Review of Basic Circuit Theory
Potential Difference (V or E)
Like charges repel
Opposite charges attract
As the distance between two charges increases, force decreases
As the distance between two charges decreases, force increases
Work = bringing together two separated charges
Negative Work = with opposite charges
Positive Work = with same charges
Work =
- = Electrostatic Force
- = Initial Distance between the two charges
Potential Difference = the work that must be done to move a unit of positive charge (one coulomb) from point A to point B.
Potential Difference can also be said as the "potential energy of the charge"
One Volt = the energy required to move one positive charge (one coulomb) a distance of one meter against a force of one newton.
Current (I)
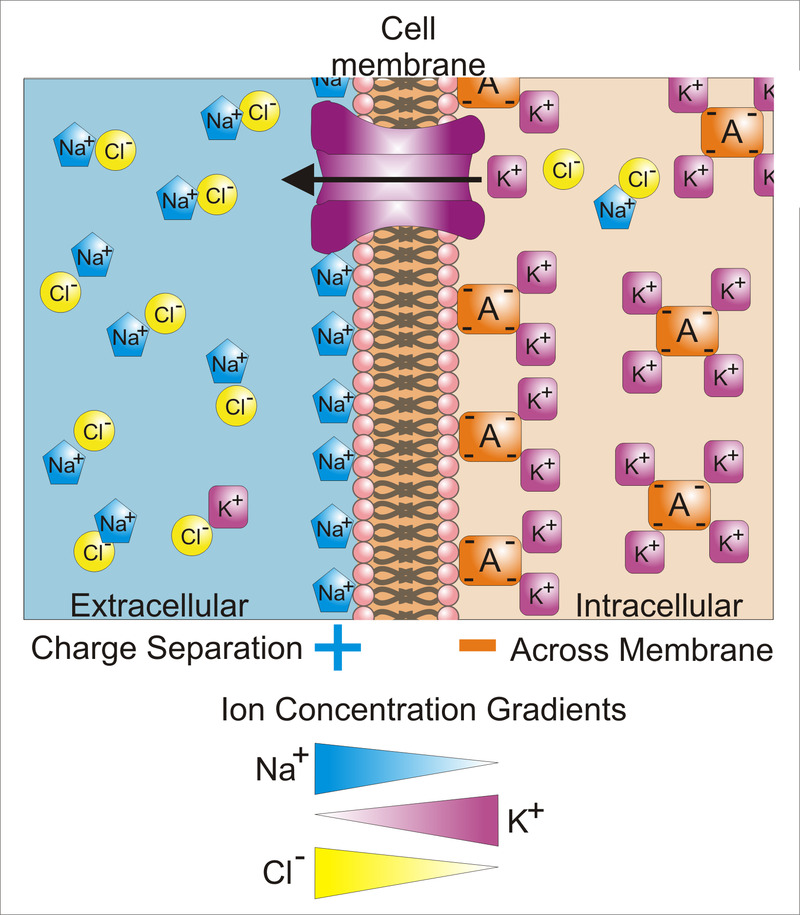
- Anytime a positive charge is separated from a negative charge, there is a potential difference
- The chemical reaction in a common battery can generate a separation of charges.
- The differences in ion concentrations across the cell membrane will cause diffusion. Flows from high to low concentrations.
- This diffusion can also generate a separation of charges.
if ( Charge Separation == True ) { Positive Charges move towards Negative Charges Negative Charges move towards Postivie Charges}- Current = the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region
- Current = the net movement of charge per unit of time.
- In nerve and muscle cells current is carried by both positive and negative ions in solution.
- One ampere (A) of current represents the movement of one coulomb (of charge) per second.
Conductance (g)
Conductor = Any object that allows electrical charges to flow through it.
We measure the strength of a conductance in units of siemens (S)
A siemen = the opposite of resistance (Ω)
A siemen = how much does the material conduct
Via Ohm's Law, the current that flows through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it
- As charges move through a conductor some of their potential energy is converted into thermal energy due to friction.
- Every material has a constant property determined by its molecular structure called conductivity ()
- Metals are very good conductors, so they have a hight conductivity
- Aqueous solutions with high-ionized salt concentrations have somewhat lower conductivity
- Lipids have very low conductivity (aka good insulators)
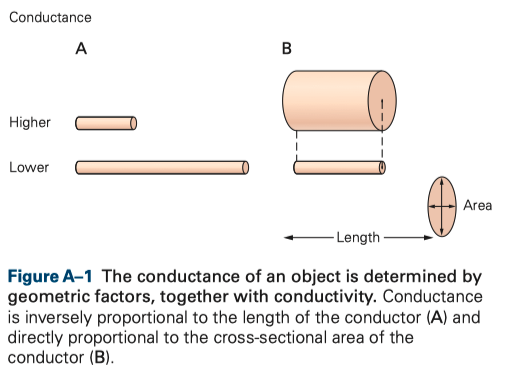
The conductance of an object is proportional to σ times its cross-sectional area divided by its length
- Length = the direction along which one measures conductance
- As the length increases , conductance decreases
- As diameter decreases , conductance decreases
Capacitance (C)
- A capacitor has two conducting plates separated by an insulating layer.
- A capacitor separates positive and negative charges via "plates"
- A potential difference is created if there is an imbalance in the amount of positive or negative charges stored on their respective "plate".
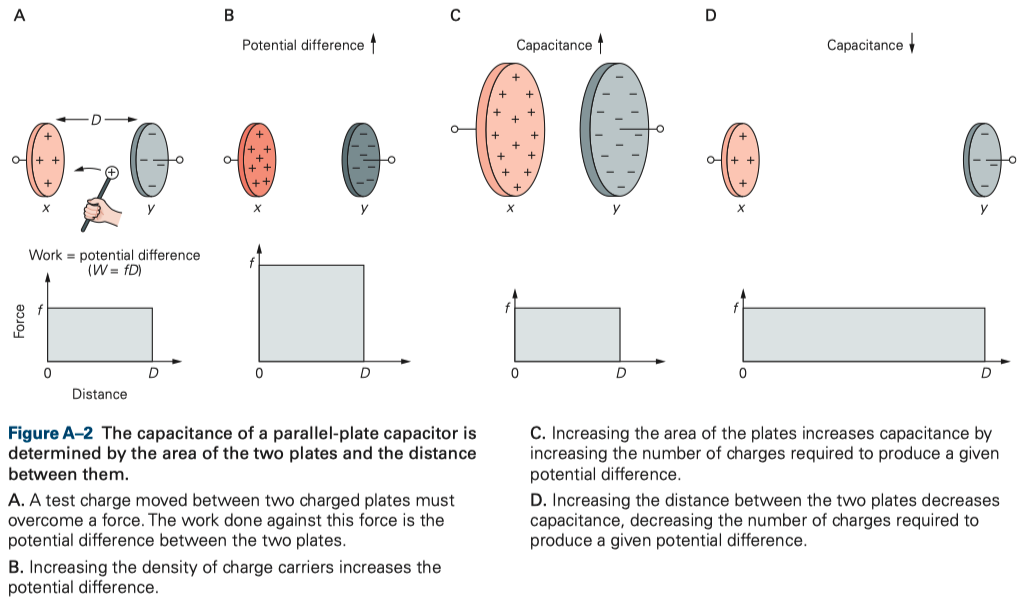
- You can measure the potential difference by calculating how much work is required to move the charge from the plate with excess to the plate that is deficient in charge balance.
- Capacitance is measured in farads (F).
- The greater the density of charges on the capacitor plates, the greater the force acting on the excess charge and the greater the resulting potential difference across the capacitor
For a given capacitor there is a linear relationship between the amount of charge (Q) stored on its plates and the potential difference across it
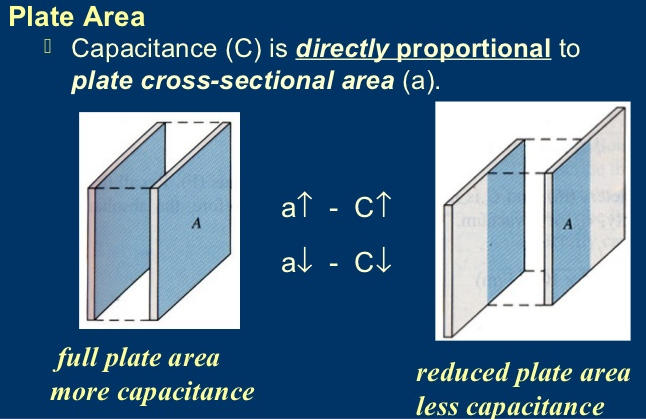
- The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is determined by the area (A) of the two plates and the distance (D) between them.
- Increasing the area of the plates increases capacitance because a greater amount of charge must be deposited on each side to produce the same charge density, which is what determines the force (f) acting on the excess charge
- Increasing the distance between the plates does not change the force acting on the excess charge, but it does increase the work that must be done to move it from one side of the capacitor to the other.
- For a given charge separation between the two plates, the potential difference between them is proportional to the distance.
- The greater the distance, the smaller the amount of charge that must be deposited on the plates to produce a given potential difference, and therefore the smaller the capacitance.
- Capacitance = The ratio of the magnitude of the charge on either conductor to the potential difference between the conductors
Resistance (R)
- A passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.
- They reduce current flow
- Used to adjust signal levels
- They divide voltages
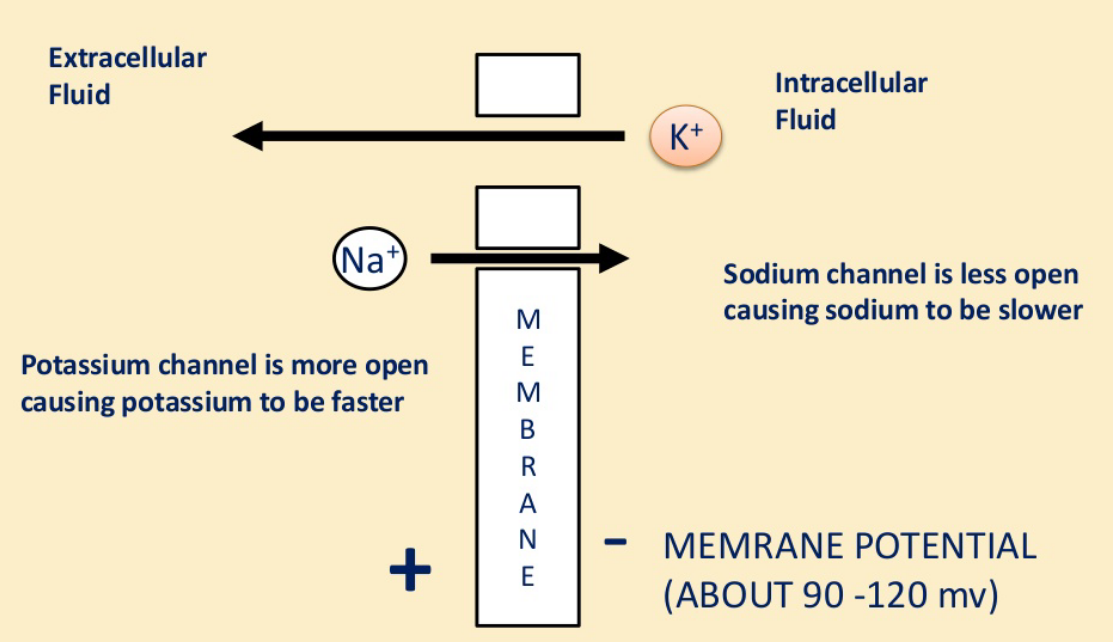
- Resistors in Parallel = Ion (Leak) Channels
- The more leak channels you have in the membrane, allows more ions through the membrane, it will resist current LESS , aka conduct current MORE
Voltage Drop
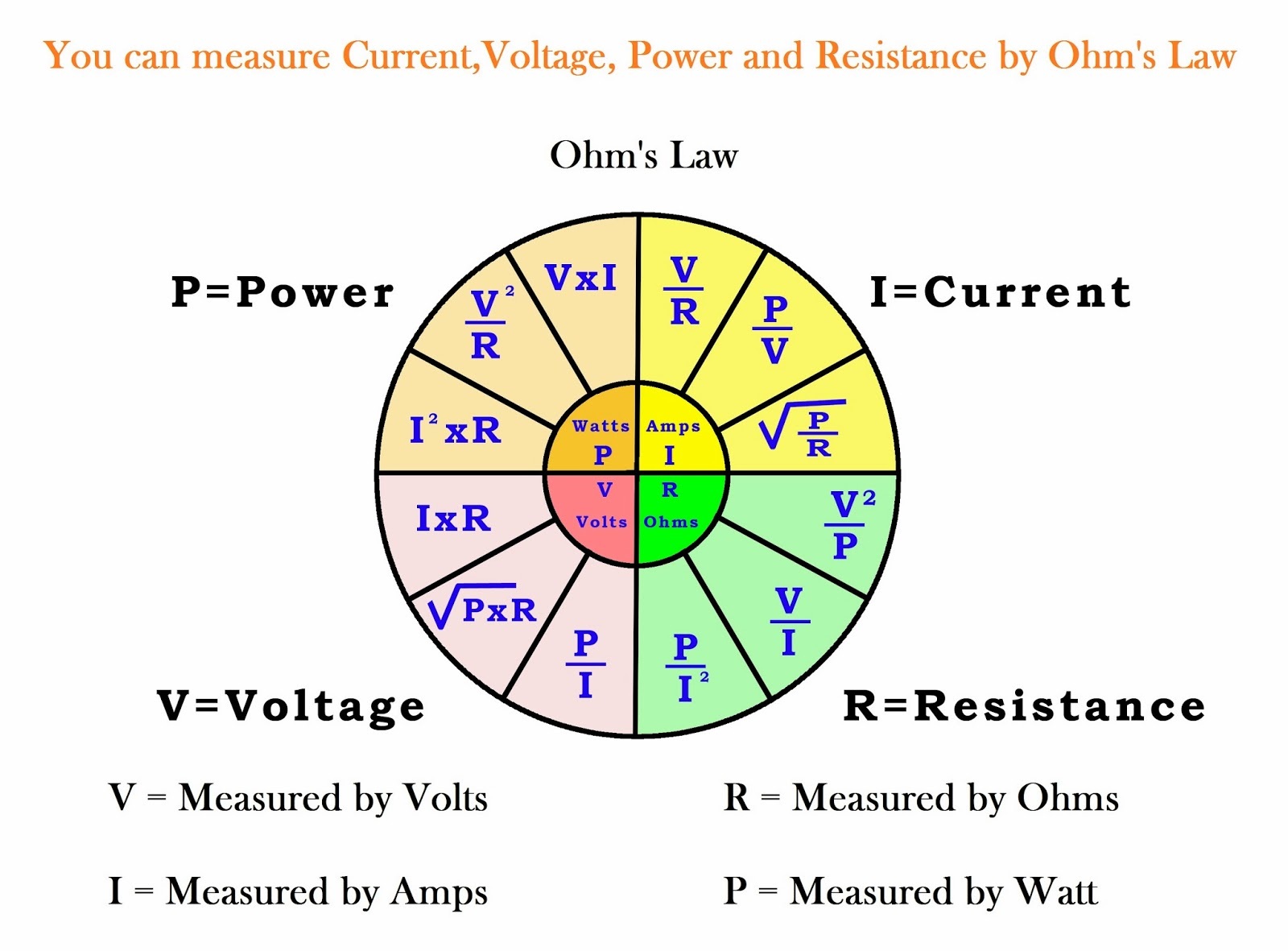
Ohm's Law
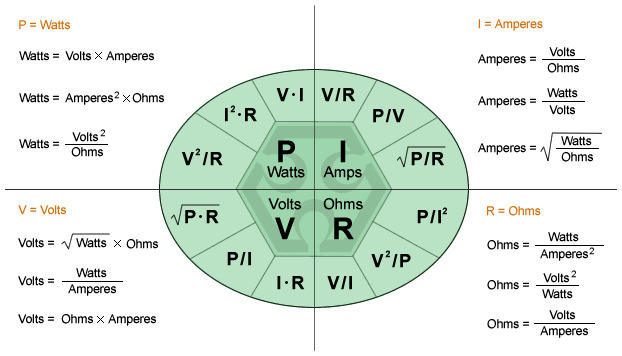
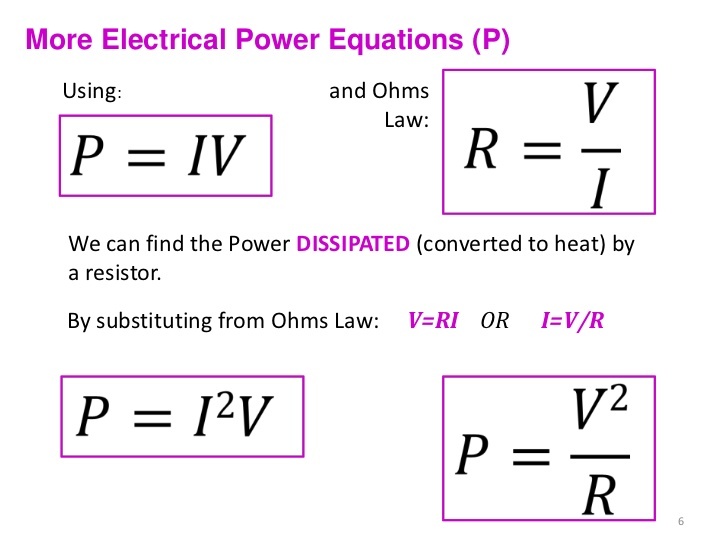
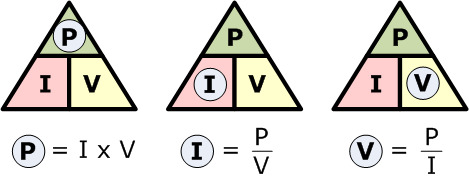
Applications to Neurons
Membrane Potential
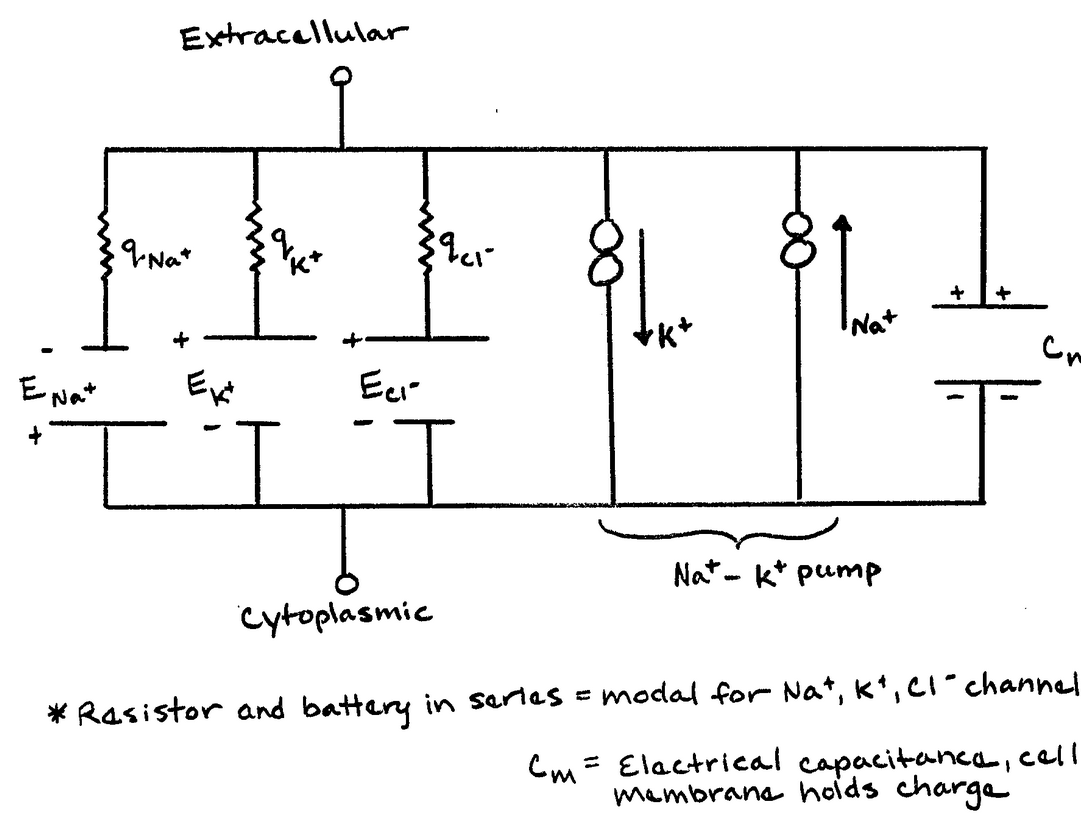
Equivalent Circuit Model of Neuron
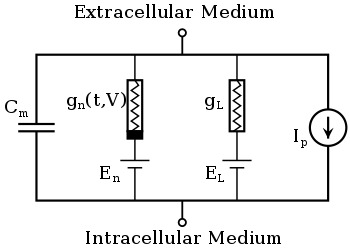
Hodgkin-Huxley Model
- The Lipid Bilayer = The Capacitor , denoted as
Nernst Equation
- The Nernst equation is how we find calculate the potential of an ion of charge (Z) across a membrane
- EZ or also referred to as Em , is the membrane potential in Volts!
- The point at which an ion will be in electrochemical equilibrium
Simplified Model , Assuming Biological Temperature
Reverse Membrane Potential
- The Current of the Ion is equal to the Conductance of the Ion multiplied by the Driving Force
- Driving Force = = Difference between the membrane potential and the ion's equilibrium potential
Parallel Conductance Equation
- This is a steady state and NOT an equilibrium calculation
- This is a way of calculating the reverse membrane potential