Dynamic Study Module - Gluconeogenesis and Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Calvin Cycle
- What is the function of the Cori cycle?
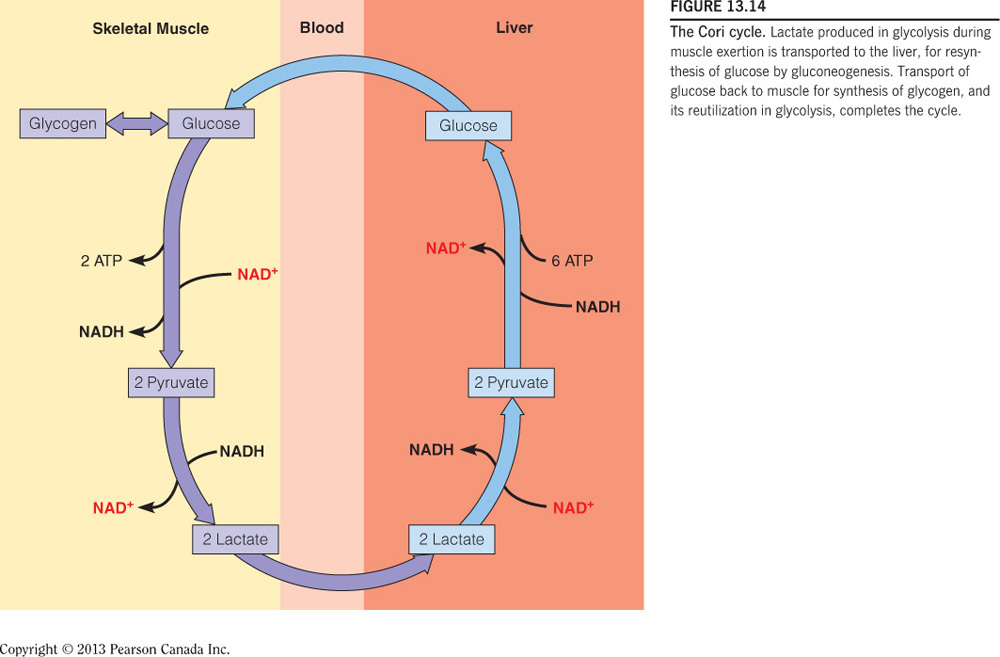
Lactate produced by glycolysis is transported from the skeletal muscle to the liver for gluconeogenesis, where the glucose produced can travel back to the skeletal muscle.
The Cori cycle occurs when the lactate produced by glycolysis is transported from the skeletal muscle to the liver for gluconeogenesis, in which the glucose produced can travel back to the skeletal muscle. The figure below diagrams the flow of molecules in the Cori cycle.
- If a person were deficient in vitamin B3, which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis would be directly affected?
The reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
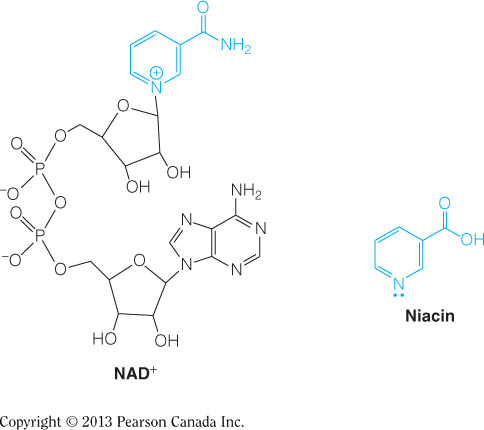
Vitamin B3 is niacin, which is added to a nucleotide to become NAD+/NADH, as seen in the figure below. The only enzyme in glycolysis that directly uses NAD+/NADH is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase use water as a substrate, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase uses GTP as a substrate. Pyruvate carboxylase uses a covalently bound biotin molecule to activate carbon dioxide for carboxylation of pyruvate.
- Which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis generates NADH?
None of the listed enzyme-catalyzed reactions in gluconeogenesis generates NADH.
None of the reactions in gluconeogenesis yield NADH, because this is an anabolic pathway and electrons are needed to build molecules, like glucose. The source of these electrons is NADH; therefore, NADH is a substrate and NAD+ is generated. This is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which in gluconeogenesis oxidizes NADH and uses the electron to reduce 1,3 BPG. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase decarboxylates OAA to yield phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide. Pyruvate carboxylase uses carbon dioxide as a substrate to carboxylate pyruvate. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyze the last two bypass reactions and use water to dephosphorylate their respective substrates, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
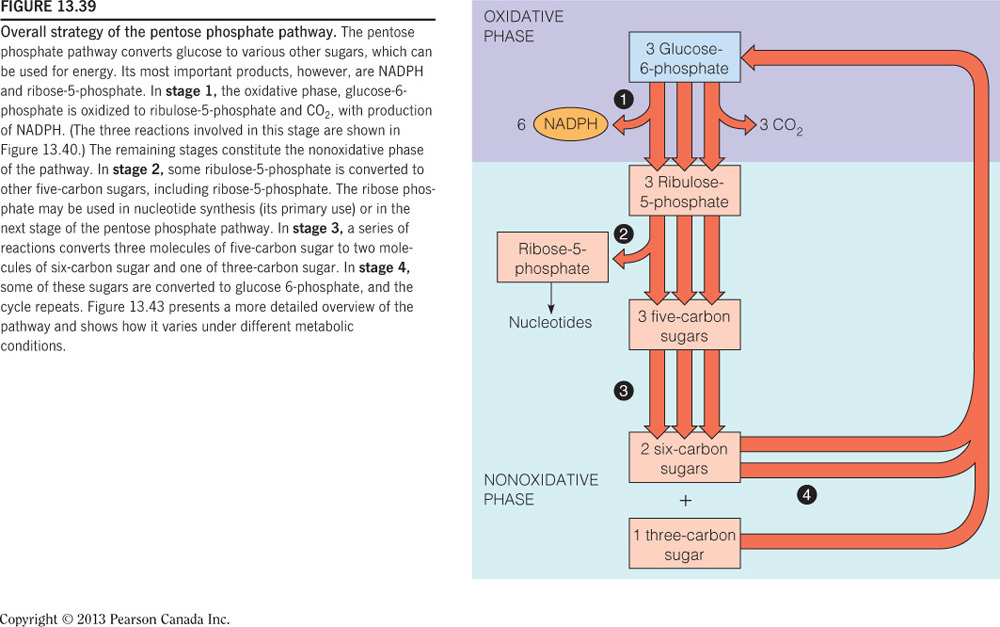
- Which of the following is a product of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Ribose-5-phosphate
The oxidative phase of PPP yields ribose-5-phosphate, which is the sugar moiety of nucleotides, such as ATP, GTP, TMP, etc. The other two products of the PPP are carbon dioxide and NADPH. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and pyruvate are carbon intermediates in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
- Does gluconeogenesis require oxygen (O2)?
No, oxygen (O2) is not a substrate for any of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Oxygen (O2) is not a substrate for any of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions of gluconeogenesis. ATP and NADH are not produced in this pathway but instead they are needed as substrates to build a glucose molecule. Furthermore, oxygen is not needed to regenerate NADH, so this pathway is entirely anaerobic. CO2, another important gas, is both used as a substrate and is a product of gluconeogenesis.
- Where in a eukaryotic cell does the pentose phosphate pathway occur?
Cytosol
The pentose phosphate pathway occurs in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells, the same cellular compartment as glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and lipid synthesis. PDC and the citric acid cycle occur in the mitochondrial matrix. Other processes occur in the other cellular compartments.
- The first reaction in gluconeogenesis converts pyruvate to __ in the __.
oxaloacetate; mitochondrial matrix
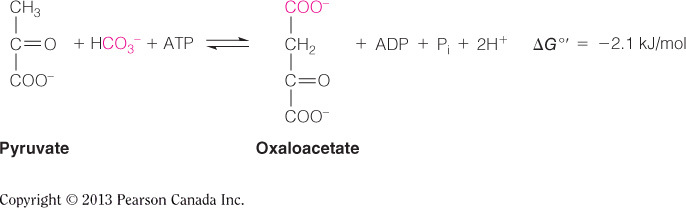
The first reaction in gluconeogenesis converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate in the mitochondrial matrix, as seen in the figure below. This is the first part of the pyruvate kinase bypass (i.e., how gluconeogenesis gets around the irreversible enzymes in glycolysis for a pathway whose direction is toward glucose, not pyruvate). The second part of the pyruvate kinase bypass is catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and converts OAA to phosphoenolpyruvate; this occurs in the cytosol. The other choices are fates of pyruvate that are not related to gluconeogenesis.
- Where in a eukaryotic cell does gluconeogenesis primarily occur?
Cytosol
The majority of gluconeogenesis occurs in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells, with the exception of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase because this enzyme is located in the mitochondrial matrix. All other enzymes are located in the cytosol.
- Which of the following enzymes does NOT catalyze an irreversible reaction in gluconeogenesis?
Hexokinase
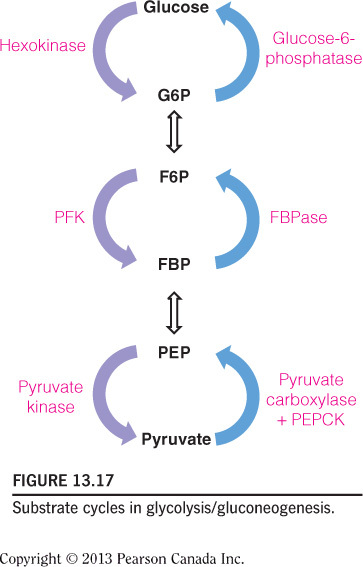
Hexokinase catalyzes the first irreversible step in glycolysis, not gluconeogenesis. The bypass for this glycolytic, irreversible reaction in gluconeogenesis is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphatase. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyzes the bypass for the PFK reaction in glycolysis. Pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase catalyze the bypass for the pyruvate kinase reaction in glycolysis. These bypasses are illustrated in the figure below.
- Which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis generates an NTP?
None of the listed enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis generates an NTP
None of the reactions in gluconeogenesis generates an NTP. Pyruvate carboxylase uses an ATP to drive the carboxylation of pyruvate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase uses a GTP to drive the decarboxylation. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyze the last two bypass reactions and use water to dephosphorylate their respective substrates, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in gluconeogenesis oxidizes NADH and uses the electron to reduce 1,3 BPG.
- If a person were deficient in vitamin B7, which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis would be directly affected?
The reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase
Pyruvate carboxylase uses a covalently bound biotin (vitamin B7) molecule to activate carbon dioxide for carboxylation of pyruvate. Vitamin B3 is niacin, which is added to a nucleotide to become NAD+/NADH. The only enzyme in glycolysis that directly uses NAD+/NADH is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase use water as a substrate, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase uses GTP as a substrate.
- Where in a eukaryotic cell does the Calvin cycle occur?
Stroma
The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast in eukaryotic cells, such as those in plants. In photosynthetic bacteria, the cycle occurs in the cytosol. The light reactions occur on the thylakoid membrane.
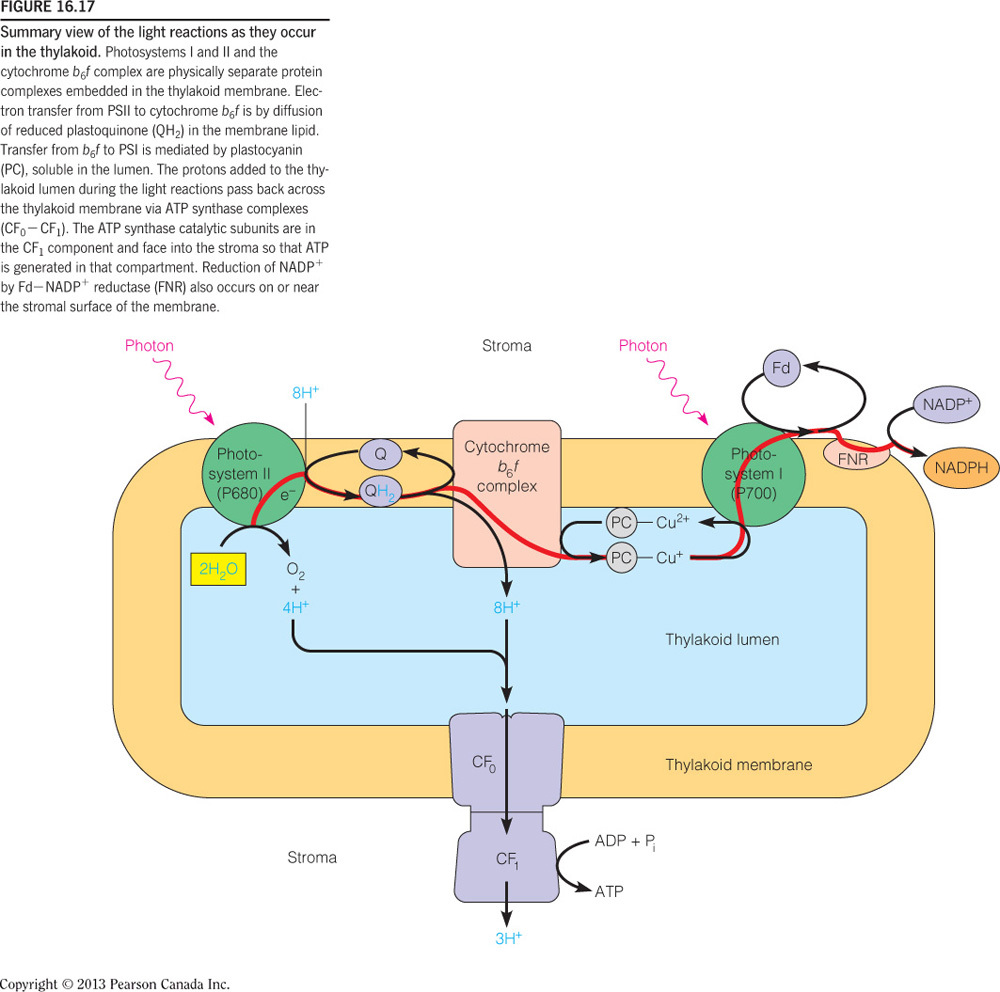
- The NADPH and ATP needed to fuel the calvin cycle are generated by this pathway: __.
the light reactions
Photosynthetic cells generate ATP and NADPH via the light reactions. These molecules are produced on the stroma side of the thylakoid lumen, as seen in the figure below. This is essential as the calvin cycle occurs in the stroma, so these molecules do not need to be transported in order to be used for making hexoses and pentoses.
- Which of the following is NOT a product of gluconeogenesis?
ATP
ATP is required for substrate phosphorylation, and is therefore a substrate and not a product of gluconeogenesis. Although carbon dioxide is a substrate of the first step, this molecule is also a product of the second reaction, catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. NAD+ and Pi are products of the pathway.
- Which of the following is NOT a reason that gluconeogenesis is not the exact reverse of glycolysis?
Gluconeogenesis yields NAD+, whereas glycolysis uses NAD+
“Gluconeogenesis yields NAD+, whereas glycolysis uses NAD+ is not a reason that gluconeogenesis is not the exact reverse of glycolysis. This suggests that the two pathways are exact reverses of one another, but gluconeogenesis is not the exact reverse due to the use of two cellular compartments (mitochondrial matrix and cytosol). Also, gluconeogenesis has four irreversible reactions, whereas glycolysis only has three. This means that gluconeogenesis has one extra enzyme-catalyzed reaction (11 total reactions using a completely unique intermediate, oxaloacetate or OAA).
- Which of the following is NOT a product of the Calvin cycle?
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is fixed by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCo) to ribulose-5-phosphate and therefore carbon dioxide is a substrate of the pathway. ATP is required for substrate phosphorylation and therefore is a substrate and not a product of the calvin cycle. Because this is an anabolic pathway, electrons are needed to build the five- and six-carbon sugars (hexoses and pentoses). The source of these electrons is NADPH and therefore NADP+ is a product.
- Which of the following enzymes does NOT catalyze a bypass reaction in gluconeogenesis?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase participates in gluconeogenesis by oxidizing NADH and using the electron to reduce 1,3 BPG. This same enzyme is used in both gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. The bypass for hexokinase is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphatase. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyzes the bypass for the phosphofructokinase reaction in glycolysis. Pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase catalyze the bypass for the pyruvate kinase reaction in glycolysis. The figure highlights the bypass enzymes in gluconeogenesis.
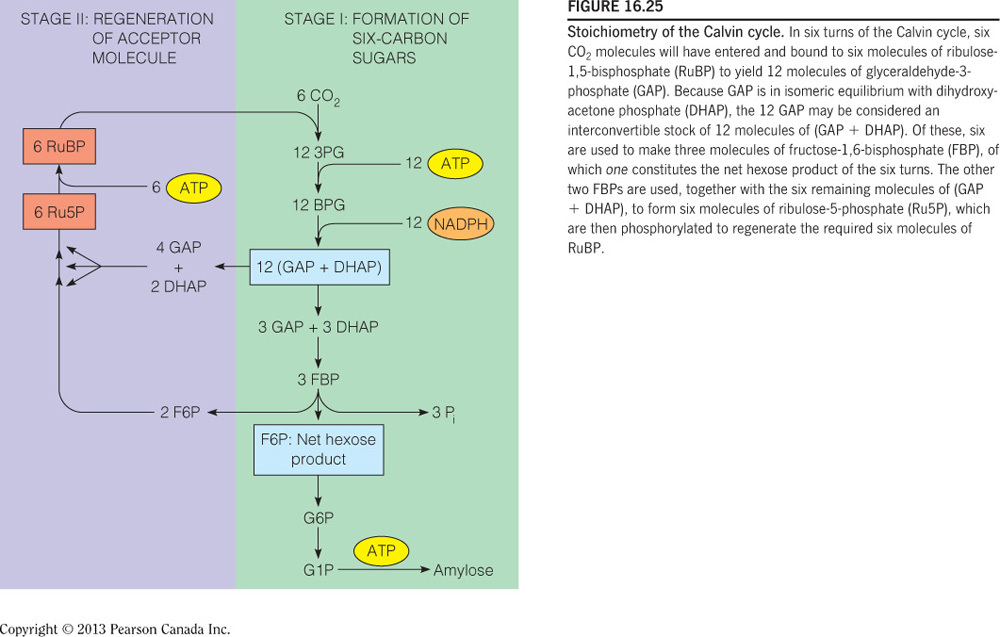
- The net cost of making a six-carbon sugar from the Calvin cycle is __.
18 ATP and 12 NADPH
A six-carbon sugar (hexose) will require six carbon dioxides, meaning six turns of the Calvin cycle. This generates 12 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphates, 12 ATP, and 12 NADPH molecules. During the regeneration phase, six ATPs are needed to generate six ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate molecules. The total cost, therefore, is 18 ATP and 12 NADPH molecules. The figure below diagrams the generation of a hexose via the Calvin cycle.
- Which of the following is a use for the end carbon product from the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Ribose-5-phosphate is the sugar moiety of nucleotides, such as ATP, GTP, TMP, etc.
The oxidative phase of the PPP yields ribose-5-phosphate, which is the sugar moiety of nucleotides (like ATP, GTP, TMP, etc.). The other two products of the PPP are carbon dioxide and NADPH. These products can be seen in the figure below. Carbon dioxide will be exhaled eventually. NADPH, not NADP+, is the source of electrons for lipid synthesis. NADH is not a product of PPP.
- Which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis generates CO2?
The reaction catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase decarboxylates OAA to yield phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide. Pyruvate carboxylase uses carbon dioxide as a substrate to carboxylate pyruvate. Note that there is no net fixation of carbon dioxide in gluconeogenesis. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in gluconeogenesis oxidizes NADH and uses the electron to reduce 1,3 BPG. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyze the last two bypass reactions and use water to dephosphorylate their respective substrates, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- The net cost of gluconeogenesis is __.
four ATP, two NADH, and two GTP
To go from pyruvate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, the cost is two ATP, one NADH, and one GTP. Building a glucose molecule requires two pyruvate molecules; therefore, all substrates for the reactions, up to and including the one catalyzed by aldolase, need to be doubled. Therefore, four ATP, two NADH, and two GTP are needed.
- Which enzyme-catalyzed reaction in gluconeogenesis yields NAD+?
The reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
The gluconeogenesis reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase yields NAD+, in which it oxidizes NADH and uses the electron to reduce 1,3 BPG. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase decarboxylates OAA to yield phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide. Pyruvate carboxylase uses carbon dioxide as a substrate to carboxylate pyruvate. Glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase catalyze the last two bypass reactions and use water to dephosphorylate their respective substrates, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- Which glycolysis intermediate is the starting point of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose-6-phosphate is the starting point of the pentose phosphate pathway. Ribose-5-phosphate is the end product of the oxidative phase of PPP. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, and pyruvate are other carbon intermediates in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis.
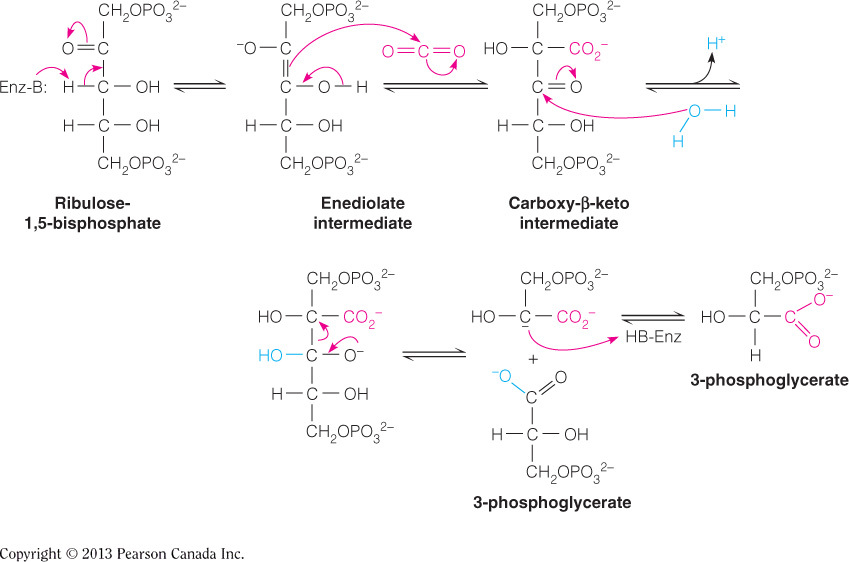
- The first reaction in the Calvin cycle fixes __ to ribulose-5-phosphate, as catalyzed by __.
carbon dioxide; RuBisCo
The figure below illustrates carbon fixation of carbon dioxide to ribulose-5-phosphate as catalyzed by RuBisCo. This enzyme also catalyzes the lytic cleavage of the six-carbon carboxy-beta-keto intermediate into two three-carbon intermediates: 3-phosphoglycerate.