Dynamic Study Module - Glycogen Synthesis and Regulation
- A deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase in the liver can lead to __.
hypoglycemia
- Glucose-6-phosphatase cleaves the phosphate of glucose-6-phosphate via phosphorolysis so that the product, glucose, can be transported out of the liver cell.
- Since glycogen is primarily stored in the liver, this enzyme is also found primarily in the liver to help replenish blood glucose levels.
- A deficiency in this enzyme means glucose-6-phosphate will accumulate in the liver and be unable to leave, because the phosphate traps this molecule inside the cell.
- The result is that blood glucose levels cannot be restored and hypoglycemia results.
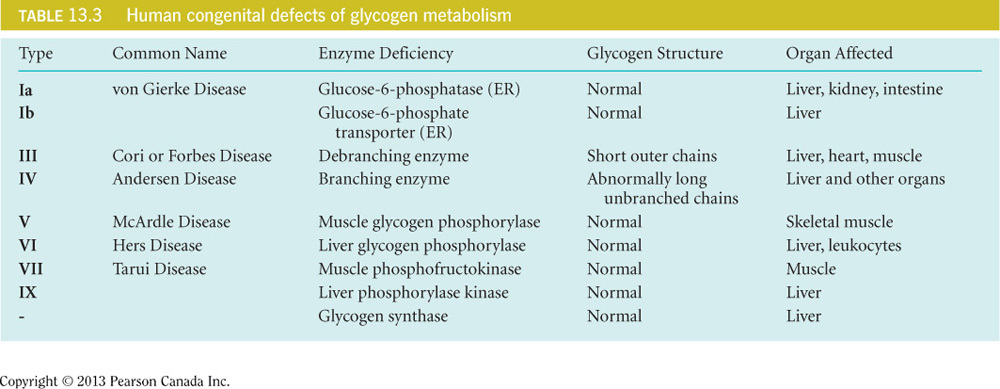
- A deficiency in the branching enzyme will result in an abnormally long and unbranched chain of glycogen.
- These and other congenital defects of glycogen metabolism are shown in the table below.
- In humans, most glycogen is stored in the __.
liver
- In humans, glycogen is stored mostly in liver cells, as the liver is responsible for maintaining appropriate blood glucose levels.
- The glycogen stored in the liver will enter the bloodstream when broken down, because the liver does not utilize glucose as its primary energy source, unlike the brain, which does use glucose as its primary energy source.
- The brain, however, does not store glycogen.
- Skeletal muscle cells also store glycogen for their own use.
- Blood is used to transport glucose.
- The pancreas does not store glycogen and glycogen is stored in the cytosol of liver cells primarily and not in the mitochondria.
- Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogen synthesis?
Glycogen Synthase
- Glycogen synthase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogen synthesis and is the site of regulatory control for this pathway.
- Glycogen synthase can only add successive glucose monomers to an already started chain and the protein that initiates this chain is glycogenin.
- Glycogen synthase also cannot introduce branching in the glycogen structure, and the branching enzyme (amylo-1,4 1,6-transglycosylase) is required for this action.
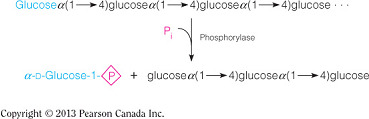
- Glycogen phosphorylase is the primary enzyme in the breakdown of glycogen into glucose monomers.
- Which of the following is NOT a reason why glycogen breakdown occurs via phosphorolysis instead of hydrolysis?
Phosphorolysis enables the monosaccharide to readily leave the cell and travel to different tissues.
- Phosphorolysis, the mechanism used to cleave glycosidic bonds in glycogen, adds a phosphate across the glycosidic bond.
- The phosphorylated monosaccharide is trapped in the cell and can readily enter into glycolysis without costing an ATP.
- Hydrolysis cleaves glycosidic bonds in dietary polysaccharides (like amylose) and these monosaccharides are not phosphorylated and can travel through the blood stream and enter into cells needing energy or those needing to store energy.
- Which glycolysis intermediate is the starting point of the pathway that leads to the synthesis of glycogen?
Glucose-6-phosphate
- Glucose-6-phosphate is the starting molecule for glycogen synthesis.
- Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized to glucose-1-phosphate in glycogen synthesis.
- For all of the other glycolysis intermediate options, glucose is the starting molecule and fructose-6-phosphate is the second intermediate.
- A decrease in blood glucose concentration to below about 5 mM (90 mg/100 ml) normally stimulates the release of the hormone __ from the pancreas.
glucagon
- When blood glucose levels are low, a peptide hormone called glucagon is released from the pancreas.
- Its target is the liver, where a signal cascade will trigger glycogen breakdown into glucose monomers.
- These monomers will leave the liver and enter the bloodstream to increase blood glucose levels.
- Insulin is also released from the pancreas, but has the opposite effect of glucagon.
- Epinephrine also causes a signal cascade similar to that of glucagon but this hormone is released from the adrenal medulla and its target is skeletal muscle.
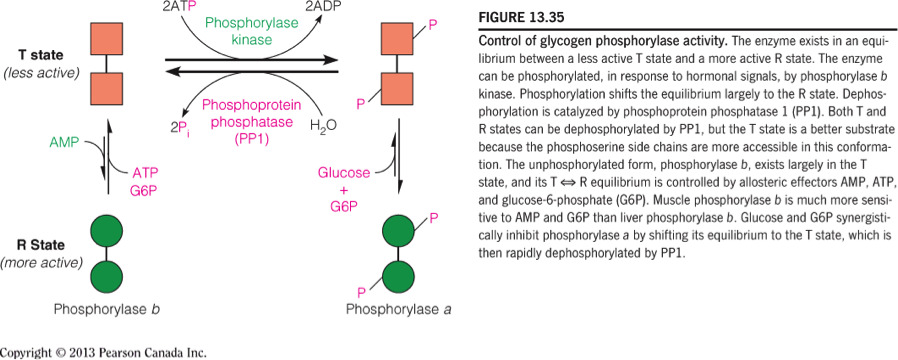
- The enzyme __ will be active due to __ caused by insulin binding to receptors on hepatocytes.
glycogen synthase ; dephosphorylation
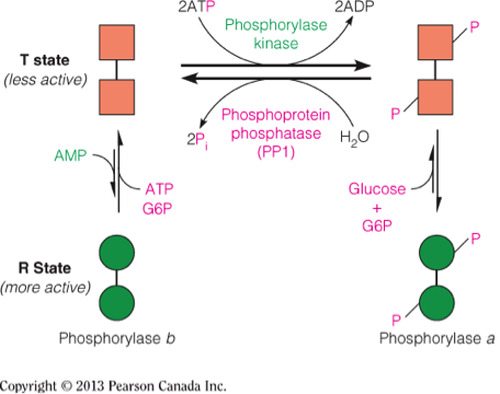
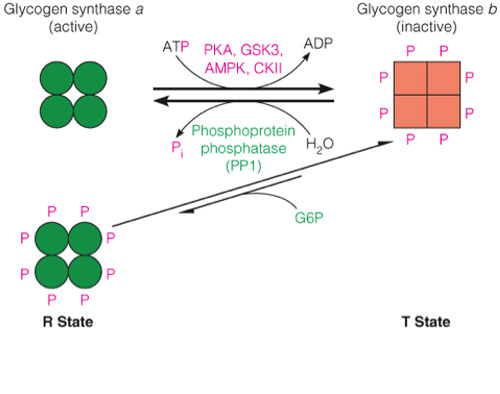
Insulin signals a decrease in glycogen breakdown and an increase in glycogen synthesis and therefore phosphorylase will be inactive and glycogen synthase will be active.
The active conformation of glycogen synthase (glycogen synthase a) is dephosphorylated.
The inactive conformation of phosphorylase (phosphorylase b) is also dephosphorylated.
The figure below illustrates the different phosphorylation states and the relative activities of phosphorylase and glycogen synthase.
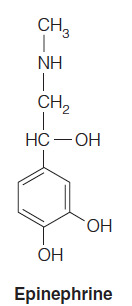
- Which of the following is NOT a peptide hormone?
Epinephrine
- Epinephrine is a small molecule, as seen in the figure below, and it is not a peptide hormone.
- This molecule is released from the adrenal medulla, unlike insulin and glucagon, which are peptide hormones released from the pancreas.
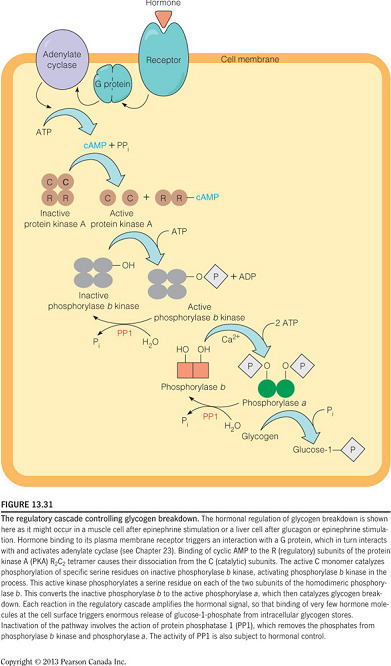
- Which of the following represents the correct sequence of events occurring upon glucagon binding to receptors on hepatocytes?
Dissociation of PKA C monomer phosphorylation (activation) of phosphorylase b kinase phosphorylation (activation) of phosphorylase a breakdown of glycogen
- Binding of glucagon to hepatocytes triggers a signal cascade that will increase blood glucose levels by triggering glycogen breakdown.
- Upon binding, adenylate cyclase is activated and produces cAMP, which causes the dissociation of PKA into its monomers.
- The C monomer of PKA phosphorylates phosphorylase b kinase, causing the kinase to become activated.
- The kinase will then phosphorylate glycogen phosphorylase and activate the a conformation.
- This activates phosphorylated phosphorylase then catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen.
- This is demonstrated in the figure below.
- Phosphorylation of the dimer conformation __ of glycogen phosphorylase will __ this enzyme.
phosphorylase b ; activate
- Phosphorylation of the phosphorylase b conformation to phosphorylase a of glycogen phosphorylase activates this enzyme and triggers an increase in glycogen breakdown.
- Dephosphorylation of phosphorylase a yields the inactive conformation (phosphorylase b) of glycogen phosphorylase and decreases glycogen breakdown.
- The breakdown of glycogen uses which enzyme?
Phosphorylase
- Glycogen breakdown uses phosphorylase enzymes to catalyze the addition of phosphate across the glycosidic bond (i.e., phosphorolysis), which yields a phosphorylated monosaccharide that readily enters into glycolysis (as demonstrated in the figure below).
- Hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond using water is the mechanism used to break down dietary polysaccharides, like starch.
- Phosphatases catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphate ester bonds and kinases use ATP to add a phosphate to amino acids with hydroxyl functional groups (Thr, Tyr, and Ser).
- A rapid increase in blood glucose normally stimulates the release of the hormone __ from the pancreas.
insulin
- When blood glucose levels are high, a peptide hormone called insulin is released from the pancreas.
- Upon receptor binding, a signal cascade will trigger a number of events including, but not limited to, an increase in glucose transports (so glucose enters into cells), a decrease in glycogen breakdown, and an increase in glycogen synthesis.
- Glucagon is also released from the pancreas, but has the opposite effect of insulin.
- Epinephrine causes a signal cascade similar to that of glucagon but this hormone is released from the adrenal medulla and its target is skeletal muscle.
- The enzyme __ will be active due to __ caused by glucagon binding to receptors on hepatocytes.
phosphorylase ; phosphorylation
- Glucagon signals an increase in glycogen breakdown and a decreased rate of glycogen synthesis and therefore phosphorylase will be active and glycogen synthase will be inactive.
- The active conformation of phosphorylase (phosphorylase a) is phosphorylated.
- The inactive conformation of glycogen synthase (glycogen synthase b) is also phosphorylated.
- The figure below illustrates the different phosphorylation states and the relative activities of phosphorylase and glycogen synthase.
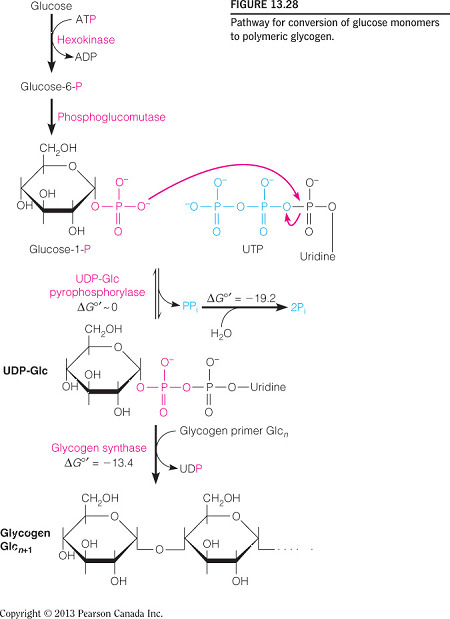
- Which of the following is the correct chemical equation for the reaction catalyzed by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase?
- The reaction catalyzed by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase synthesizes UDP-glucose when the phosphate of glucose-1-phosphate attacks the alpha-phosphate of UTP (as seen in the figure below).
- A pyrophosphate is released, which hydrolyzes to two inorganic phosphate molecules.
- The correct equation is:
- Which of the following pairs of enzymes are under reciprocal regulation in glycogen metabolism?
Glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase
- Glycogen phosphorylase is the primary enzyme in the breakdown of glycogen and glycogen synthase is the rate-limiting enzyme in glycogen synthesis.
- The regulation of these two enzymes directly affects the flow of either pathway (i.e., synthesis or breakdown) and both are reciprocally regulated by phosphorylation.
- Glycogenin and phosphoglucomutase are also involved in glycogen synthesis but neither enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step and therefore neither is a major site of regulation.
- In humans, what can be done with excess glucose when the need for ATP and glycolysis intermediates is low?
Glucose can be stored as glycogen
- Glycogen is the storage form for excess monosaccharides in humans. TAGs are the storage form of fatty acids.
- Amylose and amylopectin are the storage forms of glucose in plants.
- Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide that is found in plants; however, plants do not degrade this polymer for energy.
- Which NTP (where N = any base) is required for glycogen synthesis?
UTP
- Glycogen synthesis requires a UTP to react with glucose-1-phohsphate, yielding UDP-glucose.
- This sugar-nucleotide is an intracellular signal for glucose to be stored.
- The first reaction in glycogen synthesis converts glucose-6-phosphate to __.
glucose-1-phosphate
- Glucose-6-phosphate is first isomerized to glucose-1-phospate by phosphoglucomutase in glycogen synthesis.
- UDP-glucose is another intermediate in glycogen synthesis but fructose-1-phosphate is not an intermediate in glycogen synthesis.
- Glycogenin is the initiation enzyme for glycogen synthesis.
Which of the following indicates the “active” conformation of an enzyme?
I. b form
II. a form
III. T state
IV. R state
II and IV
- Designation of an active conformation of an enzyme can have an “a” suffix, like phosphorylase a or glycogen synthase a.
- This more active conformation can also be referred to as the R state.
- The less active conformation can have the “b” suffix and will be in the T-state.
- Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogen synthesis?
Glycogen synthase
- Glycogen synthase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogen synthesis and is the site of regulatory control for this pathway.
- Glycogen synthase can only add successive glucose monomers to an already started chain and the protein that initiates this chain is glycogenin.
- Glycogen synthase also cannot introduce branching in the glycogen structure, and the branching enzyme (amylo-1,4 1,6-transglycosylase) is required for this action.
- Glycogen phosphorylase is the primary enzyme in the breakdown of glycogen into glucose monomers.
- Where in a eukaryotic cell does glycogen synthesis occur?
Cytosol
Glycogen synthesis occurs in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. In humans, glycogen is made primarily in the liver and also in skeletal muscle cells.
- A decrease in blood glucose concentration to below about 5 mM (90 mg/100 ml) normally stimulates the release of the hormone __ from the pancreas.
glucagon
- When blood glucose levels are low, a peptide hormone called glucagon is released from the pancreas.
- Its target is the liver, where a signal cascade will trigger glycogen breakdown into glucose monomers.
- These monomers will leave the liver and enter the bloodstream to increase blood glucose levels.
- Insulin is also released from the pancreas, but has the opposite effect of glucagon.
- Epinephrine also causes a signal cascade similar to that of glucagon but this hormone is released from the adrenal medulla and its target is skeletal muscle.
- Which of the following nonhormonal intracellular conditions will trigger glycogen synthesis?
High ATP
- High-energy conditions will trigger an increased rate of glycogen synthesis and the targets for these conditions are phosphorylase and glycogen synthase.
- High concentrations of ATP, glucose, and glucose-6-phosphate are high-energy conditions that signal for energy to be stored and, since there is plenty of energy available, it will be a waste.
- In contrast, high AMP is a low-energy signal and will activate phosphorylase.