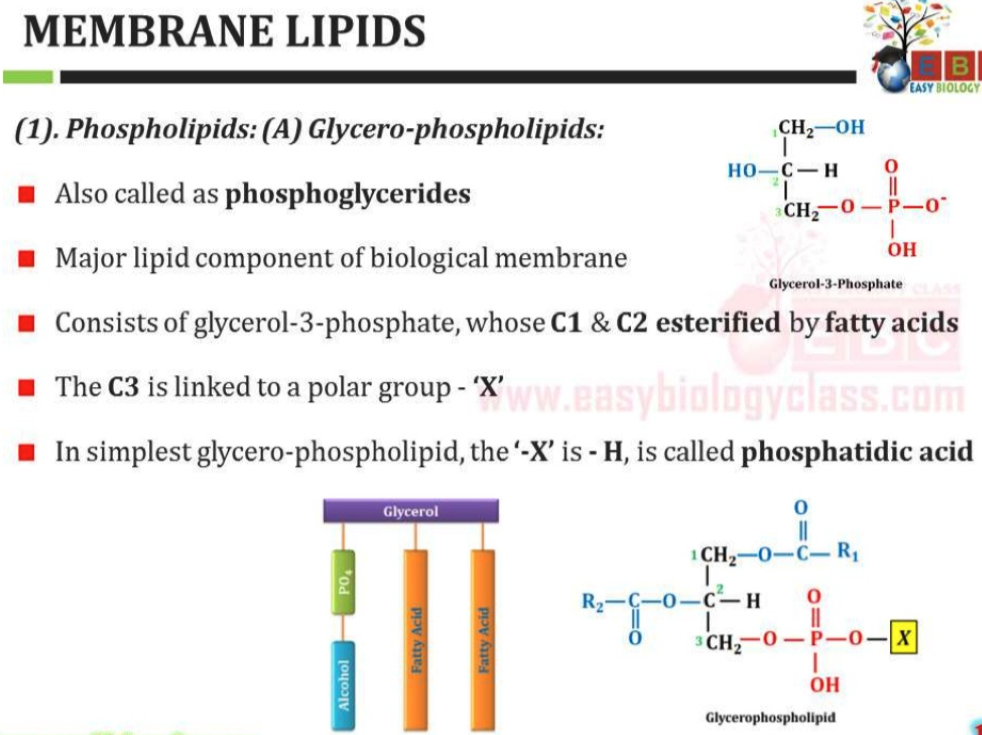
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatidic_acid
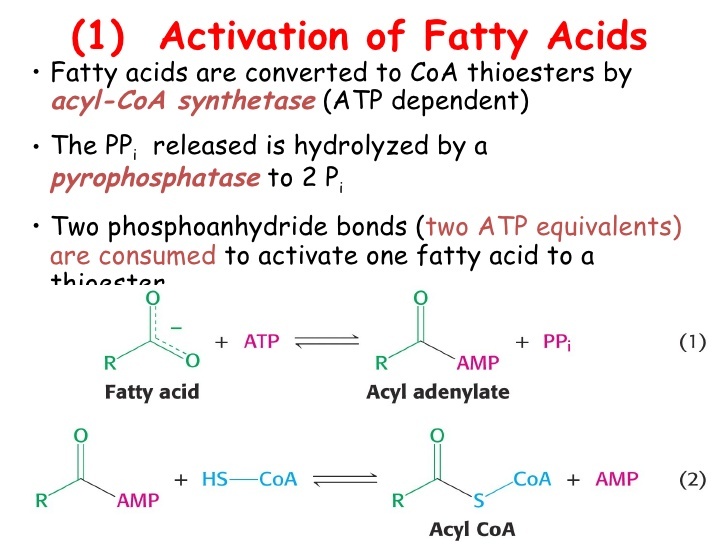
2.B. Are the fatty acids activated? How do you know?
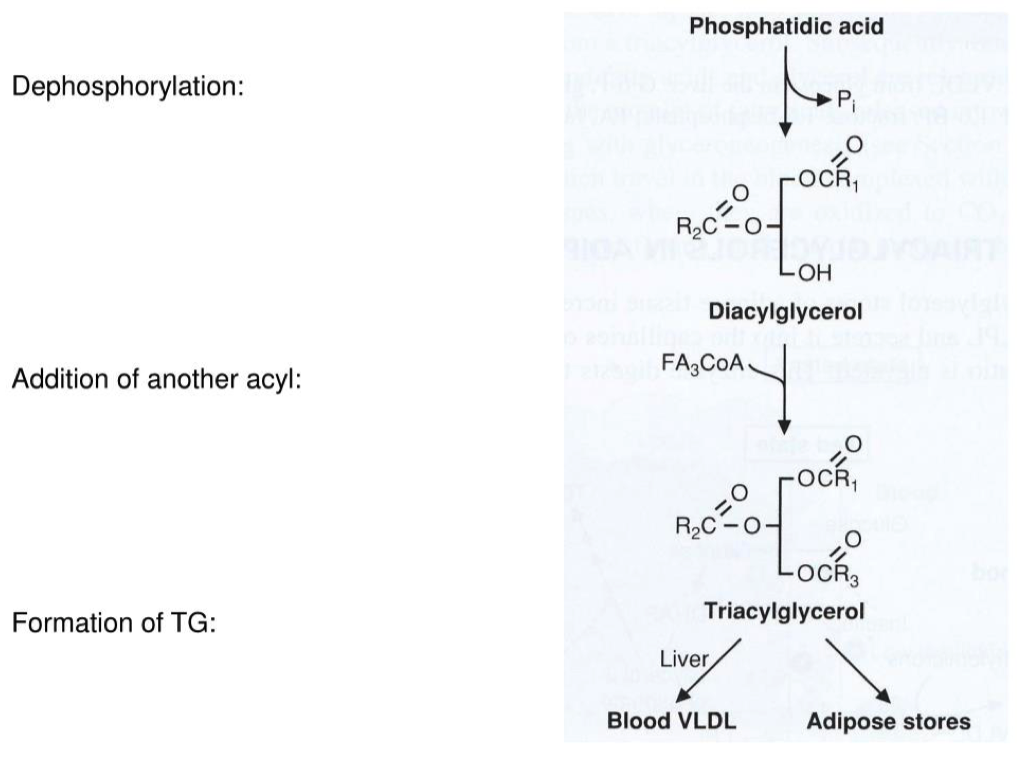
- Phosphatidic acids have two fatty acid chains, but triacylglycerols have three. What remaining steps must take place in order for triacylglycerol synthesis to be completed?
Glycerophospholipids
- Similar to triacylglycerols, the glycerophospholipids use phosphatidic acid as a precursor, indeed phosphatidic acids are glycerophospholipids themselves.
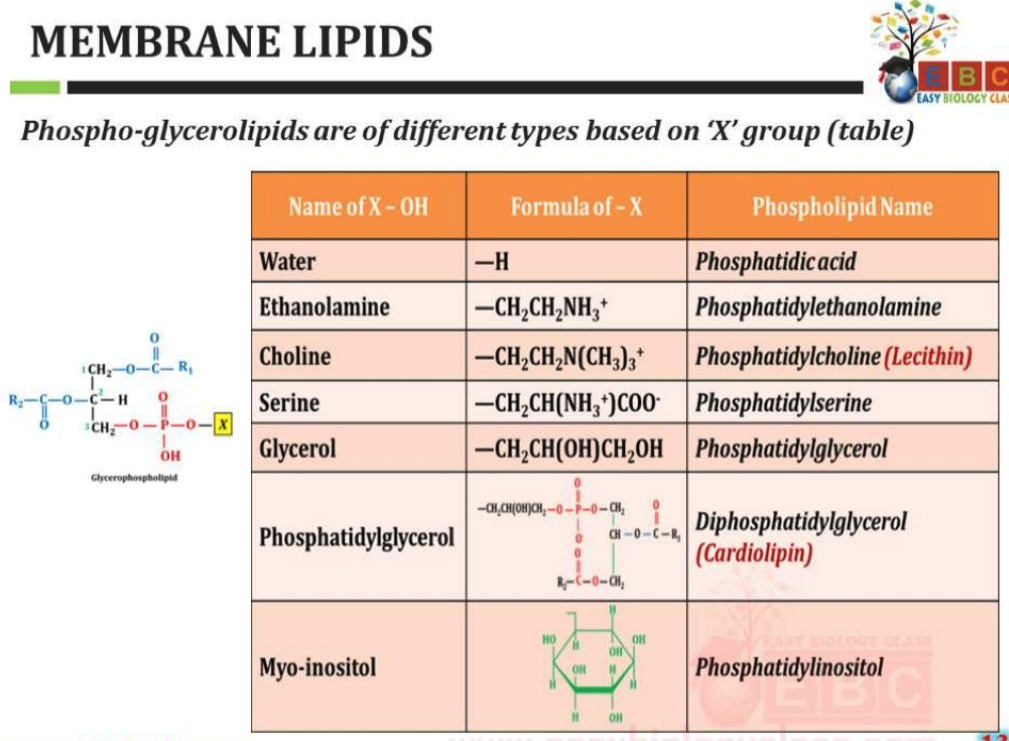
4.A. What are the six main phospholipid classes found in our membranes?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Membrane_lipid#Major_classes
- Phospholipids
- Glycolipids
- Fatty Acids
- Phosphoglycerides
- Sphinogolipids
- Sterols
4.B. How are these classes similar and different from phosphatidic acids?
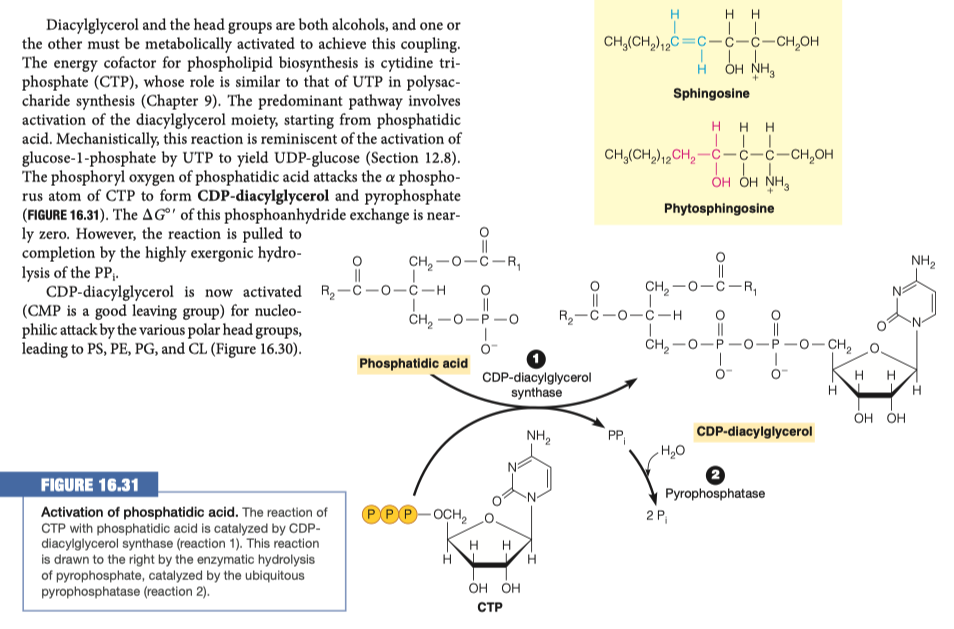
- In order to modify the phosphate group on the phospholipid it must first be activated.
5.A. How is the phosphatidic acid activated?
5.B. Where does the molecule join the phosphatidic acid?
- On the phosphate
- In order to make PI what molecule must be added to CDP-diacylglycerol and where?
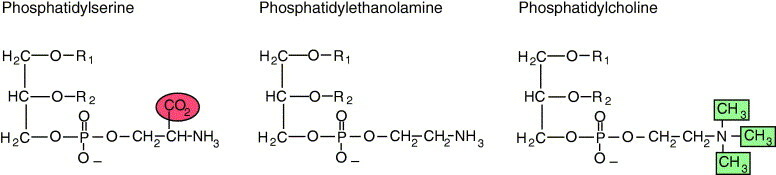
- In order to make PS, PE and PC a serine is joined to the CDP-diacylglycerol
7.A. Compare the structures of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine, how could one be converted to the other?
- Carboxylate alpha carbon
7.B. Compare the structures of PE and PC. What are the differences?
- Choline is all methylated
- Phosphatidylcholine can also be produced by three successive methylations of phosphatidyl-ethanolamine
- The methyl group donor in this pathway is an activated derivative of methionine, S-adenosyl-l-methionine (AdoMet).
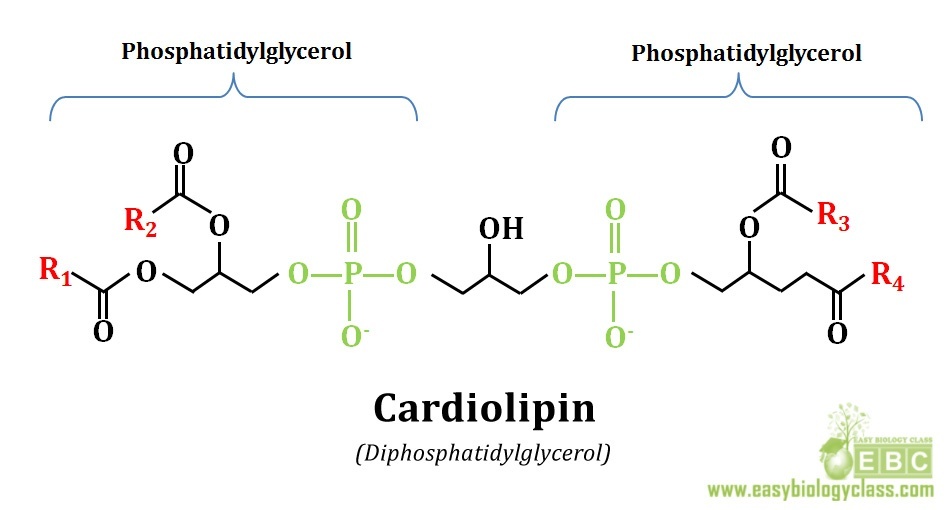
7.C. To make PG and CL a glycerol-3-phophate is added to the CDP-diacylglycerol. Compare cardiolipin and PG. What is added to PG to make CL?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiolipin
https://www.easybiologyclass.com/biochemistry-membrane-lipids-properties-structure-classification/
Sphinoglopids
- What are the two molecules needed to make sphingosine? How is this different from triacylglycerol and phospholipid synthesis?
asdf
- What must be added to sphingosine (and where) in order to make a ceramide? Is this an esterification reaction?
asdf
- What happens to the palmitoyl fatty acid to make ceramide?
asdf
- What is added to a ceramide to make sphingomyelin? What other group of lipids is this similar to?
asdf
- Cerebroside is in the class of lipids called glycosphingolipids. What molecules must be added to ceramide to make this class of lipids?
asdf