Dynamic Study Module - Chemical Logic of Metabolism
Under which condition(s) is ∆G always negative? Assume constant temperature.
I. Increase in enthalpy
II. Decrease in enthalpy
III. Increase in entropy
IV. Decrease in entropy
II and III
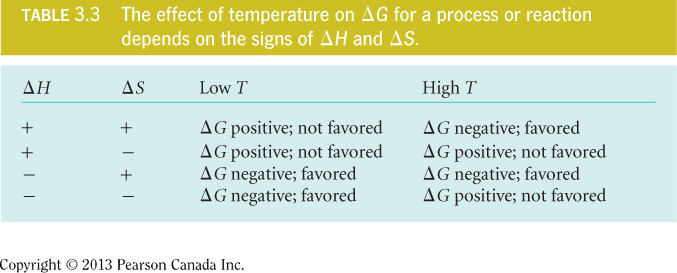
- Regardless of temperature, there is one set of conditions where ∆G is always negative: decrease in enthalpy (–∆H) and increase in entropy (+∆S).
- The table below demonstrates the temperature dependence of ; however, in biological systems, the temperature is fairly constant and is not a major factor in predicting ∆G.
Which of the following biological monomers contain an electrophilic carbonyl (C=O) functional group?
I. Nucleic acid
II. Amino acid
III. Fatty acid
IV. Monosaccharide
I, II, III, and IV
- All of the biological monomers contain an electrophilic carbonyl functional group (C=O), with the exception of the adenine base.
- This means that they all are reactive and can be attacked by a nucleophile.
- Consider the following reaction from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
If the cellular conditions are succinyl-CoA = and CoA-SH = 2nM , the equilibrium concentrations of succinate is extremely high:
Coupling this exergonic reaction to an endergonic reaction, like the phosphorylation of ADP, will not only generate ATP but also lower the succinate.
What is the for the coupled reaction?
Assume:
- Coupling the phosphorylation of ADP to the Succinyl-CoA Succinate + CoA-SH reaction means that ADP must be a substrate.
- Therefore, the reaction must be flipped before adding it to the succinyl-CoA reaction.
- This also causes the signe on to also be flipped :
- Doin so yields the overall equation
- The free energies are summative :
- Consider the following reaction from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
If the cellular conditions are succinyl-CoA = and CoA-SH = 2nM , the equilibrium concentrations of succinate is extremely high:
Coupling this exergonic reaction to an endergonic reaction, like the phosphorylation of ADP, will not only generate ATP but also lower the succinate.
What is the net chemical reaction for the proposed coupled reaction?
Assume:
- Coupling the phosphorylation of ADP to the Succinyl-CoA Succinate + CoA-SH reaction means that ADP must be a substrate.
- Therefore, the reaction must be flipped before adding it to the succinyl-CoA reaction.
- Doing so yields the overall equation
In the citric acid cycle, a metabolic pathway for completing the oxidation of saccharides, fats, and amino acids, there are four oxidation-reduction reactions. Using the table as reference, in which electron carrier can succinate pass electrons and release energy? No calculations are necessary.
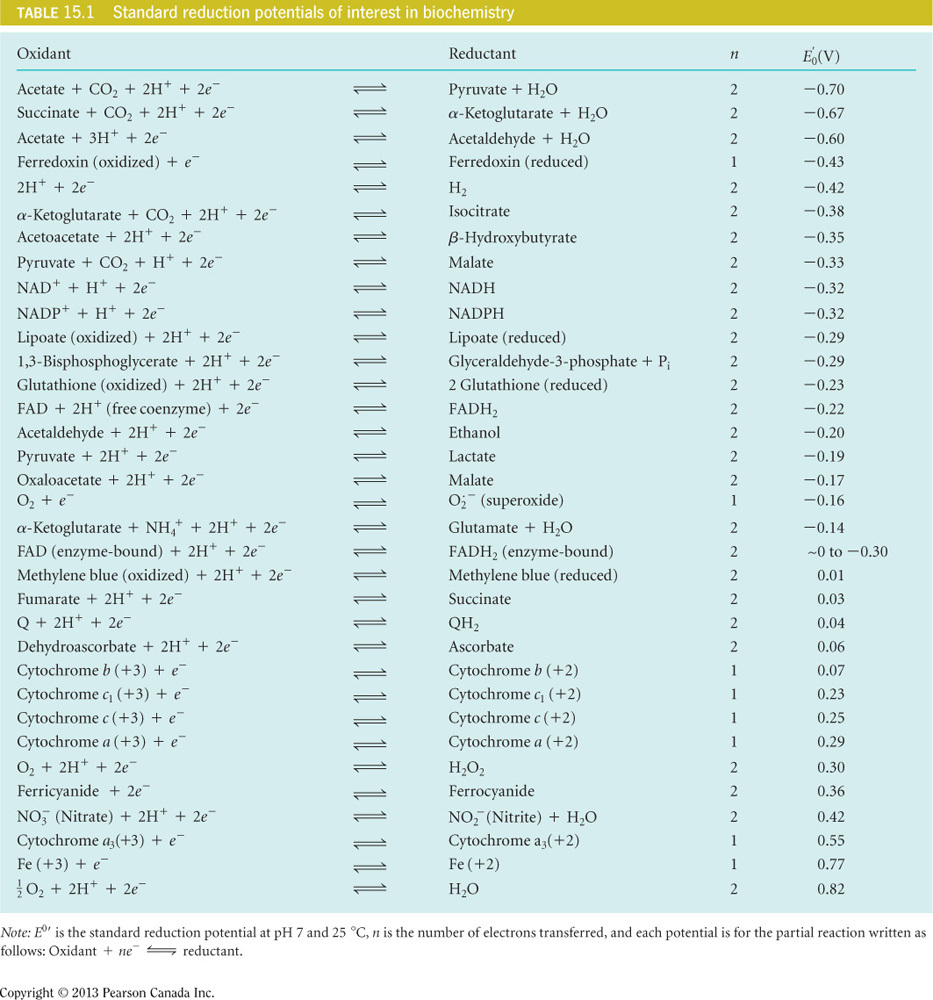
Assume that temperature is 37 °C, R = 8.314 J/mol K, and pH = 7.
Q
Of these choices, the only electron acceptor that has a higher reduction potential than succinate fumarate is Q. Therefore, passing electrons to Q will be favorable and will release energy. All other options have lower reduction potentials than this reaction.
- Which of the following equations represents the energy associated with the transport of a molecule/ion across a membrane?
- contains ∆ψ which is a change in potential, like membrane potential, that accompanies a process where a molecule/ion is moved from one region to another (represented by Q).
- This equation is used for biological processes that transport molecules/ions across a membrane.
- The equation contains ∆E° which represents a change in reduction potential (or the flow of electrons) in a chemical reaction (represented by Q) and therefore this equation is used for oxidation-reduction reactions (like those in the electron transport chain).
- Protein folding is governed by enthalpy and entropy, and does not involve concentration of reactants or products (Q) and therefore ∆G = ∆H – T∆S is the equation representing protein folding. ∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ takes into account standard conditions ∆G° and concentration of reactants and products (Q) and therefore this equation is used for reactions, like metabolic reactions.
- Which of the following equations represents the energy associated with a protein-folding event?
- Protein folding is governed by enthalpy and entropy, and does not involve concentration of reactants or products (Q) and therefore ∆G = ∆H – T∆S is the equation representing protein folding.
- ∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ takes into account standard conditions (∆G°) and the concentration of reactants and products (Q) and therefore this equation is used for reactions, like metabolic reactions.
- The ∆G = –nF∆E° + RTlnQ equation contains ∆E°, which represents a change in reduction potential (or the flow of electrons) in a chemical reaction (represented by Q), and therefore this equation is used for oxidation-reduction reactions (like those in the electron transport chain).
- ∆G = RTlnQ + nF∆ψ contains ∆ψ which is a change in potential, like membrane potential, that accompanies a process where a molecule/ion is moved from one region to another (represented by Q).
- This equation is used for biological processes that transport molecules/ions across a membrane.
- The favorable flow of electrons is __.
from low to high reduction potential
- In oxidation-reduction reactions, the favorable flow of electrons is toward higher reduction potential (from low to high reduction potential).
- These are the molecules that want the electrons most and will yield a
- When this is applied to the equation , using a positive change in reduction potential, combined with F = 96500 J/molV and n= number of electrons, the result will be a negative.
- Therefore, is favorable.

An important reaction that accompanies anaerobic glycolysis, a catabolic pathway for monosaccharides, is the regeneration of NAD+. This molecule is produced when NADH reduces pyruvate to lactate. Using the table as a reference, calculate the for the reduction of pyruvate by NADH.
-25 kJ/mol
- Here n = 2 since two electrons are passed as seen in the table.
- is determined by adding the reduction potentials of the two half-reactions appropriately.
- In the table given, all reactions are set up to show acceptance of electrons.
- In oxidation-reduction reactions, only one molecule can accept electrons and the other donates electrons.
- For this reason, one of the half-reactions needs to be flipped.
- The problem states that the electrons from NADH reduce pyruvate to lactate and therefore you will flip the half-reaction for NADH and also flip the sign on the reduction potential to become +.32 V.
- Adding the two half-reactions will now cancel the electrons (which are balanced) and then you can add the reduction potentials:
- Plugging these values into the equation gives a free energy of -25 kJ/mol of energy that is released when electrons are passed from NADH to pyruvate to lactate.
In a healthy cell which of the following conditions should be satisfied?
I.
II.
III.
IV.
I and IV
- Catabolic pathways primarily use NAD+ as an electron acceptor, whereas anabolic pathways primarily use NADPH as an electron donor.
- Therefore, in a healthy cell that is actively undergoing catabolism and anabolism, there will be higher NAD+ than NADH, and higher NADPH than NADP+
- Conditions I and IV satisfy these requirements.
- Cyclization of monosaccharides belongs to which type of chemical transformation?
Nucleophilic addition
- Cyclizations of monosaccharides undergo a nucleophilic addition transformation.
- Nucleophilic additions involve attack of the carbonyl carbon and formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, but a leaving group is not produced in these reactions and the carbonyl is not reformed.
- The nucleophile can be a carbanion, alcohol, hydride, or amine.
- Nucleophilic addition occurs with carbonyl functional groups that are not bonded to a heteroatom.
- For monosaccharides, an alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon.
- Acyl substitutions, unlike alkyl substitution (i.e., SN1 or SN2), involve the generation of a tetrahedral intermediate due to the sp3-hybridized carbonyl carbon.
- The nucleophile is often a water molecule, as it is in the chymotrypsin-catalyzed mechanism.
- When the electrons collapse back down to reform the carbonyl, a leaving group is expelled.
- In peptide bond hydrolysis, this leaving group contains the amine nitrogen of the amide.
- Examples of functional groups that can undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution include amide, ester, thioester, carboxylic acid, and acyl phosphates (these are all carbonyls bonded to heteroatoms).
- Claisen condensation is the reaction between two carbonyl reactants (one carbonyl must be part of an ester) that forms a new C-C bond.
- Which of the following symbols represents the biochemical standard state free energy?
- is the free energy under biochemical standard conditions (pH = 7 and constant H2O).
- The free energy for chemical standard state does not have a prime (‘).
- The standard chemical state conditions assumes solute = 1M.
- ∆G is the free energy release taking into account the standard state conditions and the actual conditions.
- ∆H°’ and ∆S° are enthalpy and entropy, respectively, and not free energy.
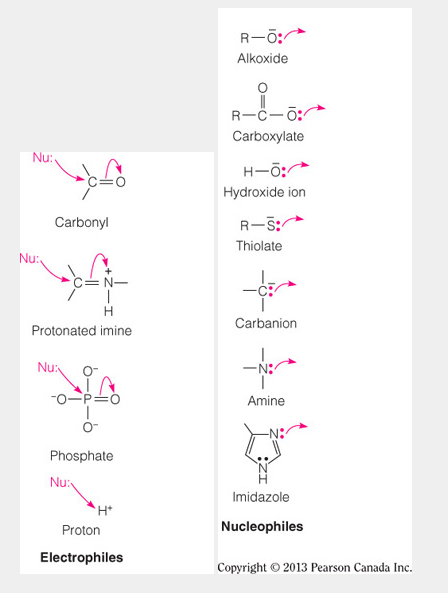
Which of the following functional groups possess only a nucleophile and no electrophilic atom?
I. Carbonyl
II. Hydroxides
III. Phosphate
IV. Thiolate
V. Imidazole
II, IV, and V
- Good nucleophiles are electron rich, with a lone pair of electrons and often a full negative charge on the strongest nucleophilic atoms.
- Of the choices given, the hydroxide oxygen, thiolate sulfur, and imidazole nitrogen are the nucleophilic atoms in functional groups that do not contain an electrophilic atom.
- Carbonyl and phosphates are good electrophiles because they contain a central atom that is electron poor, i.e., the carbon of the carbonyl and the phosphorous of the phosphate.
- The figure below demonstrates the reactivity of various biologically relevant functional groups.
- If ∆G = +6,000 J/mol for a reaction S P, which of the following statements is correct?
When the reaction reaches equilibrium, [S] > [P]
- Since substrates are lower in energy than the products, as indicated by the positive ΔG, there will be more substrate than product at equilibrium.
- In general, the molecule that is lower in energy, reactant, or product will be in higher concentration once equilibrium is achieved.
- To verify this, use the equation: where R = 8.314 J/mol K and T = 300 K.
- Solving for Keq (recalling that Keq = [P]/[S]), a positive ΔG will yield a negative Keq (< 1), meaning that [S] > [P].
An important reaction that accompanies anaerobic glycolysis, a catabolic pathway for monosaccharides, is the regeneration of NAD+. This molecule is produced when NADH reduces pyruvate to lactate. Using the table as a reference, which of the following is the overall reaction for the reduction of pyruvate to lactate by NADH?
- In the table, all reactions are set up to show acceptance of electrons.
- In oxidation-reduction reactions, only one molecule can accept and the other donates electrons.
- For this reason, one of the half-reactions needs to be flipped.
- The problem states that the electrons from NADH reduce pyruvate to lactate and therefore you will flip the half-reaction for NADH and also flip the sign on the reduction potential to become +.32 V.
- The flipped half-reaction for NADH will be:
- When the two half-reactions are added, the electrons and protons on both sides of the equation cancel each other out and can be removed, giving the final net equation
Consider the following reaction coupled from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
What is the equilibrium succinate for the coupled reaction?
Assume cellular conditions are: succinyl-CoA = 4 μM CoA-SH = 2 nM ADP = 1 mM [Pi] = 2 mM ATP = 5mM
Also assume that temperature is 37 °C, R = 8.314 J/mol K, and pH = 7
Since ∆G°, R, and T are given and K (equilibrium constant) is needed, use this:
Rearrangement of the equation:
Before plugging in the known values, a few unit conversions are necessary.
Since the gas constant R = 8.314 J/mol
- K, needs to be converted to J/mol (-36, 000 J/mol)
- and temperature needs to be converted to Kelvin (Kelvin = 273.15 K + 37°C = 300.15 K)
- Plug in the values and solve for succinate, after converting all concentrations to M (molar).
- Also recall that and that is constant and therefore negligible under biochemical standard conditions.
How many ATP molecules can be synthesized when the electrons from succinate reduce O2, assuming the process is 100 percent efficient? Assume ATP synthesis is
4
for passing electrons from succinate to oxygen.
To determine this:
Here n = 2 since two electrons are passed as seen in the table.
is determined by adding the reduction potentials of the two half-reactions appropriately.
In the table given, all reactions are set up to show acceptance of electrons.
In oxidation-reduction reactions, only one molecule can accept and the other donates electrons.
For this reason, one of the half-reactions needs to be flipped.
The problem states that the electrons from succinate reduce oxygen and therefore you will flip the half-reaction for succinate and also flip the sign on the reduction potential to become -0.03 V.
Adding the two half-reactions will now cancel the electrons (which are balanced) and then you can add the reduction potentials:
Plugging these values into the equation gives a free energy of -152 kJ/mol of energy that is released when electrons are passed from succinate to oxygen.
This energy (-152 kJ/mol) can be coupled to synthesizing an ATP and if the process is 100 percent efficient, then all the energy from passing electrons will be used to make ATP and the following will be true:
Plugging in the values and solving for (x) = 4.74 ATP molecules.
Therefore ~ 4 whole ATP molecules can be made from passing electrons from succinate to oxygen.
We round down here, because we cannot create energy to synthesize the fifth ATP and thus there is only enough energy for four whole ATP molecules.
In the citric acid cycle, a metabolic pathway for completing the oxidation of saccharides, fats, and amino acids, there are four oxidation-reduction reactions. Using the table as a reference, which of the following is the net reaction for the reduction of NAD+ by isocitrate?
- In the table given, all reactions are set up to show acceptance of electrons.
- In oxidation-reduction reactions, only one molecule can accept electrons and the other donates electrons.
- For this reason, one of the half-reactions needs to be flipped.
- The problem states that the electrons from isocitrate reduce NAD+ and therefore you will flip the half-reaction for isocitrate and also flip the sign on the reduction potential to become +.38 V.
- The flipped half-reaction for isocitrate will be:
- When the two half-reactions are added, the electrons and protons on both sides of the equation cancel each other out and can be removed, giving the final net equation:
- Consider the following reaction from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? Assume temperature is 37 °C and R = 8.314 J/mol K.
Since ∆G°, R, and T are given and K (equilibrium constant) is needed, use this:
Rearrangement of the equation:
Before plugging in the known values, a few unit conversions are necessary.
Since the gas constant R = 8.314 J/mol
- K, needs to be converted to J/mol (-36, 000 J/mol)
- and temperature needs to be converted to Kelvin (Kelvin = 273.15 K + 37°C = 300.15 K)
- All units cancel and therefore the final answer is unitless.
- Which of the following equations represents the energy associated with metabolic reactions?
- takes into account standard conditions (∆G°) and concentration of reactants and products (Q) and therefore this equation is used for reactions, like metabolic reactions.
- ∆G = RTlnQ + nF∆ψ contains ∆ψ which is a change in potential, like membrane potential, that accompanies a process where a molecule/ion is moved from one region to another (represented by Q).
- This equation is used for biological processes that transport molecules/ions across a membrane.
- The ∆G = –nF∆E° + RTlnQ equation contains ∆E° which represents a change in reduction potential (or the flow of electrons) in a chemical reaction (represented by Q) and therefore this equation is used for oxidation-reduction reactions (like those in the electron transport chain).
- Protein folding is governed by enthalpy and entropy, and does not involve concentration of reactants or products (Q) and therefore ∆G = ∆H – T∆S is the equation representing protein folding.
- If , for a process where S P, which of the following statements is true?
- It is always true that ΔG <0 if > 1.
- To verify this, use the equation where R=8.314 J/molK, T=300 K.
- Solving for Keq (recalling that Keq = [P]/[S]), a negative ΔG will yield a positive Keq (> 1), meaning that [S] < [P].
- Also, as this reaction has a large negative ΔG, it is favorable, exergonic (releases energy), and irreversible.
If ∆G = -7 kJ/mol for a reaction S P, which of the following statements is/are correct?
I. The reaction is exergonic.
II. At equilibrium, [S] > [P].
III. The reaction is unfavorable.
IV. The reaction is irreversible.
I and IV
- Since products are lower in energy than the substrates, as indicated by the negative ΔG, there will be more product than substrate at equilibrium.
- In general, the molecule that is lower in energy, reactant, or product will be in higher concentration once equilibrium is achieved.
- To verify this, use the equation: where R=8.314 J/molK, T=300 K.
- Solving for Keq (recalling that Keq = [P]/[S]), a negative ΔG will yield a positive Keq (> 1), meaning that [S] < [P].
- Also, as this reaction has a large negative ΔG, it is favorable, exergonic (releases energy), and irreversible
- Consider the following reaction from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
If the cellular conditions are succinyl-CoA = 4 μM and CoA-SH = 2 nM, what will be the equilibrium concentration of succinate?
Assume temperature is 37 °C and R = 8.314 J/mol K.
Since ∆G°, R, and T are given and K (equilibrium constant) is needed, use this:
Rearrangement of the equation:
Before plugging in the known values, a few unit conversions are necessary.
Since the gas constant R = 8.314 J/mol
- K, needs to be converted to J/mol (-36, 000 J/mol)
- and temperature needs to be converted to Kelvin (Kelvin = 273.15 K + 37°C = 300.15 K)
- Plug in the values and solve for succinate, after converting all concentrations to M (molar).
- Assuming protein folding is a favorable process and the entropy of the protein decreases during folding, what can be concluded about the folding process?
ΔH must be less than zero.
- The change in enthalpy must be less than zero for a favorable folding process.
- Favorable processes have a ΔG < 0.
- Using the equation: ΔG = ΔH – TΔS, if ΔG < 0 (-) and ΔS > 0 (+), either T must be increased or ΔH < 0 (-).
- Cells do not increase temperature to facilitate a process because an increase in temperature would cause protein, DNA, and RNA to unfold.
- Therefore, the only correct answer is that enthalpy must be less than zero.
- If ∆G = -10 kJ/mol for a reaction S P, which of the following statements is correct?
When the reaction reaches equilibrium, [S] < [P]
- Since products are lower in energy than the substrates, as indicated by the negative ΔG, there will be more product than substrate at equilibrium.
- In general, the molecule that is lower in energy, reactant or product, will be in higher concentration once equilibrium is achieved.
- To verify this, use the following equation: ΔG = -RTlnKeq, where R = 8.314 J/molK, T = 300 K.
- Solving for Keq (recalling that Keq = [P]/[S]), a negative ΔG will yield a positive Keq (> 1), meaning that [S] < [P].
- Which of the following is NOT one of the five general types of chemical transformation commonly performed by cells?
Free radical reaction
- Biological systems have fairly limited types of functional groups and are therefore limited to a certain set of organic reactions.
- Of the choices, only free radical reactions are not a common type of chemical transformation.
- There are a few enzymes that can catalyze a free radical reaction, however they are rare in comparison to the other chemical transformations.
- Which of the following equations represents the energy associated with movement of electrons?
- The equation contains ∆E° which represents a change in reduction potential (or the flow of electrons) in a chemical reaction (represented by Q) and therefore this equation is used for oxidation-reduction reactions (like those in the electron transport chain).
- Protein folding is governed by enthalpy and entropy, and does not involve concentration of reactants or products (Q) and therefore ∆G = ∆H – T∆S is the equation representing protein folding.
- ∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ takes into account standard conditions (∆G°) and concentration of reactants and products (Q) and therefore this equation is used for reactions, like metabolic reactions.
- ∆G = RTlnQ + nF∆ψ contains ∆ψ which is a change in potential, like membrane potential, that accompanies a process where a molecule/ion is moved from one region to another (represented by Q).
- This equation is used for biological processes that transport molecules/ions across a membrane.
- Which of the following is NOT a strategy used by living cells to drive unfavorable reactions forward?
Moving the reaction to a new cellular compartment, like the mitochondria
- All of these are strategies used by cells to drive an unfavorable reaction forward except for moving the reaction to a new cellular compartment.
- This is a strategy used by living cells in pathway regulation, fatty acid degradation, and fatty acid oxidation.
- For reversible reactions, keeping [P] low will trigger the reaction to move toward product (i.e., Le Châtelier’s Principle); this is similar to Q < K and indicates that the cellular concentrations of substrates and products are far from equilibrium.
- Also, coupling unfavorable reactions to favorable reactions, like ATP hydrolysis, is a common strategy to move unfavorable reactions toward product.
- The reaction mechanism catalyzed by chymotrypsin belongs to which type of chemical transformation?
Nucleophilic acyl substitution
- The peptide substrate of the reaction catalyzed by chymotrypsin undergoes nucleophilic acyl substitution.
- Acyl substitutions, unlike alkyl substitution (i.e., SN1 or SN2), involve the generation of a tetrahedral intermediate due to the sp3-hybridized carbonyl carbon.
- The nucleophile is often a water molecule, as it is in the chymotrypsin-catalyzed mechanism.
- When the electrons collapse back down to reform the carbonyl, a leaving group is expelled.
- In peptide bond hydrolysis, this leaving group contains the amine nitrogen of the amide.
- Examples of functional groups that can undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution include amide, ester, thioester, carboxylic acid, and acyl phosphates (these are all carbonyls bonded to heteroatoms).
- Nucleophilic additions also involve attack of the carbonyl carbon and formation of a tetrahedral intermediate; however, a leaving group is not produced in these reactions and the carbonyl is not reformed.
- Nucleophilic addition occurs with carbonyl functional groups that are not bonded to a heteroatom.
- Claisen condensation is a reaction between two carbonyl reactants (one carbonyl must be part of an ester) that forms a new C-C bond.
In the citric acid cycle, a metabolic pathway for completing the oxidation of saccharides, fats, and amino acids, there are four oxidation-reduction reactions. Using the table as a reference, calculate the for the reduction of NAD+ by isocitrate.
-12 kJ/mol
- Here, n = 2 since two electrons are passed as seen in the table. F = 96,500 J/mol V.
- ∆Ε**o’ is determined by adding the reduction potentials of the two half-reactions appropriately.
- In the table given, all reactions are set up to show acceptance of electrons.
- In oxidation-reduction reactions, only one molecule can accept electrons and the other donates electrons.
- For this reason, one of the half-reactions needs to be flipped.
- The problem states that the electrons from isocitrate reduce NAD+ and therefore you will flip the half-reaction for isocitrate and also flip the sign on the reduction potential to become +.38 V.
- Adding the two half-reactions will now cancel the electrons (which are balanced) and then you can add the reduction potentials:
- Plugging these values into the equation gives a free energy of -12 kJ/mol of energy that is released when electrons are passed from isocitrate to NAD+.
- Which law(s) of thermodynamics can be used to predict whether a process is thermodynamically favorable?
2nd
- According to the second law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a system will always (or will want to) increase.
- Rearrangement and substitutions of entropic equations can yield the equation ∆G = ∆H – T∆S, which is based on the concept that thermodynamically favorable processes always proceed to lower energy, and this is a restatement of the second law.
- This equation lets us predict whether a process will be favorable (–∆G) or unfavorable (+∆G).
- The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can neither be created nor destroyed.
- This law of thermodynamics deals with enthalpy.
- In biological processes, enthalpic contributions are from the making or breaking of bonds.
- If this is favorable (releases heat), then there will be a –∆H and if the process is unfavorable (requires heat to make or break a bond) then there will be a +∆H.
- The third law of thermodynamics deals with temperature, wherein the entropy approaches a constant value when temperature approaches absolute zero.
- The third law is not biologically relevant, as the temperature of a living cell will never approach absolute zero.
- To establish the change in free energy, a point of reference is needed. For living systems, the ∆G°’ is this point of reference, also known as the biochemical standard state. Which of the following are the conditions unique to ∆S°’?
I. H2O is constant. II. Solute = 1 M III. Temperature = 273.16 K IV. pH = 7 V. Pressure = 1 bar
I and IV
Biochemical standard conditions, pH = 7 and constant , are in addition to the standard chemical conditions
- where solute = 1 M, temperature = 273.15 K, and pressure = 1 bar.
Consider this series of linked reactions, where the letters represent intermediate molecules:
A B C D E
If the BC is rate limiting, which intermediate(s) in the pathway will accumulate?
A and B
- Intermediates before the rate-limiting step will be in higher concentration as they are “waiting” to get through the slowest step.
- If the slowest step in the pathway is the second step, then the substrate for the reaction will be in the highest concentration of all the intermediates.
- Due to Le Châtelier’s principle, an accumulation of B will push the reaction backward toward substrate (A) and therefore [A] also increases.
- This is due to the bottleneck created by the rate-limiting reaction.
- The intermediates after the rate-limiting reaction are in the lowest concentration.
- Consider the following functional group structures:
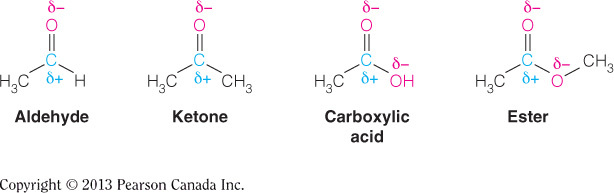
Which of the following statement is FALSE concerning the structures displayed?
The carbonyl oxygen is a strong nucleophile.
- The oxygen of the carbonyl bond is not a strong nucleophile.
- All of the other listed statements are correct.
- The strongest nucleophiles possess a full negative charge and not a partial negative charge.
- Consider the following reaction from the citric acid cycle (CoA is coenzyme A):
If the cellular conditions are succinyl-CoA = 4 μM and CoA-SH = 2 nM, the equilibrium concentration of succinate is extremely high: .
Coupling this exergonic reaction to an endergonic reaction, like the phosphorylation of ADP, will serve which two purposes?
I. Increasing the succinyl-CoA II. Generating metabolically useful ATP III. Pulling the reaction toward CoA-SH IV. Increasing the energy released by the succinyl-CoA reaction V. Decreasing the succinate
Assume the temperature is 37 °C and R = 8.314 J/mol K.
II and V
- Coupling this highly exergonic reaction to the phosphorylation of ADP will generate ATP, a metabolically useful molecule.
- Also, since the Gibbs free energies will be added together (–36 kJ/mol + 32.2 kJ/mol = -3.6 kJ/mol), the overall lower free energy released will lower the succinate concentration.
- It’s important to maintain low intermediate concentrations in a cell to ensure that all molecules will fit and not crash out.
- Which law(s) of thermodynamics deals with the energy release required for making or breaking bonds?
1st
- The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can neither be created nor destroyed.
- This law of thermodynamics deals with enthalpy. In biological processes, enthalpic contributions are from the making or breaking of bonds.
- Then there will be a –∆H and if the process is unfavorable (requiring heat to make or break a bond), then there will be a +∆H.
- According to the second law of thermodynamics, the entropy of a system will always (or will want to) increase.
- Rearrangement and substitution of entropic equations can yield the equation ∆G = ∆H – T∆S, which is based on the concept that thermodynamically favorable processes always proceed to lower energy, and this is a restatement of the second law.
- This equation lets us predict whether a process will be favorable (–∆G) or unfavorable (+∆G).
- The third law of thermodynamics deals with temperature, wherein the entropy approaches a constant value when temperature approaches absolute zero.
- The third law is not biologically relevant, as the temperature of a living cell will never approach absolute zero.
- The diagram below shows some transporters in the membrane of a hypothetical cell. The concentrations of Cl- and glucose on each side of the membrane are given, in addition to the pH. The membrane potential is 30 mV and temperature 25 °C.
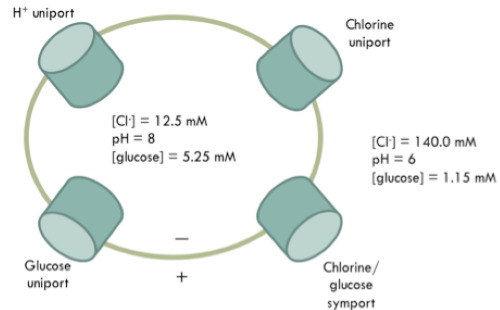
Do not use a calculator. The ΔG for transport of glucose through the uniport out of the cell is __.
Negative
Since the uncharged glucose molecule is moving from high to low concentration, which is a favorable movement, the for this process must be favorable, and therefore negative.
To calculate the magnitude:
Answering this question requires the independent analysis of each part of the equation for the free energy of transport:
- where the constants R = 8.314 J/mol K and F = 96,500 J/molV.
- Temperature needs to be in units of Kelvin, so 273 to convert 25 °C to 298 K.
The first term is dependent on concentration of the ion/molecule
- where C2 is the final concentration and C1 is initial concentration.
When molecules/ions move down the concentration gradient (from high to low concentration), this is favorable and the first term will have a negative sign.
In this case, glucose moves into the cell, C**1 = 1.15 and mM C**2 *= 5.35 mM. *
This is with the concentration gradient and therefore the first term will be negative.
- The second term (ZF∆ψ) takes into account the charge of the ion/molecule (Z) that is moving and the membrane potential (∆ψ).
- Ions moving towards the side of the membrane with the opposite charge (i.e., a chloride ion moving toward the positive side of the membrane) is favorable because opposite charges attract.
- Therefore, the second term would be a negative sign. In this case, glucose is uncharged (Z=0) so the product in the second term will be zero.
- Overall, the transport of glucose out of this cell is favorable because the sum of the two terms will be a negative number. Spontaneous reactions have a negative ΔG.
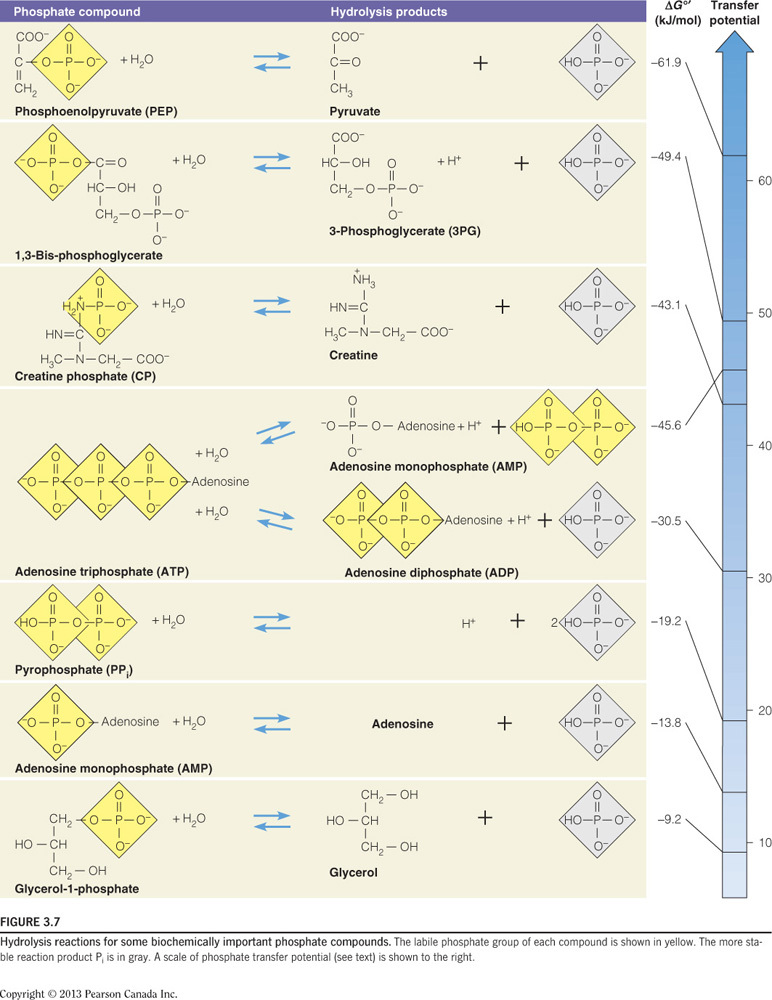
- Many biological molecules can transfer phosphate groups, for example creatine phosphate, phosphoenol pyruvate, ATP, AMP, and glycerol-1-phosphate. ATP, however, is the primary source of phosphate transfers in a cell. Why is this?
ATP is good at accepting and receiving phosphates.
- Of all the biological molecules capable of accepting and receiving phosphate, ATP is intermediary, meaning that the molecule is good at both receiving and donating phosphates, making it especially invaluable to the cell.
- The diagram below illustrates the phosphoryl group transfer potential of ATP, which is in the middle of all of these molecules.
- Consider this series of linked reactions occurring in a living cell, where the letters represent intermediate molecules:
Which step in the pathway will be under the tightest regulatory control?
- Regulation of a pathway can be applied to reactions that are far from equilibrium (i.e., irreversible).
- In this series of reactions, the far-from-equilibrium reaction is represented by a single arrow, A → B.
- Regulatory control of this step will ultimately affect the concentration of the final product of the pathway, as this represents the bottleneck.